Structural and Functional Consequences of Connexin 36 (Cx36) Interaction with Calmodulin
- PMID: 27917108
- PMCID: PMC5114276
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00120
Structural and Functional Consequences of Connexin 36 (Cx36) Interaction with Calmodulin
Abstract
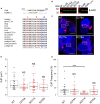
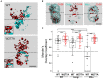
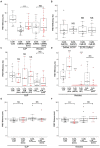
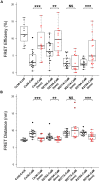
Functional plasticity of neuronal gap junctions involves the interaction of the neuronal connexin36 with calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII). The important relationship between Cx36 and CaMKII must also be considered in the context of another protein partner, Ca2+ loaded calmodulin, binding an overlapping site in the carboxy-terminus of Cx36. We demonstrate that CaM and CaMKII binding to Cx36 is calcium-dependent, with Cx36 able to engage with CaM outside of the gap junction plaque. Furthermore, Ca2+ loaded calmodulin activates Cx36 channels, which is different to other connexins. The NMR solution structure demonstrates that CaM binds Cx36 in its characteristic compact state with major hydrophobic contributions arising from W277 at anchor position 1 and V284 at position 8 of Cx36. Our results establish Cx36 as a hub binding Ca2+ loaded CaM and they identify this interaction as a critical step with implications for functions preceding the initiation of CaMKII mediated plasticity at electrical synapses.
Keywords: CaMKII; calmodulin; connexins; electrical synapse; plasticity; protein interaction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Roles of Calmodulin and CaMKII in Cx36 Plasticity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 25;22(9):4473. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094473. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33922931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calmodulin dependent protein kinase increases conductance at gap junctions formed by the neuronal gap junction protein connexin36.Brain Res. 2012 Dec 3;1487:69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.06.058. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22796294 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Distribution of Retinal Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Kinase II (CaMKII) Isoforms Indicates CaMKII-β and -δ as Specific Elements of Electrical Synapses Made of Connexin36 (Cx36).Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Dec 19;10:425. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00425. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29311815 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of Retinal Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Kinase II-β (CaMKII-β) at Bipolar Cell Gap Junctions and Cross-Reactivity of a Monoclonal Anti-CaMKII-β Antibody With Connexin36.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Aug 28;12:206. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00206. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31555090 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Connexin Gap Junctions and Hemichannels by Calcium and Calcium Binding Protein Calmodulin.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 2;21(21):8194. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218194. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33147690 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Roles of Calmodulin and CaMKII in Cx36 Plasticity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 25;22(9):4473. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094473. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33922931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cooperative cell-cell actin network remodeling to perform Gap junction endocytosis.Basic Clin Androl. 2023 Aug 3;33(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12610-023-00194-y. Basic Clin Androl. 2023. PMID: 37533006 Free PMC article.
-
cGAS and DDX41-STING mediated intrinsic immunity spreads intercellularly to promote neuroinflammation in SOD1 ALS model.iScience. 2022 May 13;25(6):104404. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104404. eCollection 2022 Jun 17. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35712074 Free PMC article.
-
Calmodulin-Mediated Regulation of Gap Junction Channels.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 12;21(2):485. doi: 10.3390/ijms21020485. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31940951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of an Aromatic-Aromatic Interaction in the Assembly and Trafficking of the Zebrafish Panx1a Membrane Channel.Biomolecules. 2020 Feb 11;10(2):272. doi: 10.3390/biom10020272. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32053881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alev C., Urschel S., Sonntag S., Zoidl G., Fort A. G., Höher T., et al. (2008). The neuronal connexin36 interacts with and is phosphorylated by CaMKII in a way similar to CaMKII interaction with glutamate receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105 20964–20969. 10.1073/pnas.0805408105 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

