Systematic tracking of disrupted modules identifies significant genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 27899995
- PMCID: PMC5103943
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.5039
Systematic tracking of disrupted modules identifies significant genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
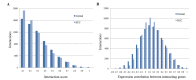
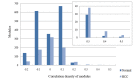
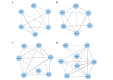
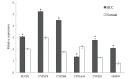
The objective of the present study is to identify significant genes and pathways associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by systematically tracking the dysregulated modules of re-weighted protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks. Firstly, normal and HCC PPI networks were inferred and re-weighted based on Pearson correlation coefficient. Next, modules in the PPI networks were explored by a clique-merging algorithm, and disrupted modules were identified utilizing a maximum weight bipartite matching in non-increasing order. Then, the gene compositions of the disrupted modules were studied and compared with differentially expressed (DE) genes, and pathway enrichment analysis for these genes was performed based on Expression Analysis Systematic Explorer. Finally, validations of significant genes in HCC were conducted using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analysis. The present study evaluated 394 disrupted module pairs, which comprised 236 dysregulated genes. When the dysregulated genes were compared with 211 DE genes, a total of 26 common genes [including phospholipase C beta 1, cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C8 and CYP2B6] were obtained. Furthermore, 6 of these 26 common genes were validated by RT-qPCR. Pathway enrichment analysis of dysregulated genes demonstrated that neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, purine and drug metabolism, and metabolism of xenobiotics mediated by CYP were significantly disrupted pathways. In conclusion, the present study greatly improved the understanding of HCC in a systematic manner and provided potential biomarkers for early detection and novel therapeutic methods.
Keywords: dysregulated gene; hepatocellular carcinoma; modules; pathway; protein-protein interaction network; reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic tracking of dysregulated modules identifies disrupted pathways in narcolepsy.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Jun 15;8(6):9384-93. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26309600 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of disrupted pathways in ulcerative colitis-related colorectal carcinoma by systematic tracking the dysregulated modules.J BUON. 2016 Mar-Apr;21(2):366-74. J BUON. 2016. PMID: 27273946
-
Dysregulated module approach identifies disrupted genes and pathways associated with acute myelocytic leukemia.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Dec;19(24):4811-26. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26744873
-
Temporal Identification of Dysregulated Genes and Pathways in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Based on Systematic Tracking of Disrupted Modules.Comput Math Methods Med. 2015;2015:313740. doi: 10.1155/2015/313740. Epub 2015 Oct 12. Comput Math Methods Med. 2015. PMID: 26543493 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Tracking of Disrupted Modules Identifies Altered Pathways Associated with Congenital Heart Defects in Down Syndrome.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Nov 2;21:3334-42. doi: 10.12659/msm.896001. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26524729 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Novel prognostic biomarkers of gastric cancer based on gene expression microarray: COL12A1, GSTA3, FGA and FGG.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Oct;18(4):3727-3736. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9368. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 30106150 Free PMC article.
-
A transcriptome-based protein network that identifies new therapeutic targets in colorectal cancer.BMC Genomics. 2017 Sep 30;18(1):758. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4139-y. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28962550 Free PMC article.
-
CommPath: An R package for inference and analysis of pathway-mediated cell-cell communication chain from single-cell transcriptomics.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Oct 26;20:5978-5983. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.10.028. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36382188 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Cullin7 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma progression and pathogenesis.BMC Cancer. 2017 Dec 6;17(1):828. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3839-7. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29207970 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the key genes and pathways of osteosarcoma with pulmonary metastasis using a gene expression microarray.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Nov;16(5):7423-7431. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7577. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28944885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaseb AO, Xiao L, Hassan MM, Chae YK, Lee JS, Vauthey JN, Krishnan S, Cheung S, Hassabo HM, Aloia T, et al. Development and validation of a scoring system using insulin-like growth factor to assess hepatic reserve in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106 doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju088. pii: dju088. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aoki T, Kokudo N, Matsuyama Y, Izumi N, Ichida T, Kudo M, Ku Y, Sakamoto M, Nakashima O, Matsui O, et al. Prognostic impact of spontaneous tumor rupture in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: An analysis of 1160 cases from a nationwide survey. Ann Surg. 2014;259:532–542. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31828846de. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
