Capture Hi-C identifies a novel causal gene, IL20RA, in the pan-autoimmune genetic susceptibility region 6q23
- PMID: 27799070
- PMCID: PMC5088679
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-016-1078-x
Capture Hi-C identifies a novel causal gene, IL20RA, in the pan-autoimmune genetic susceptibility region 6q23
Abstract
Background: The identification of causal genes from genome-wide association studies (GWAS) is the next important step for the translation of genetic findings into biologically meaningful mechanisms of disease and potential therapeutic targets. Using novel chromatin interaction detection techniques and allele specific assays in T and B cell lines, we provide compelling evidence that redefines causal genes at the 6q23 locus, one of the most important loci that confers autoimmunity risk.
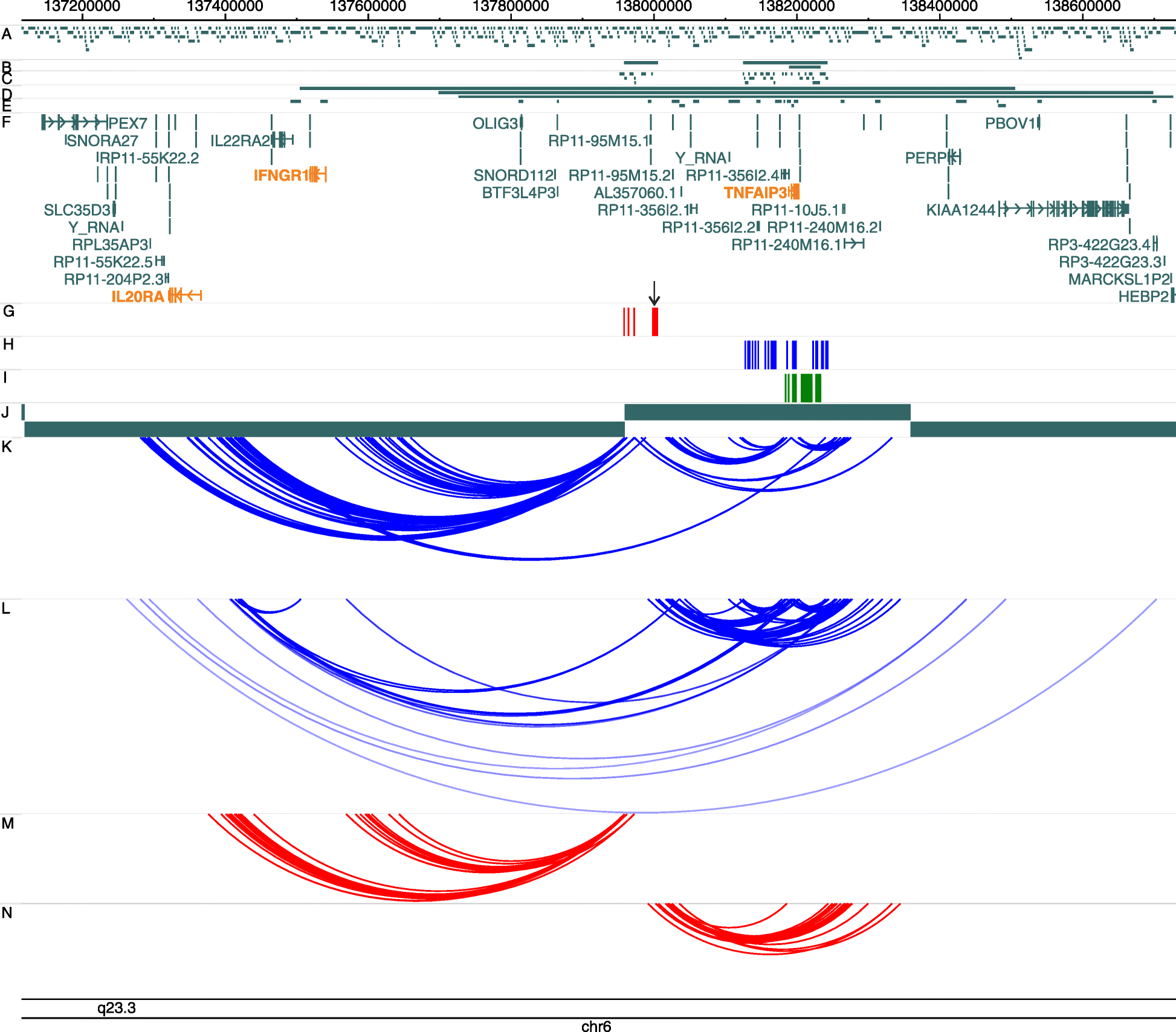
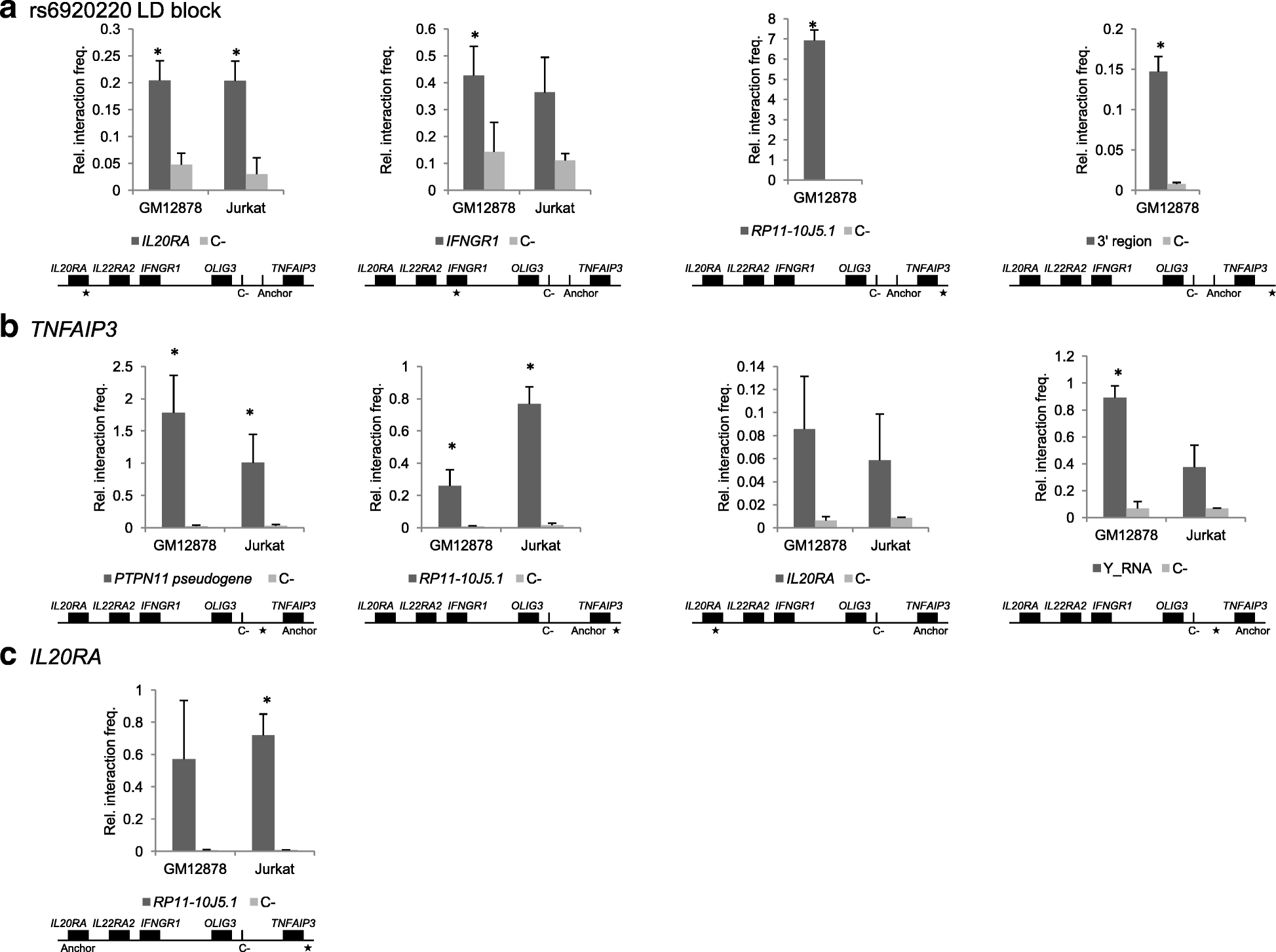
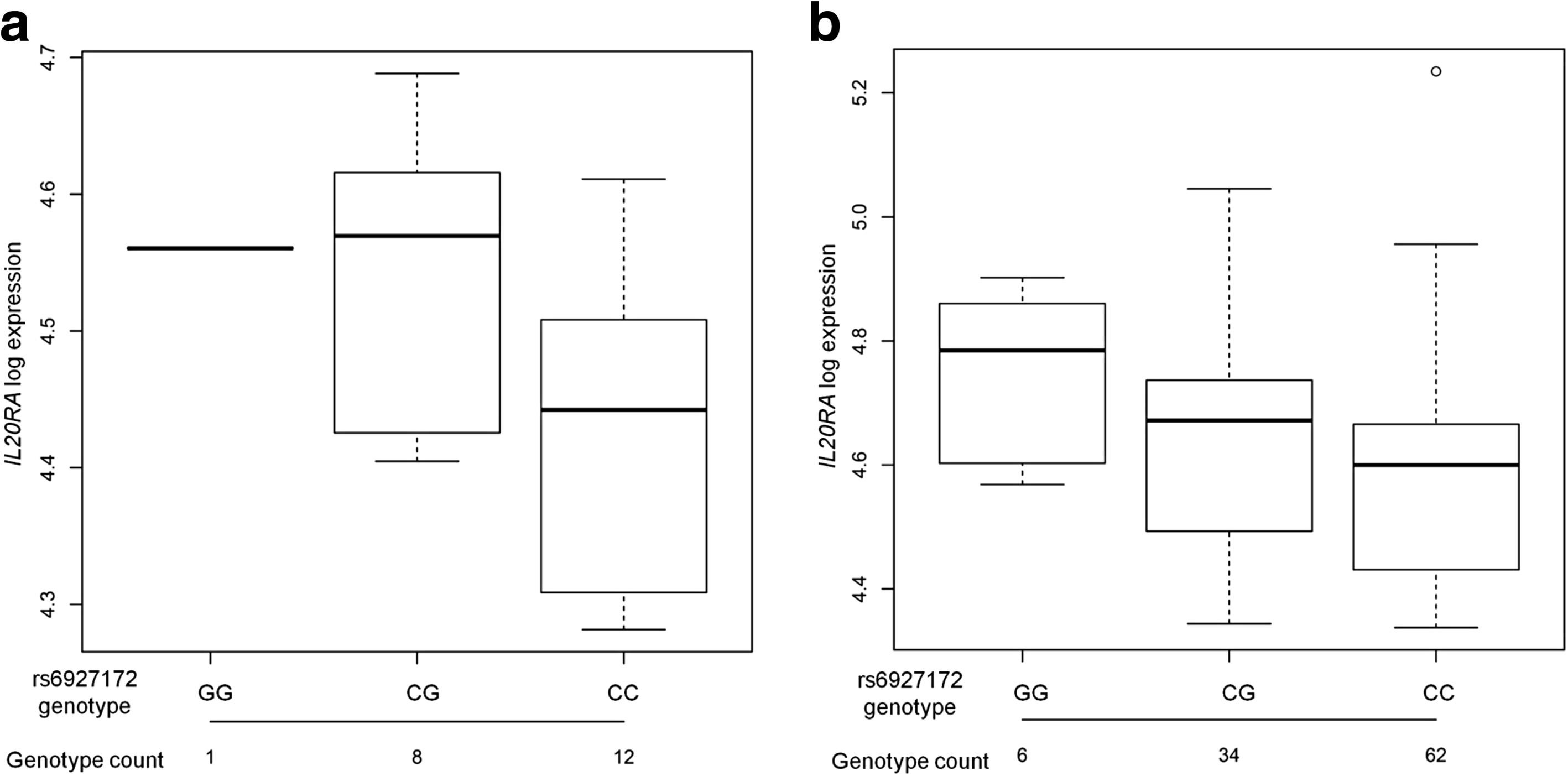
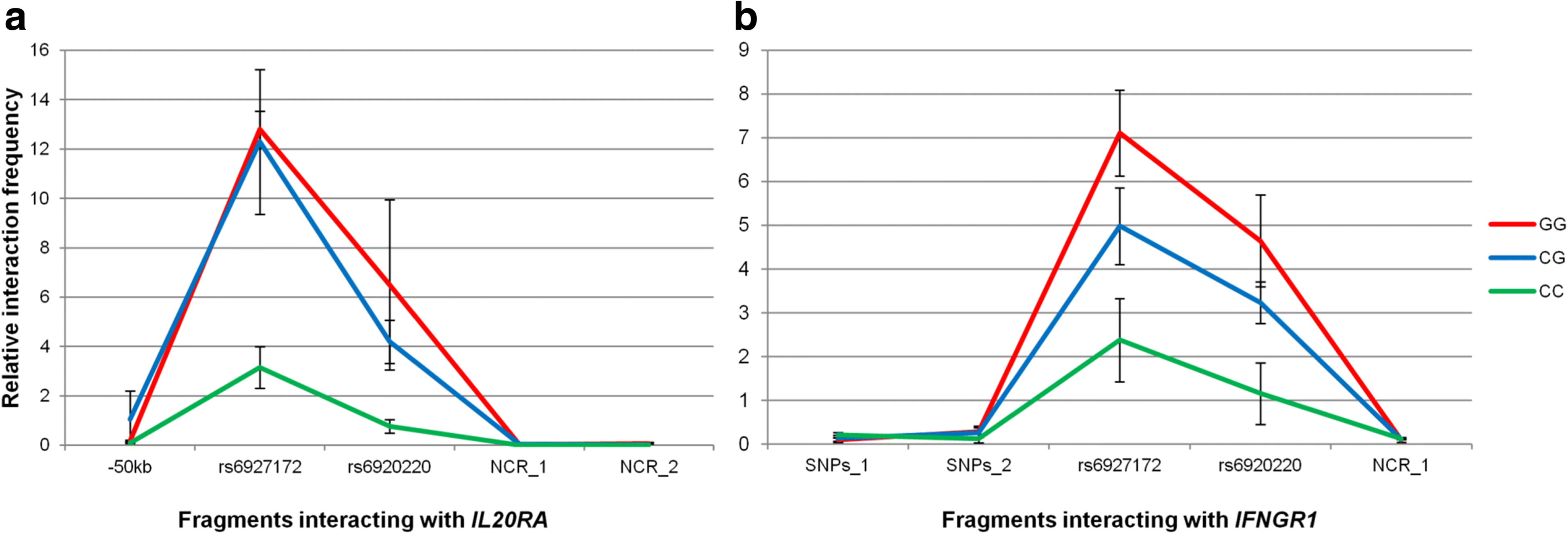
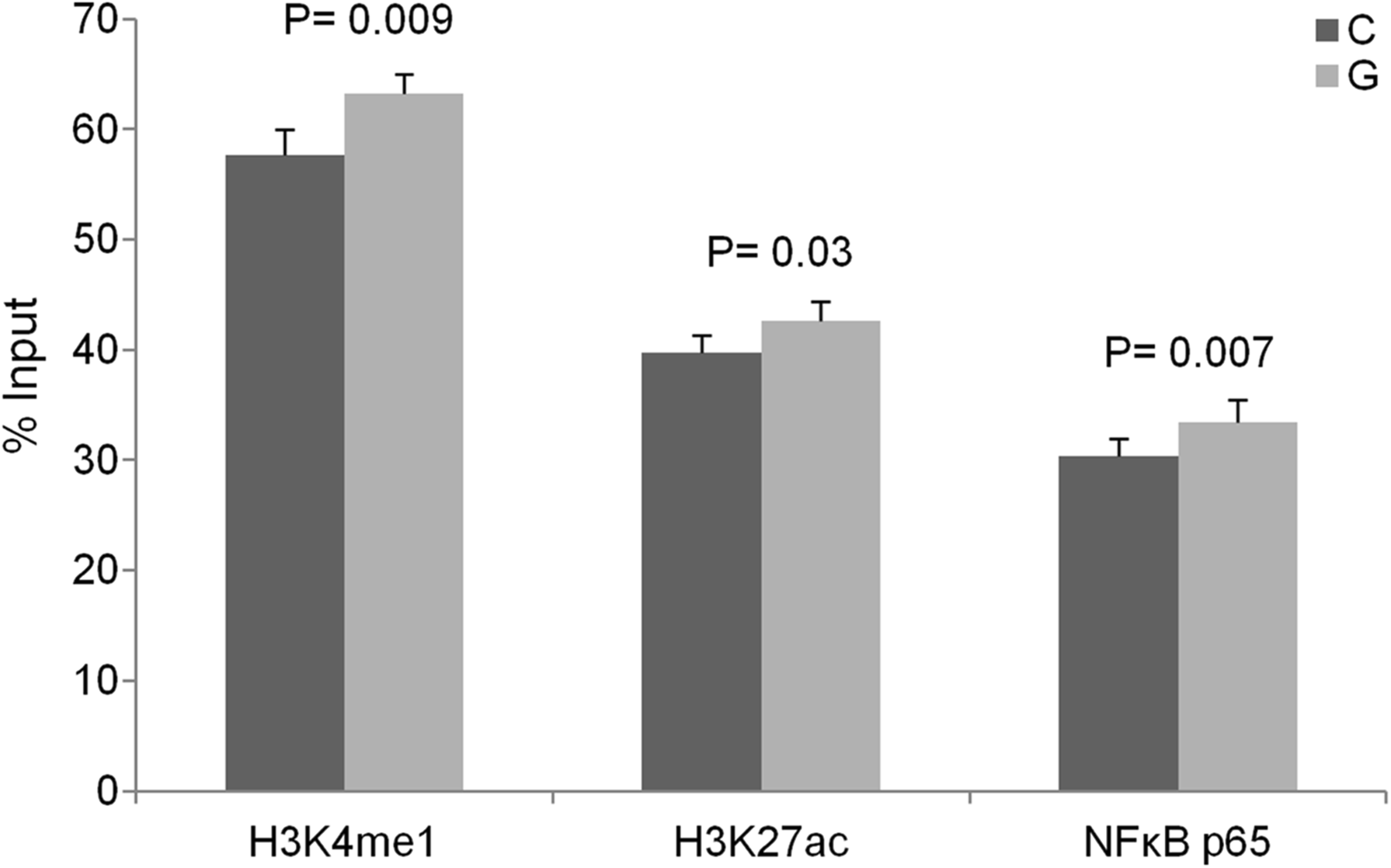
