An H4K16 histone acetyltransferase mediates decondensation of the X chromosome in C. elegans males
- PMID: 27777629
- PMCID: PMC5070013
- DOI: 10.1186/s13072-016-0097-x
An H4K16 histone acetyltransferase mediates decondensation of the X chromosome in C. elegans males
Abstract
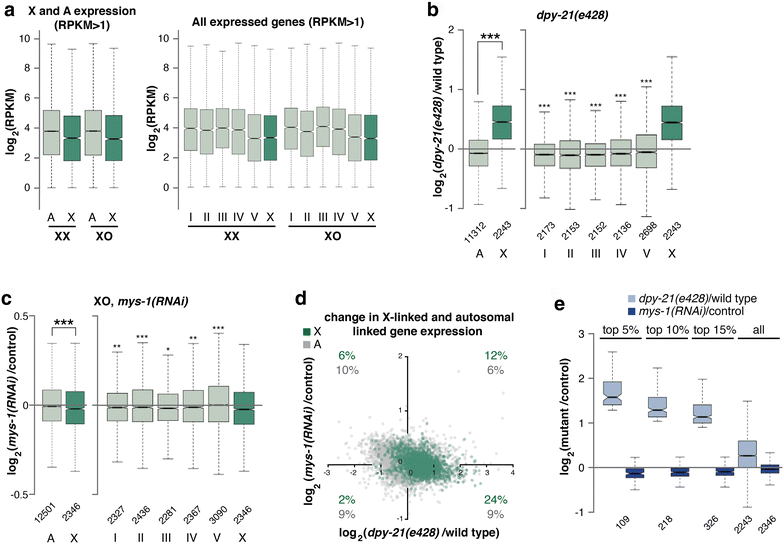
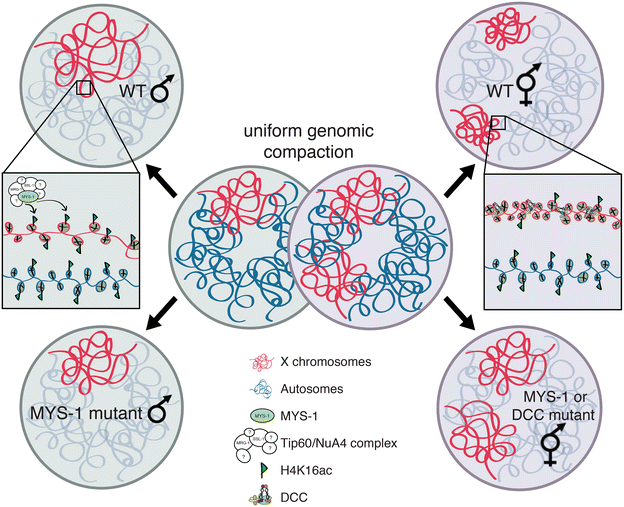
Background: In C. elegans, in order to equalize gene expression between the sexes and balance X and autosomal expression, two steps are believed to be required. First, an unknown mechanism is hypothesized to upregulate the X chromosome in both sexes. This mechanism balances the X to autosomal expression in males, but creates X overexpression in hermaphrodites. Therefore, to restore the balance, hermaphrodites downregulate gene expression twofold on both X chromosomes. While many studies have focused on X chromosome downregulation, the mechanism of X upregulation is not known.
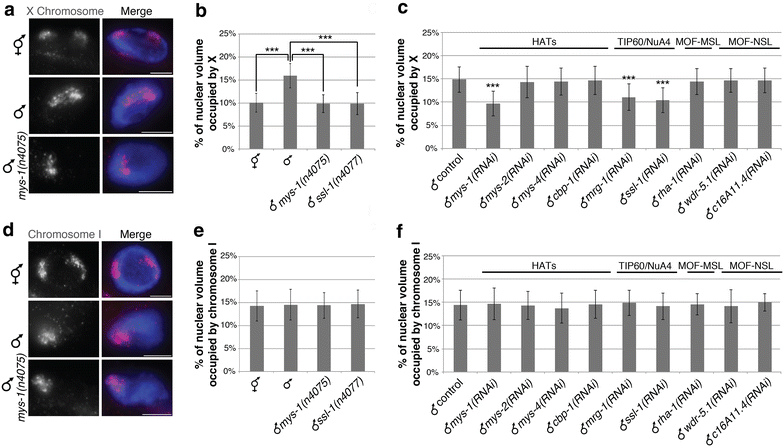
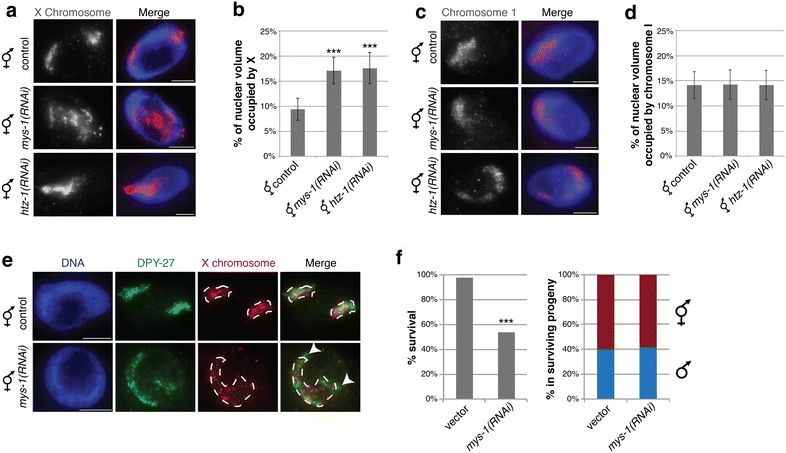
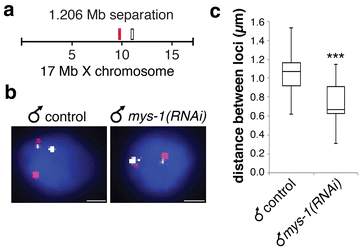
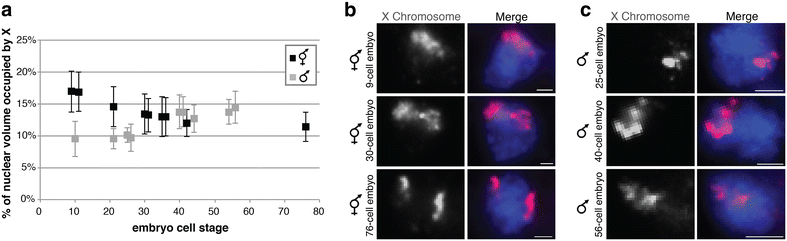
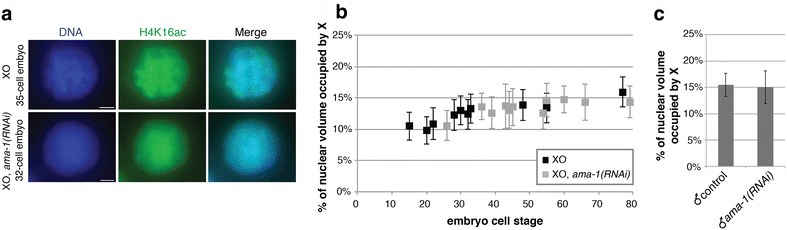
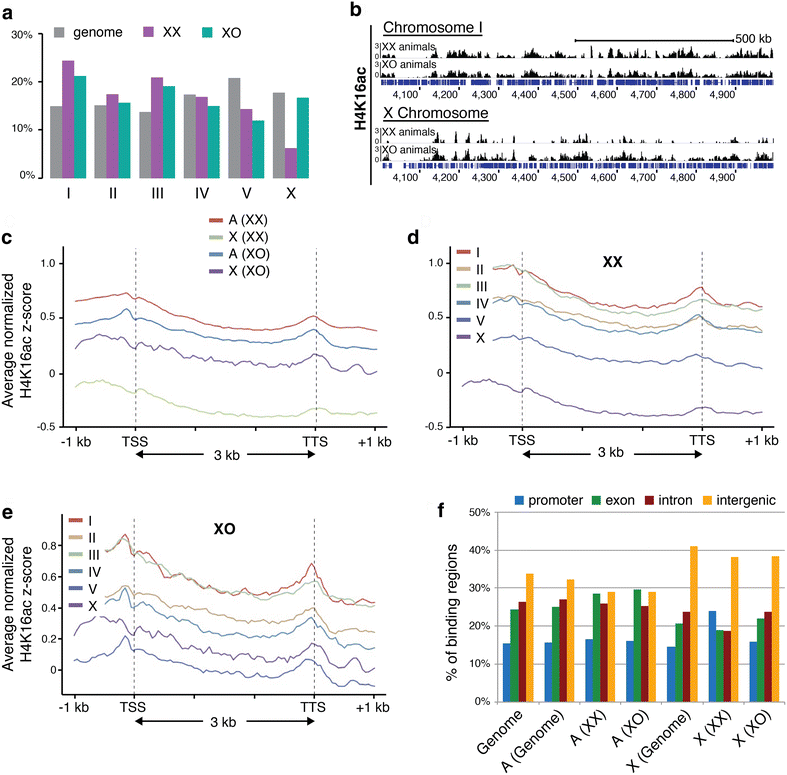
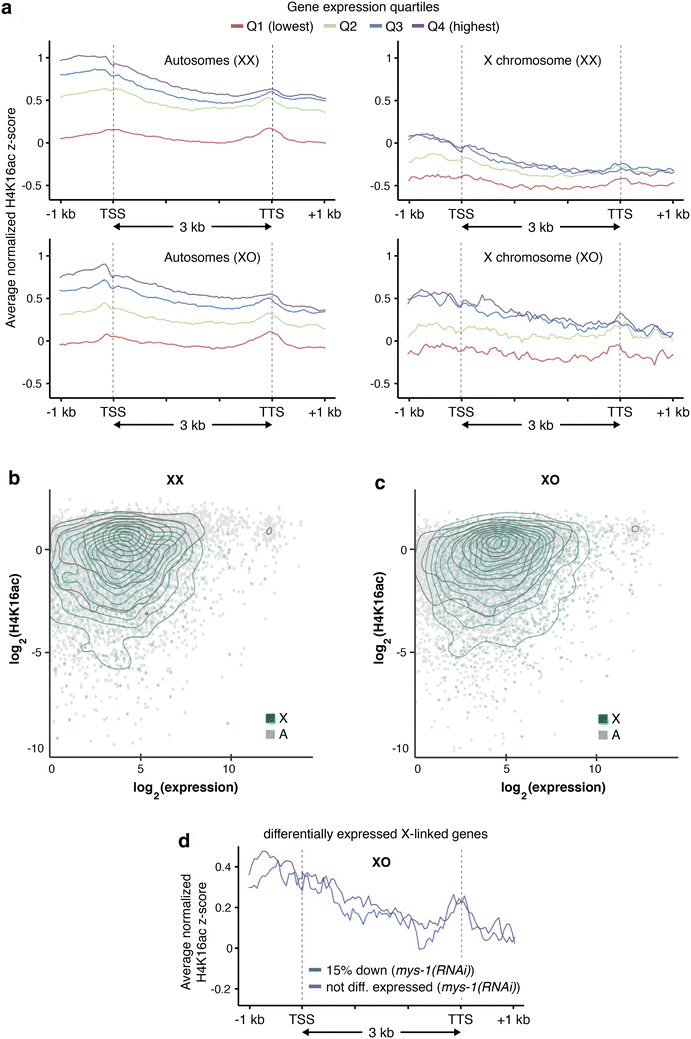
Results: To gain more insight into X upregulation, we studied the effects of chromatin condensation and histone acetylation on gene expression levels in male C. elegans. We have found that the H4K16 histone acetyltransferase MYS-1/Tip60 mediates dramatic decondensation of the male X chromosome as measured by FISH. However, RNA-seq analysis revealed that MYS-1 contributes only slightly to upregulation of gene expression on the X chromosome. These results suggest that the level of chromosome decondensation does not necessarily correlate with the degree of gene expression change in vivo. Furthermore, the X chromosome is more sensitive to MYS-1-mediated decondensation than the autosomes, despite similar levels of H4K16ac on all chromosomes, as measured by ChIP-seq. H4K16ac levels weakly correlate with gene expression levels on both the X and the autosomes, but highly expressed genes on the X chromosome do not contain exceptionally high levels of H4K16ac.
