Impact of clinical parameters and systemic inflammatory status on epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients readministration with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 27821111
- PMCID: PMC5100346
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2917-6
Impact of clinical parameters and systemic inflammatory status on epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients readministration with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Abstract
Background: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) readministration to lung cancer patients is common owing to the few options available. Impact of clinical factors on prognosis of EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients receiving EGFR-TKI readministration after first-line EGFR-TKI failure and a period of TKI holiday remains unclear. Through this retrospective study, we aimed to understand the impact of clinical factors in such patients.
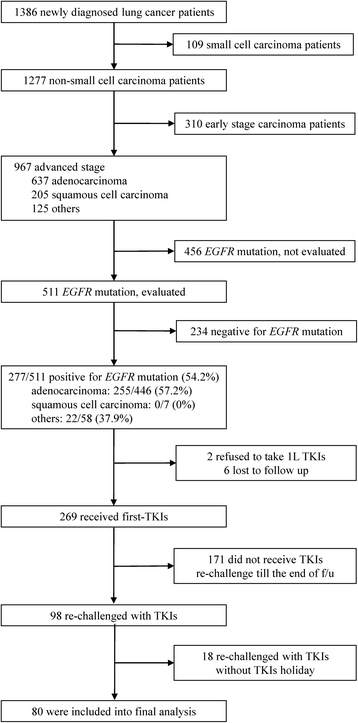
Methods: Of 1386 cases diagnosed between December 2010 and December 2013, 80 EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients who were readministered TKIs after failure of first-line TKIs and intercalated with at least one cycle of cytotoxic agent were included. We evaluated clinical factors that may influence prognosis of TKI readministration as well as systemic inflammatory status in terms of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR). Baseline NLR and LMR were estimated at the beginning of TKI readministration and trends of NLR and LMR were change amount from patients receiving first-Line TKIs to TKIs readministration.
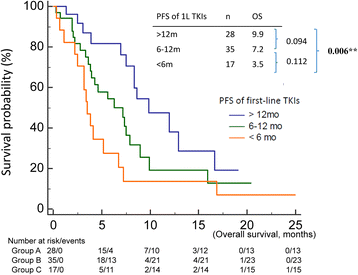
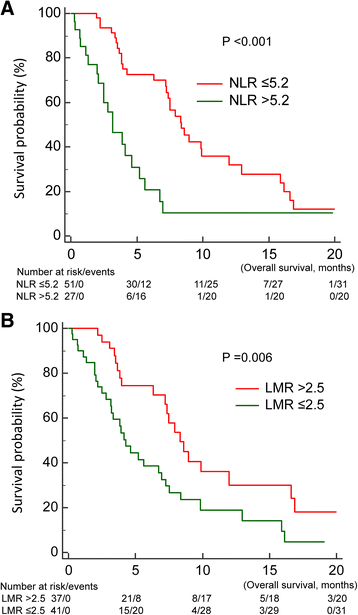
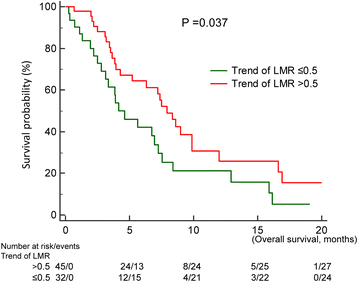
Results: Median survival time since TKI readministration was 7.0 months. In the univariable analysis, progression free survival (PFS) of first-line TKIs, baseline NLR and LMR, and trend of LMR were prognostic factors in patients receiving TKIs readministration. In the multivariate analysis, only PFS of first-line TKIs (p < 0.001), baseline NLR (p = 0.037), and trend of LMR (p = 0.004) were prognostic factors.
Conclusion: Longer PFS of first-line TKIs, low baseline NLR, and high trend of LMR were good prognostic factors in EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients receiving TKI readministration.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor receptor; Lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio; Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; Non-small cell lung cancer; Readministration; Tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Baseline and Trend of Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio as Prognostic Factors in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with First-Line Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 27;10(8):e0136252. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136252. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26313661 Free PMC article.
-
The association between clinical prognostic factors and epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) efficacy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients: a retrospective assessment of 94 cases with EGFR mutations.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):3412-3421. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13787. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27926500 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) predicts poor responses to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring activating EGFR mutations.Lung Cancer. 2015 Mar;87(3):311-7. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.01.004. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Lung Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25617986
-
Next-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in epidermal growth factor receptor -mutant non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2016 Mar;93:59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.01.003. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Lung Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26898616 Review.
-
Dacomitinib in lung cancer: a "lost generation" EGFR tyrosine-kinase inhibitor from a bygone era?Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Oct 15;9:5641-53. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S52787. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26508839 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fragment size and dynamics of EGFR-mutated tumor-derived DNA provide prognostic information regarding EGFR-TKI efficacy in patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 8;12(1):13544. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17848-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35941190 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Retreatment in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients Previously Exposed to EGFR-TKI: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Pers Med. 2024 Jul 15;14(7):752. doi: 10.3390/jpm14070752. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39064005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts treatment efficacy and prognosis of cytotoxic anticancer drugs, molecular targeted drugs, and immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021 Jan;10(1):221-232. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-777. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33569306 Free PMC article.
-
Host-Dependent Phenotypic Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors.Cancer Res. 2021 Jul 15;81(14):3862-3875. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-3555. Epub 2021 May 3. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33941614 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Polymorphisms in Inflammation Genes With the Prognosis of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Receiving Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 18;12:836117. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.836117. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35372081 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou S, Ren S, et al. Final overall survival results from a randomised, phase III study of erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment of EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802) Ann Oncol. 2015;26(9):1877–1883. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv276. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fukuoka M, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Sunpaweravong P, Leong SS, Sriuranpong V, Chao TY, Nakagawa K, Chu DT, Saijo N, et al. Biomarker analyses and final overall survival results from a phase III, randomized, open-label, first-line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer in Asia (IPASS) J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(21):2866–2874. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.4235. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wu YL, Zhou C, Hu CP, Feng J, Lu S, Huang Y, Li W, Hou M, Shi JH, Lee KY, et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(2):213–222. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70604-1. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

