Protection of Nrf2 against arsenite-induced oxidative damage is regulated by the cyclic guanosine monophosphate-protein kinase G signaling pathway
- PMID: 27774770
- PMCID: PMC5403658
- DOI: 10.1002/tox.22374
Protection of Nrf2 against arsenite-induced oxidative damage is regulated by the cyclic guanosine monophosphate-protein kinase G signaling pathway
Abstract
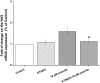
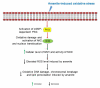
Arsenite has been shown to induce a variety of oxidative damage in mammalian cells. However, the mechanisms underlying cellular responses to its adverse effects remain unknown. We previously showed that the level of Nrf2, a nuclear transcription factor significantly increased in arsenite-treated human bronchial epithelial (HBE) cells suggesting that Nrf2 is involved in responding to arsenite-induced oxidative damage. To explore how Nrf2 can impact arsenite-induced oxidative damage, in this study, we examined Nrf2 activation and its regulation upon cellular arsenite exposure as well as its effects on arsenite-induced oxidative damage in HBE cells. We found that Nrf2 mRNA and protein levels were significantly increased by arsenite in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Furthermore, we showed that over-expression of Nrf2 significantly reduced the level of arsenite-induced oxidative damage in HBE cells including DNA damage, chromosomal breakage, lipid peroxidation and depletion of antioxidants. This indicates a protective role of Nrf2 against arsenite toxicity. This was further supported by the fact that activation of Nrf2 by its agonists, tertiary butylhydroquinone (t-BHQ) and sulforaphane (SFN) resulted in the same protective effects against arsenite toxicity. Moreover, we demonstrated that arsenite-induced activation of Nrf2 was mediated by the cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-protein kinase G (PKG) signaling pathway. This is the first evidence showing that Nrf2 protects against arsenite-induced oxidative damage through the cGMP-PKG pathway. Our study suggests that activation of Nrf2 through the cGMP-PKG signaling pathway in HBE cells may be developed as a new strategy for prevention of arsenite toxicity. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Environ Toxicol 32: 2004-2020, 2017.
Keywords: Nrf2; arsenite; cGMP-PKG signaling pathway; oxidative damage.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
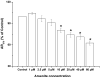






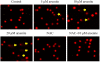
















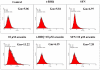





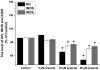






Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-155 regulates arsenite-induced malignant transformation by targeting Nrf2-mediated oxidative damage in human bronchial epithelial cells.Toxicol Lett. 2017 Aug 15;278:38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.07.215. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Toxicol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28688901
-
Continuous activation of Nrf2 and its target antioxidant enzymes leads to arsenite-induced malignant transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015 Dec 1;289(2):231-9. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2015.09.020. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26420645
-
Nrf2 protects human bladder urothelial cells from arsenite and monomethylarsonous acid toxicity.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007 Dec 1;225(2):206-13. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2007.07.016. Epub 2007 Aug 7. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17765279 Free PMC article.
-
Sulforaphane Protects against Cardiovascular Disease via Nrf2 Activation.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:407580. doi: 10.1155/2015/407580. Epub 2015 Oct 25. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26583056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging promise of sulforaphane-mediated Nrf2 signaling cascade against neurological disorders.Sci Total Environ. 2020 Mar 10;707:135624. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135624. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 31784171 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors for Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trials and Epidemiology with a Mechanistic Rationale.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2020 Jun 16;4(1):185-215. doi: 10.3233/ADR-200191. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2020. PMID: 32715279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic arsenic increases cell migration in BEAS-2B cells by increasing cell speed, cell persistence, and cell protrusion length.Exp Cell Res. 2021 Nov 1;408(1):112852. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112852. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Exp Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 34599931 Free PMC article.
-
The Foraging Gene, a New Environmental Adaptation Player Involved in Xenobiotic Detoxification.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jul 14;18(14):7508. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18147508. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34299961 Free PMC article.
-
miR-155 mediates arsenic trioxide resistance by activating Nrf2 and suppressing apoptosis in lung cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 22;7(1):12155. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06061-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28939896 Free PMC article.
-
Honokiol alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis via Nrf2 activation in vitro and in vivo.Chin Med. 2021 Nov 29;16(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s13020-021-00541-z. Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 34844623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Astort F, Mercau M, Giordanino E, Degese MS, Caldareri L, Coso O, Cymeryng CB. Nitric oxide sets off an antioxidant response in adrenal cells: involvement of sGC and Nrf2 in HO-1 induction. Nitric Oxide. 2014;37:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Bai J, Yao X, Jiang L, Qiu T, Liu S, Qi B, Zheng Y, Kong Y, Yang G, Chen M. Taurine protects against As2O3-induced autophagy in pancreas of rat offsprings through Nrf2/Trx pathway. Biochimie. 2016;123:1–6. others. - PubMed
-
- Chen C, Gu S, Jiang X, Zhang Z. Nuclear translocation of nuclear factor kappa B is regulated by G protein signaling pathway in arsenite-induced apoptosis in HBE cell line. Environ Toxicol. 2015 doi: 10.1002/tox.22183. - PubMed
-
- Chen C, Jiang X, Hu Y, Zhang Z. The protective role of resveratrol in the sodium arsenite-induced oxidative damage via modulation of intracellular GSH homeostasis. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2013a;155:119–131. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

