miRNA-200a/c as potential biomarker in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC): evidence based on miRNA meta-signature and clinical investigations
- PMID: 27835595
- PMCID: PMC5348417
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13154
miRNA-200a/c as potential biomarker in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC): evidence based on miRNA meta-signature and clinical investigations
Abstract
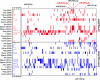
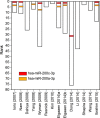
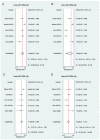
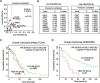
Extensive effort has been put on miRNA expression signatures in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). Unfortunately, consistent conclusion rarely yielded from diverse studies, mainly due to the high inter-lab variability and small sample sizes. To overcome above limitations, an integrated analysis of miRNA expression signature was performed by employing Robust Rank Aggregation (RRA) method. Diagnostic analysis, Kaplan-Meier survival curves and pathway enrichment analysis were used to investigate the clinical values and biological functions of meta-signature miRNAs. A total of 519 EOC and 248 noncancerous samples were included. Seven mostly dysregulated miRNAs were identified by RRA method and two miRNAs (miR-200a-3p and miR-200c-3p) remained statistically significant after Bonferroni-correction. Diagnostic meta-analysis showed reliable diagnostic capacity of miR-200a-3p (with a pooled sensitivity of 0.84 and specificity of 0.83) and miR-200c-3p (with a pooled sensitivity of 0.75 and specificity of 0.66) for EOC. Pathway enrichment analysis and expression correlation analysis suggested miR-200a/c might contribute EOC progression by affecting cellular adhesion process. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis based on two independent cohorts revealed a strong association between miR-200a/c and overall survival in EOC patients. miR-200a/c was identified as the mostly dysregulated miRNAs in EOC and might be novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for patients with EOC.
Keywords: Robust Rank Aggregation; epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC); miRNA-200a/c.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association between miR-200c and the survival of patients with stage I epithelial ovarian cancer: a retrospective study of two independent tumour tissue collections.Lancet Oncol. 2011 Mar;12(3):273-85. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70012-2. Epub 2011 Feb 21. Lancet Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21345725
-
Expression of serum miR-200a, miR-200b, and miR-200c as candidate biomarkers in epithelial ovarian cancer and their association with clinicopathological features.Clin Transl Oncol. 2015 Oct;17(10):779-87. doi: 10.1007/s12094-015-1303-1. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Clin Transl Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26063644
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic implications of the miR-200 family in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Apr 15;7(5):2392-401. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24966949 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-associated miRNAs in ovarian carcinoma, with highlight on the miR-200 family: prognostic value and prospective role in ovarian cancer therapeutics.Cancer Lett. 2014 Sep 1;351(2):173-81. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.05.022. Epub 2014 Jun 18. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 24952258 Review.
-
Epithelial ovarian cancer: the molecular genetics of epithelial ovarian cancer.Ann Oncol. 2016 Apr;27 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):i4-i10. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw083. Ann Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27141069 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circadian gene ARNTL initiates circGUCY1A2 transcription to suppress non-small cell lung cancer progression via miR-200c-3p/PTEN signaling.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Sep 4;42(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02791-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37667322 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of MicroRNAs as Clinical Biomarkers to Aid Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment.Genes (Basel). 2022 Nov 7;13(11):2054. doi: 10.3390/genes13112054. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36360295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating microRNAs as novel potential diagnostic biomarkers for ovarian cancer: a systematic review and updated meta-analysis.J Ovarian Res. 2019 Mar 21;12(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s13048-019-0482-8. J Ovarian Res. 2019. PMID: 30898156 Free PMC article.
-
RNA modification regulators as promising biomarkers in gynecological cancers.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Oct 29;40(1):92. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09924-y. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39472384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A 3-miRNA signature predicts survival of patients with hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma after post-operative radiotherapy.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Dec;23(12):8280-8291. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14702. Epub 2019 Oct 2. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31578816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–132. - PubMed
-
- Roett MA, Evans P. Ovarian cancer: An overview. Am Fam Physician. 2009;80:609–616. - PubMed
-
- Marchetti C, Pisano C, Facchini G, Bruni GS, Magazzino FP, Losito S, Pignata S. First-line treatment of advanced ovarian cancer: Current research and perspectives. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2010;10:47–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

