Epstein-Barr virus lytic reactivation regulation and its pathogenic role in carcinogenesis
- PMID: 27877083
- PMCID: PMC5118777
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.16564
Epstein-Barr virus lytic reactivation regulation and its pathogenic role in carcinogenesis
Abstract
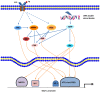
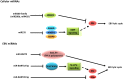
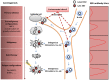
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) has been associated with several types of human cancers. In the host, EBV can establish two alternative modes of life cycle, known as latent or lytic and the switch from latency to the lytic cycle is known as EBV reactivation. Although EBV in cancer cells is found mostly in latency, a small number of lytically-infected cells promote carcinogenesis through the release of growth factors and oncogenic cytokines. This review focuses on the mechanisms by which EBV reactivation is controlled by cellular and viral factors, and discusses how EBV lytic infection contributes to human malignancies.
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus; Rta; Zta; carcinogenesis; latency; reactivation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Rta-Mediated Accumulation of DNA Methylation Interferes with CTCF Binding in both Host and Viral Genomes.J Virol. 2017 Jul 12;91(15):e00736-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00736-17. Print 2017 Aug 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28490592 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation of Epstein-Barr virus Rta promoter in EBV primary infection, reactivation and lymphoproliferation.J Med Virol. 2016 Oct;88(10):1814-20. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24524. Epub 2016 Mar 28. J Med Virol. 2016. PMID: 26990870
-
Inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus reactivation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by dietary sulforaphane.Mol Carcinog. 2013 Dec;52(12):946-58. doi: 10.1002/mc.21926. Epub 2012 May 29. Mol Carcinog. 2013. PMID: 22641235
-
Molecular Basis of Epstein-Barr Virus Latency Establishment and Lytic Reactivation.Viruses. 2021 Nov 23;13(12):2344. doi: 10.3390/v13122344. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34960613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lytic cycle switches of oncogenic human gammaherpesviruses.Adv Cancer Res. 2007;97:81-109. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(06)97004-3. Adv Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17419942 Review.
Cited by
-
A pilot study of ruxolitinib as a front-line therapy for 12 children with secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.Haematologica. 2021 Jul 1;106(7):1892-1901. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2020.253781. Haematologica. 2021. PMID: 32732367 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Traditional Herbal Diet and Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Risk: A Prospective Cohort Study in Southern China.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 21;11:715242. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.715242. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34745941 Free PMC article.
-
Role of BamHI-A Rightward Frame 1 in Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Epithelial Malignancies.Biology (Basel). 2020 Dec 11;9(12):461. doi: 10.3390/biology9120461. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33322292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein LMP1-mediated high oxidative stress suppresses EBV lytic reactivation and sensitizes tumors to radiation therapy.Theranostics. 2020 Oct 25;10(26):11921-11937. doi: 10.7150/thno.46006. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 33204320 Free PMC article.
-
Research landmarks on the 60th anniversary of Epstein-Barr virus.Sci China Life Sci. 2025 Feb;68(2):354-380. doi: 10.1007/s11427-024-2766-0. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Sci China Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39505801 Review.
References
-
- Murata T, Tsurumi T. Switching of EBV cycles between latent and lytic states. Reviews in medical virology. 2014;24:142–153. - PubMed
-
- Fang CY, Lee CH, Wu CC. et al. Recurrent chemical reactivations of EBV promotes genome instability and enhances tumor progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. International journal of cancer. 2009;124:2016–2025. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

