TWEAK activation of the non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway differentially regulates melanoma and prostate cancer cell invasion
- PMID: 27821799
- PMCID: PMC5348407
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13034
TWEAK activation of the non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway differentially regulates melanoma and prostate cancer cell invasion
Abstract
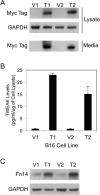
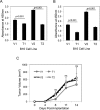
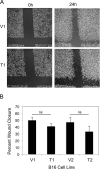
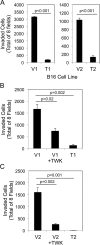
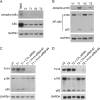
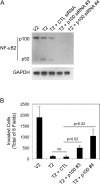
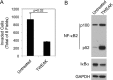
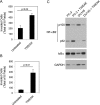
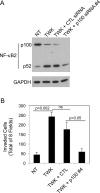
Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) is a multifunctional cytokine that binds with high affinity to a plasma membrane-anchored receptor named Fn14. Both TWEAK and Fn14 expression has been detected in human cancer tissue, and studies have shown that TWEAK/Fn14 signaling can promote either "pro-cancer" or "anti-cancer" cellular effects in vitro, depending on the cancer cell line under investigation. In this study, we engineered murine B16 melanoma cells to secrete high levels of soluble TWEAK and examined their properties. TWEAK production by B16 cells preferentially activated the non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway and increased the expression of several previously described TWEAK-inducible genes, including Fn14. TWEAK overexpression in B16 cells inhibited both cell growth and invasion in vitro. The TWEAK-mediated reduction in B16 cell invasive capacity was dependent on activation of the non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway. Finally, we found that this same signaling pathway was also important for TWEAK-stimulated human DU145 prostate cancer cell invasion. Therefore, even though TWEAK:Fn14 binding activates non-canonical NF-κB signaling in both melanoma and prostate cancer cells, this shared cellular response can trigger a very different downstream outcome (inhibition or stimulation of cell invasiveness, respectively).
Keywords: Fn14; NF-κB; TWEAK; invasion; melanoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TWEAK/Fn14 interaction induces proliferation and migration in human airway smooth muscle cells via activating the NF-κB pathway.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Apr;119(4):3528-3536. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26525. Epub 2018 Jan 11. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29143982
-
Fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 mediates macrophage infiltration in heart to promote pressure overload-induced cardiac dysfunction.Life Sci. 2020 Apr 15;247:117440. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117440. Epub 2020 Feb 15. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32070706 Free PMC article.
-
TWEAK Signaling Pathway Blockade Slows Cyst Growth and Disease Progression in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Aug;32(8):1913-1932. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020071094. Epub 2021 Jun 21. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34155062 Free PMC article.
-
Out of the TWEAKlight: Elucidating the Role of Fn14 and TWEAK in Acute Kidney Injury.Semin Nephrol. 2016 May;36(3):189-98. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2016.03.006. Semin Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27339384 Review.
-
Controversies in TWEAK-Fn14 signaling in skeletal muscle atrophy and regeneration.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Sep;77(17):3369-3381. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03495-x. Epub 2020 Mar 21. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32200423 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Road to Metastasis: The TWEAK Pathway as a Discriminant between Metastasizing and Non-Metastasizing Thick Melanomas.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 29;22(19):10568. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910568. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638912 Free PMC article.
-
Retinol dehydrogenase-10 promotes development and progression of human glioma via the TWEAK-NF-κB axis.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 27;8(62):105262-105275. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22166. eCollection 2017 Dec 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29285249 Free PMC article.
-
Biofluid quantification of TWEAK/Fn14 axis in combination with a selected biomarker panel improves assessment of prostate cancer aggressiveness.J Transl Med. 2019 Sep 9;17(1):307. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-2053-6. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31500625 Free PMC article.
-
TWEAK/Fn14 Activation Participates in Skin Inflammation.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:6746870. doi: 10.1155/2017/6746870. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 29038621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TWEAK Progress in Dermatology: A Review.Indian J Dermatol. 2023 Jul-Aug;68(4):425-429. doi: 10.4103/ijd.ijd_885_22. Indian J Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37822396 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chicheportiche Y, Bourdon PR, Xu H, Hsu YM, Scott H, Hession C, Garcia I, Browning JL. TWEAK, a new secreted ligand in the tumor necrosis factor family that weakly induces apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:32401–32410. - PubMed
-
- Saitoh T, Nakayama M, Nakano H, Yagita H, Yamamoto N, Yamaoka S. TWEAK induces NF-kappaB2 p100 processing and long lasting NF-κB activation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:36005–36012. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

