Lineage-specific SoxR-mediated Regulation of an Endoribonuclease Protects Non-enteric Bacteria from Redox-active Compounds
- PMID: 27895125
- PMCID: PMC5217672
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.757500
Lineage-specific SoxR-mediated Regulation of an Endoribonuclease Protects Non-enteric Bacteria from Redox-active Compounds
Abstract
Bacteria use redox-sensitive transcription factors to coordinate responses to redox stress. The [2Fe-2S] cluster-containing transcription factor SoxR is particularly tuned to protect cells against redox-active compounds (RACs). In enteric bacteria, SoxR is paired with a second transcription factor, SoxS, that activates downstream effectors. However, SoxS is absent in non-enteric bacteria, raising questions as to how SoxR functions. Here, we first show that SoxR of Acinetobacter oleivorans displayed similar activation profiles in response to RACs as did its homolog from Escherichia coli but controlled a different set of target genes, including sinE, which encodes an endoribonuclease. Expression, gel mobility shift, and mutational analyses indicated that sinE is a direct target of SoxR. Redox potentials and permeability of RACs determined optimal sinE induction. Bioinformatics suggested that only a few γ- and β-proteobacteria might have SoxR-regulated sinE Purified SinE, in the presence of Mg2+ ions, degrades rRNAs, thus inhibiting protein synthesis. Similarly, pretreatment of cells with RACs demonstrated a role for SinE in promoting persistence in the presence of antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis. Our data improve our understanding of the physiology of soil microorganisms by suggesting that both non-enteric SoxR and its target SinE play protective roles in the presence of RACs and antibiotics.
Keywords: Acinetobacter; Escherichia coli (E. coli); SoxR; antibiotics; bacteria; biofilm; endoribonuclease; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species (ROS); transcriptional regulation.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
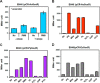
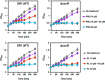
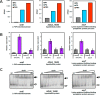
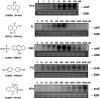

Similar articles
-
Activation of SoxR-dependent transcription in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.J Biochem. 2004 Nov;136(5):607-15. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvh168. J Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15632300
-
Two-stage control of an oxidative stress regulon: the Escherichia coli SoxR protein triggers redox-inducible expression of the soxS regulatory gene.J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(19):6054-60. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.19.6054-6060.1992. J Bacteriol. 1992. PMID: 1400156 Free PMC article.
-
Thiol-mediated disassembly and reassembly of [2Fe-2S] clusters in the redox-regulated transcription factor SoxR.Biochemistry. 1998 Dec 8;37(49):17280-6. doi: 10.1021/bi980532g. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9860842
-
Sensing and protecting against superoxide stress in Escherichia coli--how many ways are there to trigger soxRS response?Redox Rep. 2000;5(5):287-93. doi: 10.1179/135100000101535825. Redox Rep. 2000. PMID: 11145103 Review.
-
Oxidative stress sensing by the iron-sulfur cluster in the transcription factor, SoxR.J Inorg Biochem. 2014 Apr;133:87-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2013.11.008. Epub 2013 Nov 28. J Inorg Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24332474 Review.
Cited by
-
The Iron Tug-of-War between Bacterial Siderophores and Innate Immunity.J Innate Immun. 2019;11(3):249-262. doi: 10.1159/000494627. Epub 2019 Jan 3. J Innate Immun. 2019. PMID: 30605903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Catalase Expression in Azospirillum brasilense Sp7 Is Regulated by a Network Consisting of OxyR and Two RpoH Paralogs and Including an RpoE1→RpoH5 Regulatory Cascade.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Nov 15;84(23):e01787-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01787-18. Print 2018 Dec 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30217849 Free PMC article.
-
The OxyR and SoxR transcriptional regulators are involved in a broad oxidative stress response in Paraburkholderia xenovorans LB400.Biol Res. 2022 Feb 20;55(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s40659-022-00373-7. Biol Res. 2022. PMID: 35184754 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and Physiological Traits of the Marine Bacterium Alcaligenes aquatilis QD168 Isolated From Quintero Bay, Central Chile, Reveal a Robust Adaptive Response to Environmental Stressors.Front Microbiol. 2019 Apr 5;10:528. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00528. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31024465 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative fate of glyoxylate during acetate and hexadecane metabolism in Acinetobacter oleivorans DR1.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 7;9(1):14402. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50852-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31591464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dietrich L. E., and Kiley P. J. (2011) A shared mechanism of SoxR activation by redox-cycling compounds. Mol. Microbiol. 79, 1119–1122 - PubMed
-
- Okegbe C., Sakhtah H., Sekedat M. D., Price-Whelan A., and Dietrich L. E. (2012) Redox eustress: roles for redox-active metabolites in bacterial signaling and behavior. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 16, 658–667 - PubMed
-
- Ding H., Hidalgo E., and Demple B. (1996) The redox state of the [2Fe-2S] clusters in SoxR protein regulates its activity as a transcription factor. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 33173–33175 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

