Tissue factor is an angiogenic-specific receptor for factor VII-targeted immunotherapy and photodynamic therapy
- PMID: 27807692
- PMCID: PMC5306358
- DOI: 10.1007/s10456-016-9530-9
Tissue factor is an angiogenic-specific receptor for factor VII-targeted immunotherapy and photodynamic therapy
Abstract
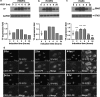
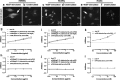
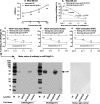
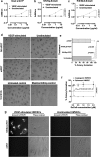
Identification of target molecules specific for angiogenic vascular endothelial cells (VEC), the inner layer of pathological neovasculature, is critical for discovery and development of neovascular-targeting therapy for angiogenesis-dependent human diseases, notably cancer, macular degeneration and endometriosis, in which vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays a central pathophysiological role. Using VEGF-stimulated vascular endothelial cells (VECs) isolated from microvessels, venous and arterial blood vessels as in vitro angiogenic models and unstimulated VECs as a quiescent VEC model, we examined the expression of tissue factor (TF), a membrane-bound receptor on the angiogenic VEC models compared with quiescent VEC controls. We found that TF is specifically expressed on angiogenic VECs in a time-dependent manner in microvessels, venous and arterial vessels. TF-targeted therapeutic agents, including factor VII (fVII)-IgG1 Fc and fVII-conjugated photosensitizer, can selectively bind angiogenic VECs, but not the quiescent VECs. Moreover, fVII-targeted photodynamic therapy can selectively and completely eradicate angiogenic VECs. We conclude that TF is an angiogenic-specific receptor and the target molecule for fVII-targeted therapeutics. This study supports clinical trials of TF-targeted therapeutics for the treatment of angiogenesis-dependent diseases such as cancer, macular degeneration and endometriosis.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Factor VII-targeted therapy; Tissue factor; VEGF; Vascular endothelial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Z.H. is co-inventor of US patents on neovascular-targeted immunoconjugates (ICON) and is co-inventor of two US patent applications on “Factor VII conjugates for selectively treating neovascularization disorders.” W.R. is currently serving as a consultant for Iconic Therapeutics, a startup biotech based on ICON patents. Other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting tissue factor on tumour cells and angiogenic vascular endothelial cells by factor VII-targeted verteporfin photodynamic therapy for breast cancer in vitro and in vivo in mice.BMC Cancer. 2010 May 26;10:235. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-235. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20504328 Free PMC article.
-
Selective and effective killing of angiogenic vascular endothelial cells and cancer cells by targeting tissue factor using a factor VII-targeted photodynamic therapy for breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Apr;126(3):589-600. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-0957-1. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 20514515 Free PMC article.
-
Effective treatment of chemoresistant breast cancer in vitro and in vivo by a factor VII-targeted photodynamic therapy.Br J Cancer. 2011 Apr 26;104(9):1401-9. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.88. Epub 2011 Mar 22. Br J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21427724 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms in retinal angiogenesis and DiGeorge syndrome.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2005;67(4):229-76. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2005. PMID: 16334858 Review.
-
Cells and the activation of factor VII.Haemostasis. 1996;26 Suppl 1:1-5. doi: 10.1159/000217229. Haemostasis. 1996. PMID: 8904164 Review.
Cited by
-
Divergent Impact of Breast Cancer Laterality on Clinicopathological, Angiogenic, and Hemostatic Profiles: A Potential Role of Tumor Localization in Future Outcomes.J Clin Med. 2020 Jun 2;9(6):1708. doi: 10.3390/jcm9061708. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32498398 Free PMC article.
-
Role of angiogenesis in adenomyosis-associated abnormal uterine bleeding and subfertility: a systematic review.Hum Reprod Update. 2019 Sep 11;25(5):647-671. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmz024. Hum Reprod Update. 2019. PMID: 31504506 Free PMC article.
-
TAZ inhibition promotes IL-2-induced apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating the JNK/F-actin/mitochondrial fission pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2018 Aug 14;18:117. doi: 10.1186/s12935-018-0615-y. eCollection 2018. Cancer Cell Int. 2018. PMID: 30127666 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue factor as a new target for tumor therapy-killing two birds with one stone: a narrative review.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Nov;10(22):1250. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5067. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36544632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic effect of Sirtuin 3 on ameliorating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The role of the ERK-CREB pathway and Bnip3-mediated mitophagy.Redox Biol. 2018 Sep;18:229-243. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.07.011. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 30056271 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