Results: Although the function of disease-associated non-coding single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) at 6q23 is unknown, the association is generally assigned to TNFAIP3, the closest gene. However, the DNA fragment containing the associated SNPs interacts through chromatin looping not only with TNFAIP3, but also with IL20RA, located 680 kb upstream. The risk allele of the most likely causal SNP, rs6927172, is correlated with both a higher frequency of interactions and increased expression of IL20RA, along with a stronger binding of both the NFκB transcription factor and chromatin marks characteristic of active enhancers in T-cells.
Conclusions: Our results highlight the importance of gene assignment for translating GWAS findings into biologically meaningful mechanisms of disease and potential therapeutic targets; indeed, monoclonal antibody therapy targeting IL-20 is effective in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis, both with strong GWAS associations to this region.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; Capture Hi-C; Causal genes; Functional genomics; Genome-wide association studies (GWAS); Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identifying Causal Genes at the Multiple Sclerosis Associated Region 6q23 Using Capture Hi-C.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 18;11(11):e0166923. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166923. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27861577 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of TNFAIP3, a feedback inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB and the neighbor intergenic 6q23 region in rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility.Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(2):R42. doi: 10.1186/ar2650. Epub 2009 Mar 17. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19292917 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide association study of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis identifies new disease loci.PLoS Genet. 2008 Mar 28;4(3):e1000041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000041. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18369459 Free PMC article.
