Morphological and Taxonomic Properties of Tokyovirus, the First Marseilleviridae Member Isolated from Japan
- PMID: 27867160
- PMCID: PMC5158117
- DOI: 10.1264/jsme2.ME16107
Morphological and Taxonomic Properties of Tokyovirus, the First Marseilleviridae Member Isolated from Japan
Abstract
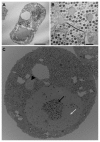
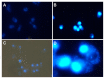
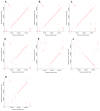
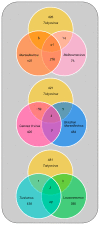
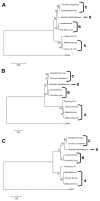
Members of the Marseilleviridae family are large DNA viruses with icosahedral particle structures that infect Acanthamoeba cells. The first Marseillevirus to be discovered was isolated in 2009. Since then, several other members of the Marseilleviridae family have been reported, including Lausannevirus, Senegalvirus, Cannes 8 virus, Insectomime virus, Tunisvirus, Melbournevirus, Port-Miou virus, and Brazilian Marseillevirus, which have been isolated from Europe, Africa, Australia, and South America. The morphological and genomic properties of a new Marseilleviridae family member, Tokyovirus, discovered in a water/soil sample from a Japanese river in Tokyo, were described in the present study. Tokyovirus possesses icosahedral particles of up to 200 nm in diameter, as revealed by a transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis, which form a giant virion factory in Acanthamoeba cells. A preliminary genome analysis predicted 487 coding sequences. A dot plot analysis and phylogenetic analysis using family B DNA polymerase, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), and DNA-directed RNA polymerase alpha subunit genes revealed that Tokyovirus shares similarities with Marseillevirus, Melbournevirus, and Cannes 8 virus (Marseilleviridae subclade A), but not with Lausannevirus and Port-Miou virus (subclade B), Tunisvirus and Insectomime virus (subclade C), or Brazilian Marseillevirus (subclade D), suggesting that Tokyovirus has evolved separately from the previously described Marseilleviridae members.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome analysis of the first Marseilleviridae representative from Australia indicates that most of its genes contribute to virus fitness.J Virol. 2014 Dec;88(24):14340-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02414-14. Epub 2014 Oct 1. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25275139 Free PMC article.
-
Complete genome sequence of Tunisvirus, a new member of the proposed family Marseilleviridae.Arch Virol. 2014 Sep;159(9):2349-58. doi: 10.1007/s00705-014-2023-5. Epub 2014 Apr 26. Arch Virol. 2014. PMID: 24770845
-
A Brazilian Marseillevirus Is the Founding Member of a Lineage in Family Marseilleviridae.Viruses. 2016 Mar 10;8(3):76. doi: 10.3390/v8030076. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 26978387 Free PMC article.
-
The expanding family Marseilleviridae.Virology. 2014 Oct;466-467:27-37. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.07.014. Epub 2014 Aug 5. Virology. 2014. PMID: 25104553 Review.
-
Sputnik, a virophage infecting the viral domain of life.Adv Virus Res. 2012;82:63-89. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394621-8.00013-3. Adv Virus Res. 2012. PMID: 22420851 Review.
Cited by
-
Taxon Richness of "Megaviridae" Exceeds those of Bacteria and Archaea in the Ocean.Microbes Environ. 2018 Jul 4;33(2):162-171. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME17203. Epub 2018 May 25. Microbes Environ. 2018. PMID: 29806626 Free PMC article.
-
Medusavirus Ancestor in a Proto-Eukaryotic Cell: Updating the Hypothesis for the Viral Origin of the Nucleus.Front Microbiol. 2020 Sep 3;11:571831. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.571831. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33013805 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of a Marseillevirus Transcriptome Reveals Temporal Gene Expression Profile and Host Transcriptional Shift.Front Microbiol. 2020 Apr 14;11:651. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00651. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32390970 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological and Taxonomic Properties of the Newly Isolated Cotonvirus japonicus, a New Lineage of the Subfamily Megavirinae.J Virol. 2021 Aug 25;95(18):e0091921. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00919-21. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34191583 Free PMC article.
-
Medusavirus, a Novel Large DNA Virus Discovered from Hot Spring Water.J Virol. 2019 Apr 3;93(8):e02130-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02130-18. Print 2019 Apr 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30728258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abergel C., Legendre M., Claverie J.-M. The rapidly expanding universe of giant viruses: Mimivirus, Pandoravirus, Pithovirus and Mollivirus. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2015;39:779–796. - PubMed
-
- Aherfi S., Pagnier I., Fournous G., Raoult D., La Scola B., Colson P. Complete genome sequence of Cannes 8 virus, a new member of the proposed family “Marseilleviridae”. Virus Genes. 2013;47:550–555. - PubMed
-
- Aherfi S., Boughalmi M., Pagnier I., Fournous G., La Scola B., Raoult D., Colson P. Complete genome sequence of Tunisvirus, a new member of the proposed family Marseilleviridae. Arch Virol. 2014;159:2349–2358. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

