Alcohol-dependent molecular adaptations of the NMDA receptor system
- PMID: 27906494
- PMCID: PMC5444330
- DOI: 10.1111/gbb.12363
Alcohol-dependent molecular adaptations of the NMDA receptor system
Abstract
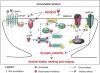
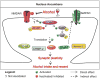
Phenotypes such as motivation to consume alcohol, goal-directed alcohol seeking and habit formation take part in mechanisms underlying heavy alcohol use. Learning and memory processes greatly contribute to the establishment and maintenance of these behavioral phenotypes. The N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) is a driving force of synaptic plasticity, a key cellular hallmark of learning and memory. Here, we describe data in rodents and humans linking signaling molecules that center around the NMDARs, and behaviors associated with the development and/or maintenance of alcohol use disorder (AUD). Specifically, we show that enzymes that participate in the regulation of NMDAR function including Fyn kinase as well as signaling cascades downstream of NMDAR including calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CamKII), the α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR) and the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) play a major role in mechanisms underlying alcohol drinking behaviors. Finally, we emphasize the brain region specificity of alcohol's actions on the above-mentioned signaling pathways and attempt to bridge the gap between the molecular signaling that drive learning and memory processes and alcohol-dependent behavioral phenotypes. Finally, we present data to suggest that genes related to NMDAR signaling may be AUD risk factors.
Keywords: AMPA; Addiction; CaMKII; Fyn; NMDA; PTPalpha; STEP; alcohol; amygdala; kinase; mTOR; nucleus accumbens; phosphatase; signaling; striatum.
© 2016 John Wiley & Sons Ltd and International Behavioural and Neural Genetics Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role for mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 signaling in neuroadaptations underlying alcohol-related disorders.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Nov 16;107(46):20093-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005554107. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 21041654 Free PMC article.
-
The First Alcohol Drink Triggers mTORC1-Dependent Synaptic Plasticity in Nucleus Accumbens Dopamine D1 Receptor Neurons.J Neurosci. 2016 Jan 20;36(3):701-13. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2254-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26791202 Free PMC article.
-
mTORC1 inhibition in the nucleus accumbens 'protects' against the expression of drug seeking and 'relapse' and is associated with reductions in GluA1 AMPAR and CAMKIIα levels.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014 Jun;39(7):1694-702. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.16. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24469593 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR complex 1: a key player in neuroadaptations induced by drugs of abuse.J Neurochem. 2014 Jul;130(2):172-84. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12725. Epub 2014 Apr 19. J Neurochem. 2014. PMID: 24666346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of neuronal PKA signaling through AKAP targeting dynamics.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):627-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504338 Review.
Cited by
-
The association between frequent alcohol drinking and opioid consumption after abdominal surgery: A retrospective analysis.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 16;12(3):e0171275. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171275. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28301483 Free PMC article.
-
Substance abuse and neurotransmission.Adv Pharmacol. 2022;93:403-441. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2021.10.007. Epub 2022 Jan 17. Adv Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35341573 Free PMC article.
-
The Fyn kinase inhibitor, AZD0530, suppresses mouse alcohol self-administration and seeking.Addict Biol. 2019 Nov;24(6):1227-1234. doi: 10.1111/adb.12699. Epub 2018 Dec 7. Addict Biol. 2019. PMID: 30536923 Free PMC article.
-
Ketamine normalizes binge drinking-induced defects in glutamatergic synaptic transmission and ethanol drinking behavior in female but not male mice.Neuropharmacology. 2019 May 1;149:35-44. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.02.003. Epub 2019 Feb 4. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30731135 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic plasticity mechanisms common to learning and alcohol use disorder.Learn Mem. 2018 Aug 16;25(9):425-434. doi: 10.1101/lm.046722.117. Print 2018 Sep. Learn Mem. 2018. PMID: 30115764 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abraham WC. Metaplasticity: tuning synapses and networks for plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9:387. - PubMed
-
- Allen JA, Halverson-Tamboli RA, Rasenick MM. Lipid raft microdomains and neurotransmitter signalling. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:128–140. - PubMed
-
- APA. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC: 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

