Preclinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor that evades paradoxical MAPK pathway activation in protein kinase BRAF-mutant lung cancer
- PMID: 27834212
- PMCID: PMC5127364
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1610456113
Preclinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor that evades paradoxical MAPK pathway activation in protein kinase BRAF-mutant lung cancer
Abstract
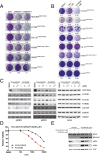
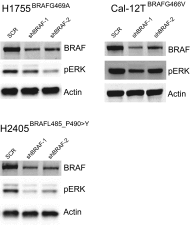
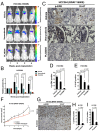
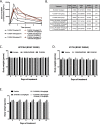
Oncogenic activation of protein kinase BRAF drives tumor growth by promoting mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway signaling. Because oncogenic mutations in BRAF occur in ∼2-7% of lung adenocarcinoma (LA), BRAF-mutant LA is the most frequent cause of BRAF-mutant cancer mortality worldwide. Whereas most tumor types harbor predominantly the BRAFV600E-mutant allele, the spectrum of BRAF mutations in LA includes BRAFV600E (∼60% of cases) and non-V600E mutant alleles (∼40% of cases) such as BRAFG469A and BRAFG466V The presence of BRAFV600E in LA has prompted clinical trials testing selective BRAF inhibitors such as vemurafenib in BRAFV600E-mutant patients. Despite promising clinical efficacy, both innate and acquired resistance often result from reactivation of MAPK pathway signaling, thus limiting durable responses to the current BRAF inhibitors. Further, the optimal therapeutic strategy to block non-V600E BRAF-mutant LA remains unclear. Here, we report the efficacy of the Raf proto-oncogene serine/threonine protein kinase (RAF) inhibitor, PLX8394, that evades MAPK pathway reactivation in BRAF-mutant LA models. We show that PLX8394 treatment is effective in both BRAFV600E and certain non-V600 LA models, in vitro and in vivo. PLX8394 was effective against treatment-naive BRAF-mutant LAs and those with acquired vemurafenib resistance caused by an alternatively spliced, truncated BRAFV600E that promotes vemurafenib-insensitive MAPK pathway signaling. We further show that acquired PLX8394 resistance occurs via EGFR-mediated RAS-mTOR signaling and is prevented by upfront combination therapy with PLX8394 and either an EGFR or mTOR inhibitor. Our study provides a biological rationale and potential polytherapy strategy to aid the deployment of PLX8394 in lung cancer patients.
Keywords: BRAF; cancer; lung; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
G.B. and A.R. are employees of Plexxikon, Inc., which produced vemurafenib and PLX8394. T.G.B. is a consultant to Driver Group, Novartis, Astellas, Natera, Array Biopharma, Ariad, Teva, Astrazeneca, and a recipient of research grants from Servier and Ignyta.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RAF inhibitors that evade paradoxical MAPK pathway activation.Nature. 2015 Oct 22;526(7574):583-6. doi: 10.1038/nature14982. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26466569
-
PLX8394, a new generation BRAF inhibitor, selectively inhibits BRAF in colonic adenocarcinoma cells and prevents paradoxical MAPK pathway activation.Mol Cancer. 2017 Jun 28;16(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0684-x. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28659148 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Acquired Resistance to RAF Inhibitor Combinations in BRAF-Mutant Colorectal Cancer through MAPK Pathway Alterations.Cancer Discov. 2015 Apr;5(4):358-67. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-1518. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Cancer Discov. 2015. PMID: 25673644 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting oncogenic Raf protein-serine/threonine kinases in human cancers.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Sep;135:239-258. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.08.013. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 30118796 Review.
-
BRAF as a target for cancer therapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011 Mar;11(3):285-95. doi: 10.2174/187152011795347469. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21426297 Review.
Cited by
-
Primary and metastatic tumors exhibit systems-level differences in dependence on mitochondrial respiratory function.PLoS Biol. 2022 Sep 22;20(9):e3001753. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001753. eCollection 2022 Sep. PLoS Biol. 2022. PMID: 36137002 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Oncogenic BRAF: Past, Present, and Future.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 16;11(8):1197. doi: 10.3390/cancers11081197. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31426419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BRAF Mutations and the Utility of RAF and MEK Inhibitors in Primary Brain Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 28;11(9):1262. doi: 10.3390/cancers11091262. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31466300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RAF inhibitor PLX8394 selectively disrupts BRAF dimers and RAS-independent BRAF-mutant-driven signaling.Nat Med. 2019 Feb;25(2):284-291. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0274-5. Epub 2018 Dec 17. Nat Med. 2019. PMID: 30559419 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Landscape of BRAF-Mutant NSCLC Reveals an Association Between Clonality and Driver Mutations and Identifies Targetable Non-V600 Driver Mutations.J Thorac Oncol. 2020 Oct;15(10):1611-1623. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2020.05.021. Epub 2020 Jun 13. J Thorac Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32540409 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

