Prognostic significance of regulatory T lymphocytes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 27921403
- PMCID: PMC5172602
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1600264
Prognostic significance of regulatory T lymphocytes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
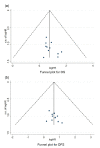
We investigated the prognostic role of regulatory T cells (Tregs) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Relevant evidence regarding prognostic significance of Tregs was systematically searched in MEDLINE and Embase databases. A meta-analysis was performed to compare survival in patients with high or low Tregs level (either in peripheral blood or tumor). Eighteen studies were identified that fulfilled for the eligibility criteria and were included for data synthesis. Our pooled hazard ratios (HRs) demonstrated that increased Tregs intratumoral accumulation was significantly associated with worse overall survival (HR=2.04, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.72-2.42) and disease-free survival (HR=1.82, 95% CI: 1.58-2.09). Three studies evaluated the role of Tregs in peripheral blood, and all of them showed that increased peripheral Tregs correlated with shortened disease-free and overall survival. Collectively, our results showed that the increased Tregs count is tightly associated with the shortened survivals. Its measurement in either primary tumor or even circulation might be a candidate marker of prognostic significance in HCC patients.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Prognosis; Regulatory T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethics guidelines: Ai-bin ZHANG, Yi-gang QIAN, and Shu-sen ZHENG declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor-infiltrating FoxP3+ Tregs and CD8+ T cells affect the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients.Digestion. 2012;86(4):329-37. doi: 10.1159/000342801. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Digestion. 2012. PMID: 23207161
-
Intratumoral balance of regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection.J Clin Oncol. 2007 Jun 20;25(18):2586-93. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.09.4565. J Clin Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17577038
-
Intrahepatic interleukin-17+ T cells and FoxP3+ regulatory T cells cooperate to promote development and affect the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 Apr;29(4):851-9. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12418. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24303990
-
Roles of Tregs in development of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jun 28;20(24):7971-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7971. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24976734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for the prognostic assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 19;7(29):45283-45301. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9942. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27304193 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Key oncogenic signaling pathways affecting tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma: basic principles and recent advances.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 15;15:1354313. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1354313. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38426090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Peripheral and Intratumoral Immune Cell Landscape in Cancer Patients: A Proxy for Tumor Biology and a Tool for Outcome Prediction.Biomedicines. 2018 Feb 24;6(1):25. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines6010025. Biomedicines. 2018. PMID: 29495308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying a Novel Endoplasmic Reticulum-Related Prognostic Model for Hepatocellular Carcinomas.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jul 22;2022:8248355. doi: 10.1155/2022/8248355. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35915607 Free PMC article.
-
Research on Predicting the Occurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on Notch Signal-Related Genes Using Machine Learning Algorithms.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2023 Jul;34(7):760-770. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2023.22357. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37051625 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of chronic viral hepatitis on prognostic value of inflammatory biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2021 Aug;10(16):5395-5404. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3573. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34318618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cai MY, Xu YF, Qiu SJ, et al. Human leukocyte antigen-G protein expression is an unfavorable prognostic predictor of hepatocellular carcinoma following curative resection. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(14):4686–4693. (Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0463) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen KJ, Lin SZ, Zhou L, et al. Selective recruitment of regulatory T cell through CCR6-CCL20 in hepatocellular carcinoma fosters tumor progression and predicts poor prognosis. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(9):e24671. (Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0024671) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Das SL, Singh PP, Phillips AR, et al. Newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus after acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut. 2014;63(5):818–831. (Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305062) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fu J, Xu D, Liu Z, et al. Increased regulatory T cells correlate with CD8 T-cell impairment and poor survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(7):2328–2339. (Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.102) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gao Q, Qiu SJ, Fan J, et al. Intratumoral balance of regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(18):2586–2593. (Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2006.09.4565) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical