The Ly49E Receptor Inhibits the Immune Control of Acute Trypanosoma cruzi Infection
- PMID: 27891126
- PMCID: PMC5103623
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00472
The Ly49E Receptor Inhibits the Immune Control of Acute Trypanosoma cruzi Infection
Abstract
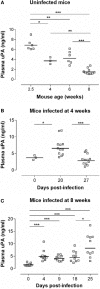
The protozoan parasite Trypanosoma cruzi circulates in the blood upon infection and invades various cells. Parasites intensively multiply during the acute phase of infection and persist lifelong at low levels in tissues and blood during the chronic phase. Natural killer (NK) and NKT cells play an important role in the immune control of T. cruzi infection, mainly by releasing the cytokine IFN-γ that activates the microbicidal action of macrophages and other cells and shapes a protective type 1 immune response. The mechanisms by which immune cells are regulated to produce IFN-γ during T. cruzi infection are still incompletely understood. Here, we show that urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) is induced early upon T. cruzi infection and remains elevated until day 20 post-infection. We previously demonstrated that the inhibitory receptor Ly49E, which is expressed, among others, on NK and NKT cells, is triggered by uPA. Therefore, we compared wild type (WT) to Ly49E knockout (KO) mice for their control of experimental T. cruzi infection. Our results show that young, i.e., 4- and 6-week-old, Ly49E KO mice control the infection better than WT mice, indicated by a lower parasite load and less cachexia. The beneficial effect of Ly49E depletion is more obvious in 4-week-old male than in female mice and weakens in 8-week-old mice. In young mice, the lower T. cruzi parasitemia in Ly49E KO mice is paralleled by higher IFN-γ production compared to their WT controls. Our data indicate that Ly49E receptor expression inhibits the immune control of T. cruzi infection. This is the first demonstration that the inhibitory Ly49E receptor can interfere with the immune response to a pathogen in vivo.
Keywords: IFN-γ; Ly49E receptor; Trypanosoma cruzi; immune control; natural killer cells; urokinase plasminogen activator.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contribution of the Ly49E natural killer receptor in the immune response to Plasmodium berghei infection and control of hepatic parasite development.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 30;9(1):e87463. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087463. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24498110 Free PMC article.
-
Trypanosoma cruzi: IL-10, TNF, IFN-gamma, and IL-12 regulate innate and acquired immunity to infection.Exp Parasitol. 1996 Nov;84(2):231-44. doi: 10.1006/expr.1996.0109. Exp Parasitol. 1996. PMID: 8932773
-
Expression of the inhibitory Ly49E receptor is not critically involved in the immune response against cutaneous, pulmonary or liver tumours.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 29;6:30564. doi: 10.1038/srep30564. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27469529 Free PMC article.
-
[TH1 response in the experimental infection with Trypanosoma cruzi].Medicina (B Aires). 1999;59 Suppl 2:84-90. Medicina (B Aires). 1999. PMID: 10668248 Spanish.
-
[Role of cytokines in resistance and pathology in Trypanosoma cruzi infection].Rev Argent Microbiol. 1996 Apr-Jun;28(2):99-109. Rev Argent Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8768488 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
The transcription factor RUNX2 drives the generation of human NK cells and promotes tissue residency.Elife. 2022 Jul 6;11:e80320. doi: 10.7554/eLife.80320. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35793229 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Killer Cell Integrins and Their Functions in Tissue Residency.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 10;12:647358. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.647358. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33777044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ly49E separates liver ILC1s into embryo-derived and postnatal subsets with different functions.J Exp Med. 2022 May 2;219(5):e20211805. doi: 10.1084/jem.20211805. Epub 2022 Mar 29. J Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 35348580 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

