The Spectrum of CHM Gene Mutations in Choroideremia and Their Relationship to Clinical Phenotype
- PMID: 27820636
- PMCID: PMC5102569
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.16-20230
The Spectrum of CHM Gene Mutations in Choroideremia and Their Relationship to Clinical Phenotype
Abstract
Purpose: We report the underlying genotype and explore possible genotypic-phenotypic correlations in a large cohort of choroideremia patients.
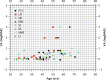
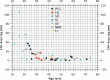
Methods: We studied prospectively a cohort of 79 patients diagnosed within a tertiary referral service for patients with retinal dystrophies. Phenotypic evaluation consisted of clinical examination, including visual acuity and residual retinal area by fundus autofluorescence (FAF). Genotype was established by sequencing. We also investigated whether particular genotypes were associated with more severe phenotypes by performing analysis of covariance (ANCOVA), with visual acuity and FAF as the dependent variables and age as the covariant.
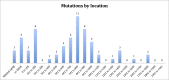
Results: A total of 74 (94%) of patients in our cohort had causative mutations by sequencing, the majority of which were anticipated to be null. Of these, 35 (47%) had insertions and deletions, 13 (18%) had mutations predicted to affect splicing, and 26 (35%) had single point mutations. In the latter case, 13 of 21 (62%) pedigrees with single point mutations were C to T transitions at C-phosphate-G (CpG) dinucleotides. These mutations were spread across 5 of only 24 CpG dinucleotides in the entire CHM cDNA. Furthermore, these 5 locations are the only sites at which C to T transitions result in a stop codon. No clear evidence was found for genotype-phenotype correlation except in the instance of a patient with a large deletion involving neighbouring sequences.
Conclusions: In patients with a diagnosis of choroideremia made by a specialty service, there is a high likelihood of establishing a genetic diagnosis. The majority of causative mutations appear to be null and, therefore, may benefit from gene replacement therapy. A disproportionate number of single point mutations observed were C to T transitions, consistent with the evolutionary decay of CpG dinucleotides through methylation and subsequent deamination. Hence, the development of choroideremia in such patients may represent the unwanted consequence of human evolution; de novo mutations are predicted to arise at these sites in future generations. (ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT01461213.).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Retinal dystrophy and subretinal drusenoid deposits in female choroideremia carriers.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017 Nov;255(11):2099-2111. doi: 10.1007/s00417-017-3751-5. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28752371
-
High-resolution images of retinal structure in patients with choroideremia.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Feb 1;54(2):950-61. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-10707. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23299470 Free PMC article.
-
Novel mutation in the choroideremia gene and multi-Mendelian phenotypes in Spanish families.Br J Ophthalmol. 2018 Oct;102(10):1378-1386. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2017-311427. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Br J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29367200
-
CHM mutation spectrum and disease: An update at the time of human therapeutic trials.Hum Mutat. 2021 Apr;42(4):323-341. doi: 10.1002/humu.24174. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Hum Mutat. 2021. PMID: 33538369 Review.
-
Choroideremia: molecular mechanisms and therapies.Trends Mol Med. 2022 May;28(5):378-387. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2022.02.011. Epub 2022 Mar 24. Trends Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35341685 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterizing the Natural History of Visual Function in Choroideremia Using Microperimetry and Multimodal Retinal Imaging.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017 Oct 1;58(12):5575-5583. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-22486. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017. PMID: 29084330 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Molecular Therapies for Choroideremia.Genes (Basel). 2019 Sep 23;10(10):738. doi: 10.3390/genes10100738. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31548516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors as Versatile Tools for Neurological Disorders: Focus on Delivery Routes and Therapeutic Perspectives.Biomedicines. 2022 Mar 23;10(4):746. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040746. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35453499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multimodal imaging reveals retinoschisis masquerading as retinal detachment in patients with choroideremia.Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2022 Apr 20;26:101543. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2022.101543. eCollection 2022 Jun. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35496760 Free PMC article.
-
Bilateral visual acuity decline in males with choroideremia: a pooled, cross-sectional meta-analysis.BMC Ophthalmol. 2022 Jan 16;22(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12886-022-02250-z. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35034620 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mauthner L. Ein Fall von Choroideremia. Ber Naturw Med Vereins. 1871; 11.
-
- Seabra MC,, Brown MS,, Goldstein JL. Retinal degeneration in choroideremia: deficiency of rab geranylgeranyl transferase. Science. 1993; 259: 377–381. - PubMed
-
- Freund P,, Furgoch M,, MacDonald I. Genotype-phenotype analysis of male subjects affected by choroideremia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013; 54: 1567–1567.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

