In silico and in vitro drug screening identifies new therapeutic approaches for Ewing sarcoma
- PMID: 27863422
- PMCID: PMC5354814
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13385
In silico and in vitro drug screening identifies new therapeutic approaches for Ewing sarcoma
Abstract
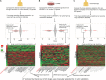
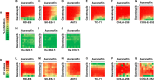
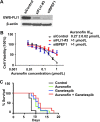
The long-term overall survival of Ewing sarcoma (EWS) patients remains poor; less than 30% of patients with metastatic or recurrent disease survive despite aggressive combinations of chemotherapy, radiation and surgery. To identify new therapeutic options, we employed a multi-pronged approach using in silico predictions of drug activity via an integrated bioinformatics approach in parallel with an in vitro screen of FDA-approved drugs. Twenty-seven drugs and forty-six drugs were identified, respectively, to have anti-proliferative effects for EWS, including several classes of drugs in both screening approaches. Among these drugs, 30 were extensively validated as mono-therapeutic agents and 9 in 14 various combinations in vitro. Two drugs, auranofin, a thioredoxin reductase inhibitor, and ganetespib, an HSP90 inhibitor, were predicted to have anti-cancer activities in silico and were confirmed active across a panel of genetically diverse EWS cells. When given in combination, the survival rate in vivo was superior compared to auranofin or ganetespib alone. Importantly, extensive formulations, dose tolerance, and pharmacokinetics studies demonstrated that auranofin requires alternative delivery routes to achieve therapeutically effective levels of the gold compound. These combined screening approaches provide a rapid means to identify new treatment options for patients with a rare and often-fatal disease.
Keywords: Ewing sarcoma; auranofin; drug repurposing; ganetespib; high-throughput screening.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors claim there is no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signature-based small molecule screening identifies cytosine arabinoside as an EWS/FLI modulator in Ewing sarcoma.PLoS Med. 2007 Apr;4(4):e122. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040122. PLoS Med. 2007. PMID: 17425403 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the EWS-ETS transcriptional program by BET bromodomain inhibition in Ewing sarcoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 12;7(2):1451-63. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6385. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26623725 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression signature based screening identifies ribonucleotide reductase as a candidate therapeutic target in Ewing sarcoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 27;7(39):63003-63019. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11416. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27557498 Free PMC article.
-
Ewing's sarcoma: standard and experimental treatment options.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2009 Apr;10(1-2):126-40. doi: 10.1007/s11864-009-0104-6. Epub 2009 Jun 17. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19533369 Review.
-
Blocking the road, stopping the engine or killing the driver? Advances in targeting EWS/FLI-1 fusion in Ewing sarcoma as novel therapy.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014 Nov;18(11):1315-28. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2014.947963. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014. PMID: 25162919 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasensitive quantification of tumor mRNAs in extracellular vesicles with an integrated microfluidic digital analysis chip.Lab Chip. 2018 Dec 4;18(24):3790-3801. doi: 10.1039/c8lc01071d. Lab Chip. 2018. PMID: 30474100 Free PMC article.
-
Giving Drugs a Second Chance: Overcoming Regulatory and Financial Hurdles in Repurposing Approved Drugs As Cancer Therapeutics.Front Oncol. 2017 Nov 14;7:273. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00273. eCollection 2017. Front Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29184849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reversal of cancer gene expression identifies repurposed drugs for diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022 Oct 23;10(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s40478-022-01463-z. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022. PMID: 36274161 Free PMC article.
-
Inducing Mitotic Catastrophe as a Therapeutic Approach to Improve Outcomes in Ewing Sarcoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 10;15(20):4911. doi: 10.3390/cancers15204911. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894278 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing big 'omics' data and AI for drug discovery in hepatocellular carcinoma.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Apr;17(4):238-251. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0240-9. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31900465 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pinkerton CR, Bataillard A, Guillo S, Oberlin O, Fervers B, Philip T. Treatment strategies for metastatic Ewing's sarcoma. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37:1338–44. doi. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