-
What have genome-wide studies told us about psoriatic arthritis?Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2012 Aug;14(4):364-8. doi: 10.1007/s11926-012-0255-5. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22532288 Review.
-
The Functional Impact of Alternative Splicing and Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2021;22(8):1014-1029. doi: 10.2174/1389201021666201001142416. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33001009 Review.
Cited by
-
Using functional genomics to advance the understanding of psoriatic arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020 Nov 1;59(11):3137-3146. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa283. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020. PMID: 32778885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alzheimer's Disease Risk Variant rs2373115 Regulates GAB2 and NARS2 Expression in Human Brain Tissues.J Mol Neurosci. 2018 Sep;66(1):37-43. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1144-9. Epub 2018 Aug 7. J Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30088171
-
Resolving mechanisms of immune-mediated disease in primary CD4 T cells.EMBO Mol Med. 2020 May 8;12(5):e12112. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202012112. Epub 2020 Apr 1. EMBO Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32239644 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of inherited noncoding genetic variation impacting the pharmacogenomics of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia treatment.Nat Commun. 2024 May 1;15(1):3681. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48124-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38693155 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of chromatin organization and gene expression in T cells identifies functional genes for rheumatoid arthritis.Nat Commun. 2020 Sep 2;11(1):4402. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18180-7. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32879318 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

