Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews
- PMID: 27919275
- PMCID: PMC5139140
- DOI: 10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4
Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews
Abstract
Background: Synthesis of multiple randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in a systematic review can summarize the effects of individual outcomes and provide numerical answers about the effectiveness of interventions. Filtering of searches is time consuming, and no single method fulfills the principal requirements of speed with accuracy. Automation of systematic reviews is driven by a necessity to expedite the availability of current best evidence for policy and clinical decision-making. We developed Rayyan ( http://rayyan.qcri.org ), a free web and mobile app, that helps expedite the initial screening of abstracts and titles using a process of semi-automation while incorporating a high level of usability. For the beta testing phase, we used two published Cochrane reviews in which included studies had been selected manually. Their searches, with 1030 records and 273 records, were uploaded to Rayyan. Different features of Rayyan were tested using these two reviews. We also conducted a survey of Rayyan's users and collected feedback through a built-in feature.
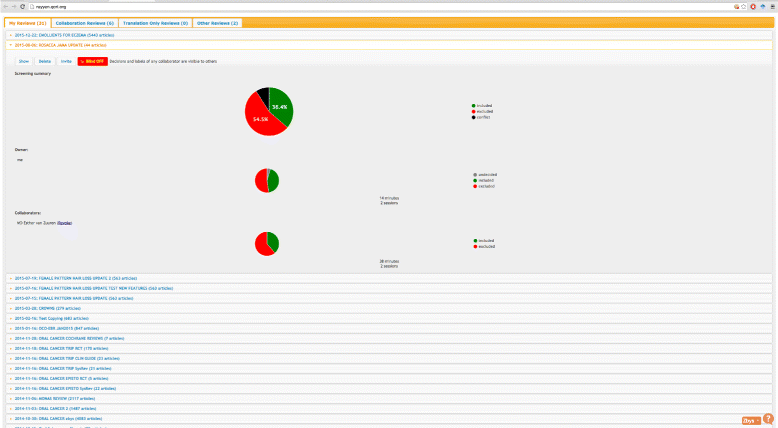
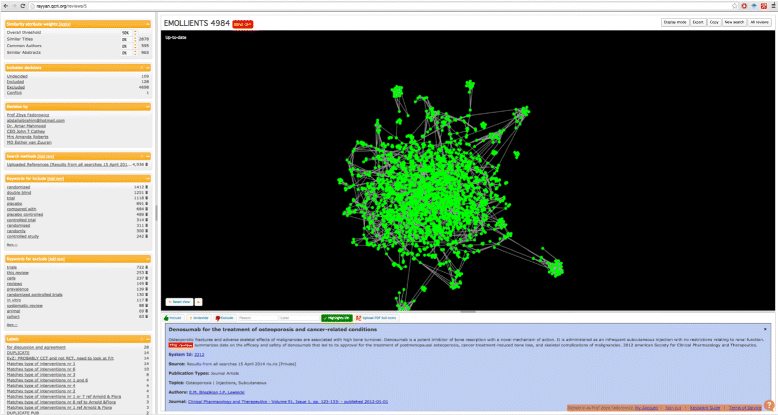
Results: Pilot testing of Rayyan focused on usability, accuracy against manual methods, and the added value of the prediction feature. The "taster" review (273 records) allowed a quick overview of Rayyan for early comments on usability. The second review (1030 records) required several iterations to identify the previously identified 11 trials. The "suggestions" and "hints," based on the "prediction model," appeared as testing progressed beyond five included studies. Post rollout user experiences and a reflexive response by the developers enabled real-time modifications and improvements. The survey respondents reported 40% average time savings when using Rayyan compared to others tools, with 34% of the respondents reporting more than 50% time savings. In addition, around 75% of the respondents mentioned that screening and labeling studies as well as collaborating on reviews to be the two most important features of Rayyan. As of November 2016, Rayyan users exceed 2000 from over 60 countries conducting hundreds of reviews totaling more than 1.6M citations. Feedback from users, obtained mostly through the app web site and a recent survey, has highlighted the ease in exploration of searches, the time saved, and simplicity in sharing and comparing include-exclude decisions. The strongest features of the app, identified and reported in user feedback, were its ability to help in screening and collaboration as well as the time savings it affords to users.
Conclusions: Rayyan is responsive and intuitive in use with significant potential to lighten the load of reviewers.
Keywords: Automation; Evidence-based medicine; Systematic reviews.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Can abstract screening workload be reduced using text mining? User experiences of the tool Rayyan.Res Synth Methods. 2017 Sep;8(3):275-280. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1237. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Res Synth Methods. 2017. PMID: 28374510
-
Updating Systematic Reviews.Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2007 Sep. Report No.: 07-0087. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2007 Sep. Report No.: 07-0087. PMID: 20734512 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Software tools to support title and abstract screening for systematic reviews in healthcare: an evaluation.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020 Jan 13;20(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12874-020-0897-3. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020. PMID: 31931747 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Evidence Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet].Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2016 Apr. Report No.: 14-05205-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2016 Apr. Report No.: 14-05205-EF-1. PMID: 27170970 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Screening for Colorectal Cancer: An Updated Systematic Review [Internet].Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2008 Oct. Report No.: 08-05-05124-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2008 Oct. Report No.: 08-05-05124-EF-1. PMID: 20722162 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer care treatment attrition in adults: Measurement approaches and inequities in patient dropout rates - a rapid review.BMC Cancer. 2024 Nov 1;24(1):1345. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13096-7. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39482591 Review.
-
The Types and Effectiveness of Mobile Health Applications Used in Improving Oral Cancer Knowledge: A Mixed Methods Systematic Review.Health Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 28;7(11):e70171. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70171. eCollection 2024 Nov. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39474342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perioperative Mechanical Circulatory Support for Cardiac Assistance in Thoracic Surgery: A Scoping Review Protocol.Health Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 27;7(11):e70164. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70164. eCollection 2024 Nov. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39474339 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of colistin resistance in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 9;15:1477836. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1477836. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39473844 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy and Safety of Inclisiran for Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) in Patients With Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD): A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.Cureus. 2024 Sep 28;16(9):e70411. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70411. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39473686 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