Conclusion: These results indicate that H4K16ac and chromosome decondensation influence regulation of the male X chromosome; however, they do not fully account for the high levels of gene expression observed on the X chromosomes.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; Chromatin; Chromosome territories; Dosage compensation; Epigenetics; Gene expression; Histone acetylation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Caenorhabditis elegans dosage compensation regulates histone H4 chromatin state on X chromosomes.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 May;32(9):1710-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06546-11. Epub 2012 Mar 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22393255 Free PMC article.
-
Linking dosage compensation and X chromosome nuclear organization in C. elegans.Nucleus. 2015;6(4):266-72. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2015.1059546. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Nucleus. 2015. PMID: 26055265 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of DCC localization by HTZ-1/H2A.Z and DPY-30 does not correlate with H3K4 methylation levels.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25973. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025973. Epub 2011 Oct 5. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21998734 Free PMC article.
-
Balancing up and downregulation of the C. elegans X chromosomes.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2015 Apr;31:50-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2015.04.001. Epub 2015 May 16. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2015. PMID: 25966908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of sex determination and X-chromosome dosage compensation.Genetics. 2022 Feb 4;220(2):iyab197. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab197. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 35100381 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Non-canonical Drosophila X chromosome dosage compensation and repressive topologically associated domains.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2018 Oct 24;11(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13072-018-0232-y. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2018. PMID: 30355339 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell dynamics of chromatin activity during cell lineage differentiation in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos.Mol Syst Biol. 2021 Apr;17(4):e10075. doi: 10.15252/msb.202010075. Mol Syst Biol. 2021. PMID: 33900055 Free PMC article.
-
Histone acetylation promotes long-lasting defense responses and longevity following early life heat stress.PLoS Genet. 2019 Apr 29;15(4):e1008122. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008122. eCollection 2019 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31034475 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated -omics approach reveals persistent DNA damage rewires lipid metabolism and histone hyperacetylation via MYS-1/Tip60.Sci Adv. 2022 Feb 18;8(7):eabl6083. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abl6083. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35171671 Free PMC article.
-
Brr6 plays a role in gene recruitment and transcriptional regulation at the nuclear envelope.Mol Biol Cell. 2018 Oct 15;29(21):2578-2590. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-04-0258. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2018. PMID: 30133335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ohno S. Sex chromosomes and sex-linked genes. Berlin: Springer; 1967. pp. 1–140.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

