Effects of Aicardi-Goutières syndrome mutations predicted from ADAR-RNA structures
- PMID: 27937139
- PMCID: PMC5324757
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1267097
Effects of Aicardi-Goutières syndrome mutations predicted from ADAR-RNA structures
Abstract
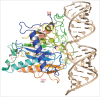
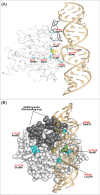
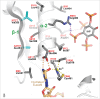
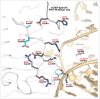
Adenosine (A) to inosine (I) RNA editing is important for life in metazoan organisms. Dysregulation or mutations that compromise the efficacy of A to I editing results in neurological disorders and a shorten life span. These reactions are catalyzed by adenosine deaminases acting on RNA (ADARs), which hydrolytically deaminate adenosines in regions of duplex RNA. Because inosine mimics guanosine in hydrogen bonding, this prolific RNA editing alters the sequence and structural information in the RNA landscape. Aicardi-Goutières syndrome (AGS) is a severe childhood autoimmune disease that is one of a broader set of inherited disorders characterized by constitutive upregulation of type I interferon (IFN) referred to as type I interferonopathies. AGS is caused by mutations in multiple genes whose protein products, including ADAR1, are all involved in nucleic acid metabolism or sensing. The recent crystal structures of human ADAR2 deaminase domain complexed with duplex RNA substrates enabled modeling of how AGS causing mutations may influence RNA binding and catalysis. The mutations can be broadly characterized into three groups; mutations on RNA-binding loops that directly affect RNA binding, "second-layer" mutations that can alter the disposition of RNA-binding loops, and mutations that can alter the position of an α-helix bearing an essential catalytic residue.
Keywords: ADAR; Aicardi-Goutieres Syndrome; base-flipping; A to I; inosine; RNA editing.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aicardi-Goutières syndrome-associated mutation at ADAR1 gene locus activates innate immune response in mouse brain.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Jul 31;18(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02217-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34332594 Free PMC article.
-
Restricting retrotransposons: ADAR1 is another guardian of the human genome.RNA Biol. 2017 Nov 2;14(11):1485-1491. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1341033. Epub 2017 Jul 21. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 28640667 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in ADAR1 cause Aicardi-Goutières syndrome associated with a type I interferon signature.Nat Genet. 2012 Nov;44(11):1243-8. doi: 10.1038/ng.2414. Epub 2012 Sep 23. Nat Genet. 2012. PMID: 23001123 Free PMC article.
-
The role of RNA editing enzyme ADAR1 in human disease.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2022 Jan;13(1):e1665. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1665. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2022. PMID: 34105255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenosine-to-inosine RNA editing in the immune system: friend or foe?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Aug;77(15):2931-2948. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03466-2. Epub 2020 Jan 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31996954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RNA Modifications Modulate Activation of Innate Toll-Like Receptors.Genes (Basel). 2019 Jan 29;10(2):92. doi: 10.3390/genes10020092. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30699960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate Viral Sensor MDA5 and Coxsackievirus Interplay in Type 1 Diabetes Development.Microorganisms. 2020 Jul 3;8(7):993. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8070993. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32635205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural impacts of two disease-linked ADAR1 mutants: a molecular dynamics study.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2024 Jul 17;38(1):25. doi: 10.1007/s10822-024-00565-1. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2024. PMID: 39014124
-
Novel insights into double-stranded RNA-mediated immunopathology.Nat Rev Immunol. 2024 Apr;24(4):235-249. doi: 10.1038/s41577-023-00940-3. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Nat Rev Immunol. 2024. PMID: 37752355 Review.
-
Explaining Pathogenicity of Congenital Zika and Guillain-Barré Syndromes: Does Dysregulation of RNA Editing Play a Role?Bioessays. 2019 Jun;41(6):e1800239. doi: 10.1002/bies.201800239. Epub 2019 May 20. Bioessays. 2019. PMID: 31106880 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grosjean H. Fine-tuning of RNA functions by modification and editing. Berlin; New York: Springer, 2005.
-
- Zipeto MA, Jiang Q, Melese E, Jamieson CH. RNA rewriting, recoding, and rewiring in human disease. Trends Mol Med 2015; 21:549-59; PMID:26259769; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2015.07.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bass BL, Weintraub H. An unwinding activity that covalently modifies its double-stranded RNA substrate. Cell 1988; 55:1089-98; PMID:3203381; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(88)90253-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Macbeth MR, Schubert HL, Vandemark AP, Lingam AT, Hill CP, Bass BL. Inositol hexakisphosphate is bound in the ADAR2 core and required for RNA editing. Science 2005; 309:1534-9; PMID:16141067; http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1113150 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Picardi E, Manzari C, Mastropasqua F, Aiello I, D'Erchia AM, Pesole G. Profiling RNA editing in human tissues: towards the inosinome Atlas. Sci Rep 2015; 5:14941; PMID:26449202; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/srep14941 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
