Analysis of alcohol use disorders from the Nathan Kline Institute-Rockland Sample: Correlation of brain cortical thickness with neuroticism
- PMID: 27875803
- PMCID: PMC5183556
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2016.10.040
Analysis of alcohol use disorders from the Nathan Kline Institute-Rockland Sample: Correlation of brain cortical thickness with neuroticism
Abstract
Background: Although differences in both neuroanatomical measures and personality traits, in particular neuroticism, have been associated with alcohol use disorders (AUD), whether lifetime AUD diagnosis alters the relationship between neuroticism and neuroanatomical structures remains to be determined.
Methods: Data from 65 patients with lifetime AUD diagnoses and 65 healthy comparisons (HC) group-matched on age, sex and race were extracted from the Nathan Kline Institute - Rockland Sample data set. Each subject completed personality trait measures and underwent MRI scanning. Cortical thickness measures at 68 Desikan-Killiany Atlas regions were obtained using FreeSurfer 5.3.0. Regression analyses were performed to identify brain regions at which the neuroticism-cortical thickness relationship was altered by lifetime AUD status.
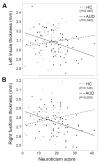
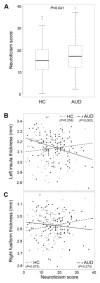
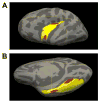
Results: As expected, AUDs had higher neuroticism scores than HCs. Correlations between neuroticism and cortical thickness in the left insula and right fusiform differed significantly across groups. Higher neuroticism score in AUD and the interaction between the insular cortical thickness-neuroticism correlation and AUD status were confirmed in a replication study using the Human Connectome Project data set.
Conclusions: Results confirmed the relationship between neuroticism and AUD and suggests that specific cortical regions, particularly the left insula, represent anatomic substrates underlying this association in AUD.
Keywords: Alcohol use disorders; Chronic pain disorder; Fusiform gyrus; Insula; Neuroticism; Personality.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest related to this research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brain Imaging-Guided Analysis Reveals DNA Methylation Profiles Correlated with Insular Surface Area and Alcohol Use Disorder.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019 Apr;43(4):628-639. doi: 10.1111/acer.13971. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019. PMID: 30830696 Free PMC article.
-
Resting-state functional connectivity predicts neuroticism and extraversion in novel individuals.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2018 Feb 1;13(2):224-232. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsy002. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29373729 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical thickness and trait empathy in patients and people at high risk for alcohol use disorders.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Dec;234(23-24):3521-3533. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4741-3. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28971228
-
Association between cortical thickness and anxiety measures: A scoping review.Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. 2022 Jan;319:111423. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2021.111423. Epub 2021 Nov 27. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. 2022. PMID: 34896960 Review.
-
White matter volume in alcohol use disorders: a meta-analysis.Addict Biol. 2013 May;18(3):581-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2012.00441.x. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Addict Biol. 2013. PMID: 22458455 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Brain Imaging-Guided Analysis Reveals DNA Methylation Profiles Correlated with Insular Surface Area and Alcohol Use Disorder.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019 Apr;43(4):628-639. doi: 10.1111/acer.13971. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019. PMID: 30830696 Free PMC article.
-
"Nothing to see here": No structural brain differences as a function of the Big Five personality traits from a systematic review and meta-analysis.Personal Neurosci. 2022 Aug 9;5:e8. doi: 10.1017/pen.2021.5. eCollection 2022. Personal Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35991756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replication of Resting State-Task Network Correspondence and Novel Findings on Brain Network Activation During Task fMRI in the Human Connectome Project Study.Sci Rep. 2018 Dec 3;8(1):17543. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35209-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30510165 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Distinct neurocognitive fingerprints reflect differential associations with risky and impulsive behavior in a neurotypical sample.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 21;13(1):11782. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38991-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37479846 Free PMC article.
-
The Cortical Neuroimmune Regulator TANK Affects Emotional Processing and Enhances Alcohol Drinking: A Translational Study.Cereb Cortex. 2019 Apr 1;29(4):1736-1751. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhy341. Cereb Cortex. 2019. PMID: 30721969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Royal Stat Soc Series B. 1995;57:289–300.
-
- Bernard JF, Bester H, Besson JM. Involvement of the spino-parabrachio-amygdaloid and -hypothalamic pathways in the autonomic and affective emotional aspects of pain. Prog Brain Res. 1996;107:243–255. - PubMed
-
- Bjornebekk A, Fjell AM, Walhovd KB, Grydeland H, Torgersen S, Westlye LT. Neuronal correlates of the five factor model (FFM) of human personality: multimodal imaging in a large healthy sample. Neuroimage. 2013;65:194–208. - PubMed
-
- Buhler M, Mann K. Alcohol and the human brain: a systematic review of different neuroimaging methods. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011;35:1771–1793. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

