A reference data set of 5.4 million phased human variants validated by genetic inheritance from sequencing a three-generation 17-member pedigree
- PMID: 27903644
- PMCID: PMC5204340
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.210500.116
A reference data set of 5.4 million phased human variants validated by genetic inheritance from sequencing a three-generation 17-member pedigree
Abstract
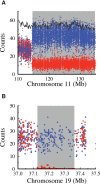
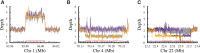
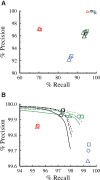
Improvement of variant calling in next-generation sequence data requires a comprehensive, genome-wide catalog of high-confidence variants called in a set of genomes for use as a benchmark. We generated deep, whole-genome sequence data of 17 individuals in a three-generation pedigree and called variants in each genome using a range of currently available algorithms. We used haplotype transmission information to create a phased "Platinum" variant catalog of 4.7 million single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) plus 0.7 million small (1-50 bp) insertions and deletions (indels) that are consistent with the pattern of inheritance in the parents and 11 children of this pedigree. Platinum genotypes are highly concordant with the current catalog of the National Institute of Standards and Technology for both SNVs (>99.99%) and indels (99.92%) and add a validated truth catalog that has 26% more SNVs and 45% more indels. Analysis of 334,652 SNVs that were consistent between informatics pipelines yet inconsistent with haplotype transmission ("nonplatinum") revealed that the majority of these variants are de novo and cell-line mutations or reside within previously unidentified duplications and deletions. The reference materials from this study are a resource for objective assessment of the accuracy of variant calls throughout genomes.
© 2017 Eberle et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimized detection of insertions/deletions (INDELs) in whole-exome sequencing data.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 9;12(8):e0182272. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182272. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28792971 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome sequencing is more powerful than whole-exome sequencing for detecting exome variants.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 28;112(17):5473-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1418631112. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25827230 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of pathogenic variants from the ClinVar database in healthy people using next-generation sequencing.Genet Res (Camb). 2017 Aug 30;99:e6. doi: 10.1017/S0016672317000040. Genet Res (Camb). 2017. PMID: 28851476 Free PMC article.
-
Toward better understanding of artifacts in variant calling from high-coverage samples.Bioinformatics. 2014 Oct 15;30(20):2843-51. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu356. Epub 2014 Jun 27. Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24974202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in Next-Generation Sequencing.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2016 Aug 31;17:95-115. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-083115-022413. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27362342 Review.
Cited by
-
URMAP, an ultra-fast read mapper.PeerJ. 2020 Jun 24;8:e9338. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9338. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32612885 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Reporting for Healthy Populations-Pipeline for Genomic Screening from the GENCOV COVID-19 Study.Curr Protoc. 2022 Oct;2(10):e534. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.534. Curr Protoc. 2022. PMID: 36205462 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of Rare and Common Variants Driving Triglyceride Levels in a Nevada Population.Front Genet. 2021 Mar 2;12:639418. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.639418. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33763119 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting genotype-specific gene regulatory networks.Genome Res. 2022 Mar;32(3):524-533. doi: 10.1101/gr.275107.120. Epub 2022 Feb 22. Genome Res. 2022. PMID: 35193937 Free PMC article.
-
Considerations of Autonomy in Guiding Decisions around the Feedback of Individual Genetic Research Results from Genomics Research: Expectations of and Preferences from Researchers in Botswana.Glob Health Epidemiol Genom. 2022 Mar 31;2022:3245206. doi: 10.1155/2022/3245206. eCollection 2022. Glob Health Epidemiol Genom. 2022. PMID: 35441036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR. 2002. Merlin—rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet 30: 97–101. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
