A Transformation-Defective Polyomavirus Middle T Antigen with a Novel Defect in PI3 Kinase Signaling
- PMID: 27852846
- PMCID: PMC5215327
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01774-16
A Transformation-Defective Polyomavirus Middle T Antigen with a Novel Defect in PI3 Kinase Signaling
Abstract
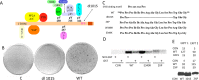
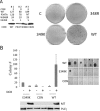
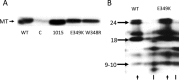
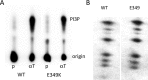
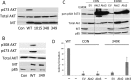
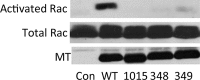
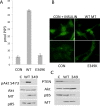
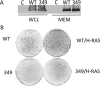
Middle T antigen (MT), the principal oncoprotein of murine polyomavirus, transforms by association with cellular proteins. Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), YAP, Src family tyrosine kinases, Shc, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), and phospholipase C-γ1 (PLCγ1) have all been implicated in MT transformation. Mutant dl1015, with deletion of residues 338 to 347 in the C-terminal region, has been an enigma, because the basis for its transformation defect has not been apparent. This work probes the dl1015 region of MT. Because the region is proline rich, the hypothesis that it targets Src homology domain 3 (SH3) domains was tested, but mutation of the putative SH3 binding motif did not affect transformation. During this work, two point mutants, W348R and E349K, were identified as transformation defective. Extensive analysis of the E349K mutant is described here. Similar to wild-type MT, the E349K mutant associates with PP2A, YAP, tyrosine kinases, Shc, PI3 kinase, and PLCγ1. The E349K mutant was examined to determine the mechanism for its transformation defect. Assays of cell localization and membrane targeting showed no obvious difference in localization. Src association was normal as assayed by in vitro kinase and MT phosphopeptide mapping. Shc activation was confirmed by its tyrosine phosphorylation. Association of type 1 PI3K with MT was demonstrated by coimmunoprecipitation, showing both PI3K subunits and in vitro activity. Nonetheless, expression of the mutants failed to lead to the activation of two known downstream targets of PI3K, Akt and Rac-1. Strikingly, despite normal association of the E349K mutant with PI3K, cells expressing the mutant failed to elevate phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PIP3) in mutant-expressing cells. These results indicate a novel unsuspected aspect to PI3K control.
Importance: The gene coding for middle T antigen (MT) is the murine polyomavirus oncogene most responsible for tumor formation. Its study has a history of uncovering novel aspects of mammalian cell regulation. The importance of PI3K activity and tyrosine phosphorylation are two examples of insights coming from MT. This study describes new mutants unable to transform like the wild type that point to novel regulation of PI3K signaling. Previous mutants were defective in PI3K because they failed to bind the enzyme and bring the activity to the membrane. These mutants recruit PI3K activity like the wild type, but fail to elevate the cellular level of PIP3, the product used to signal downstream of PI3K. As a result, they fail to activate either Akt or Rac1, explaining the transformation defect.
Keywords: Akt; PI3 kinase; Rac; middle T antigen; polyomavirus; transformation.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The p110alpha isoform of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is essential for polyomavirus middle T antigen-mediated transformation.J Virol. 2007 Jul;81(13):7069-76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00115-07. Epub 2007 Apr 18. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17442716 Free PMC article.
-
Transformation by Polyomavirus Middle T Antigen Involves a Unique Bimodal Interaction with the Hippo Effector YAP.J Virol. 2016 Jul 27;90(16):7032-7045. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00417-16. Print 2016 Aug 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27194756 Free PMC article.
-
Transformation-defective mutants of polyomavirus middle T antigen associate with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase) but are unable to maintain wild-type levels of PI 3-kinase products in intact cells.J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1702-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.66.3.1702-1708.1992. J Virol. 1992. PMID: 1371171 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons from polyoma middle T antigen on signaling and transformation: A DNA tumor virus contribution to the war on cancer.Virology. 2009 Feb 20;384(2):304-16. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.09.042. Epub 2008 Nov 20. Virology. 2009. PMID: 19022468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell transformation by the middle T-antigen of polyoma virus.Oncogene. 2001 Nov 26;20(54):7908-16. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204859. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11753673 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation and mechanism of YAP/TAZ in the mechanical microenvironment of stem cells (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jul;24(1):506. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12145. Epub 2021 May 13. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33982785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S100A10 Has a Critical Regulatory Function in Mammary Tumor Growth and Metastasis: Insights Using MMTV-PyMT Oncomice and Clinical Patient Sample Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 7;12(12):3673. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123673. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33297495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eddy B. 1969. Polyoma virus. Virol Monogr 7:1–114.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

