The lipid droplet-associated protein perilipin 3 facilitates hepatitis C virus-driven hepatic steatosis
- PMID: 27941027
- PMCID: PMC5282958
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M073734
The lipid droplet-associated protein perilipin 3 facilitates hepatitis C virus-driven hepatic steatosis
Abstract
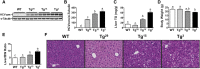
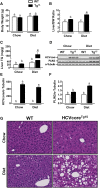
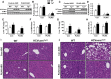
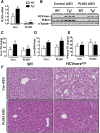
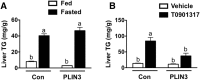
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is an enveloped RNA virus responsible for 170 million cases of viral hepatitis worldwide. Over 50% of chronically infected HCV patients develop hepatic steatosis, and steatosis can be induced by expression of HCV core protein (core) alone. Additionally, core must associate with cytoplasmic lipid droplets (LDs) for steatosis development and viral particle assembly. Due to the importance of the LD as a key component of hepatic lipid storage and as a platform for HCV particle assembly, it seems this dynamic subcellular organelle is a gatekeeper in the pathogenesis of viral hepatitis. Here, we hypothesized that core requires the host LD scaffold protein, perilipin (PLIN)3, to induce hepatic steatosis. To test our hypothesis in vivo, we have studied core-induced hepatic steatosis in the absence or presence of antisense oligonucleotide-mediated knockdown of PLIN3. PLIN3 knockdown blunted HCV core-induced steatosis in transgenic mice fed either chow or a moderate fat diet. Collectively, our studies demonstrate that the LD scaffold protein, PLIN3, is essential for HCV core-induced hepatic steatosis and provide new insights into the pathogenesis of HCV.
Keywords: lipid droplets; lipoproteins/metabolism; liver; triglyceride.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Perilipin 5 alleviates HCV NS5A-induced lipotoxic injuries in liver.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Apr 6;18(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1022-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 30954078 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C Virus-Induced Degradation of Cell Death-Inducing DFFA-Like Effector B Leads to Hepatic Lipid Dysregulation.J Virol. 2016 Mar 28;90(8):4174-85. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02891-15. Print 2016 Apr. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26865724 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo analysis at the cellular level reveals similar steatosis induction in both hepatitis C virus genotype 1 and 3 infections.J Viral Hepat. 2018 Mar;25(3):262-271. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12816. Epub 2017 Nov 20. J Viral Hepat. 2018. PMID: 29086446
-
Hepatitis C virus and lipid droplets: finding a niche.Trends Mol Med. 2015 Jan;21(1):34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2014.11.003. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Trends Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25496657 Review.
-
Hepatitis C virus infection and liver steatosis.Antiviral Res. 2003 Oct;60(2):125-7. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2003.08.007. Antiviral Res. 2003. PMID: 14638408 Review.
Cited by
-
Obesity-linked suppression of membrane-bound O-acyltransferase 7 (MBOAT7) drives non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Elife. 2019 Oct 17;8:e49882. doi: 10.7554/eLife.49882. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31621579 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts Protect ob/ob Mice From Obesity and Metabolic Complications.Endocrinology. 2018 Sep 1;159(9):3275-3286. doi: 10.1210/en.2018-00561. Endocrinology. 2018. PMID: 30085057 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting lipid droplets and lipid droplet-associated proteins: a new perspective on natural compounds against metabolic diseases.Chin Med. 2024 Sep 4;19(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00988-w. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39232826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs as a Novel Tool in the Diagnosis of Liver Lipid Dysregulation and Fatty Liver Disease.Molecules. 2019 Jan 9;24(2):230. doi: 10.3390/molecules24020230. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30634538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Cytosolic Lipid Droplets in Hepatitis C Virus Replication, Assembly, and Release.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Apr 14;2023:5156601. doi: 10.1155/2023/5156601. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37090186 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mohd Hanafiah K., Groeger J., Flaxman A. D., and Wiersma S. T.. 2013. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection: new estimates of age-specific antibody to HCV seroprevalence. Hepatology. 57: 1333–1342. - PubMed
-
- Moriya K., Yotsuyanagi H., Shintani Y., Fujie H., Ishibashi K., Matsuura Y., Miyamura T., and Koike K.. 1997. Hepatitis C virus core protein induces hepatic steatosis in transgenic mice. J. Gen. Virol. 78: 1527–1531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

