Intranasal treatment with a novel immunomodulator mediates innate immune protection against lethal pneumonia virus of mice
- PMID: 27771388
- PMCID: PMC7126411
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.10.008
Intranasal treatment with a novel immunomodulator mediates innate immune protection against lethal pneumonia virus of mice
Abstract
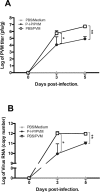
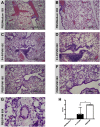
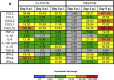
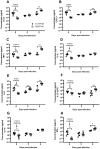
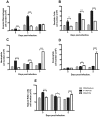
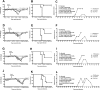
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the leading cause of acute lower respiratory tract infections in infants and young children. There are no licensed RSV vaccines available, and the few treatment options for high-risk individuals are either extremely costly or cause severe side effects and toxicity. Immunomodulation mediated by a novel formulation consisting of the toll-like receptor 3 agonist poly(I:C), an innate defense regulator peptide and a polyphosphazene (P-I-P) was evaluated in the context of lethal infection with pneumonia virus of mice (PVM). Intranasal delivery of a single dose of P-I-P protected adult mice against PVM when given 24 h prior to challenge. These animals experienced minimal weight loss, no clinical disease, 100% survival, and reduced lung pathology. Similar clinical outcomes were observed in mice treated up to 3 days prior to infection. P-I-P pre-treatment induced early mRNA and protein expression of key chemokine and cytokine genes, reduced the recruitment of neutrophils and eosinophils, decreased virus titers in the lungs, and modulated the delayed exacerbated nature of PVM disease without any short-term side effects. On day 14 post-infection, P-I-P-treated mice were confirmed to be PVM-free. These results demonstrate the capacity of this formulation to prevent PVM and possibly other viral respiratory infections.
Keywords: Immunomodulators; Innate immunity; PVM; Protection; RSV.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rhinovirus Reduces the Severity of Subsequent Respiratory Viral Infections by Interferon-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms.mSphere. 2021 Jun 30;6(3):e0047921. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00479-21. Epub 2021 Jun 23. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34160242 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immune protection from pneumonia virus of mice induced by a novel immunomodulator is prolonged by dual treatment and mediated by macrophages.Antiviral Res. 2019 Nov;171:104594. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.104594. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Antiviral Res. 2019. PMID: 31470041
-
Lactobacillus priming of the respiratory tract: Heterologous immunity and protection against lethal pneumovirus infection.Antiviral Res. 2013 Mar;97(3):270-9. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2012.12.022. Epub 2012 Dec 26. Antiviral Res. 2013. PMID: 23274789 Free PMC article.
-
The Pneumonia Virus of Mice (PVM) model of acute respiratory infection.Viruses. 2012 Dec;4(12):3494-510. doi: 10.3390/v4123494. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 23342367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunization strategies for the prevention of pneumovirus infections.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2007 Apr;6(2):169-82. doi: 10.1586/14760584.6.2.169. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2007. PMID: 17408367 Review.
Cited by
-
Polyphosphazene immunoadjuvants: Historical perspective and recent advances.J Control Release. 2021 Jan 10;329:299-315. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.12.001. Epub 2020 Dec 5. J Control Release. 2021. PMID: 33285104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rhinovirus Reduces the Severity of Subsequent Respiratory Viral Infections by Interferon-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms.mSphere. 2021 Jun 30;6(3):e0047921. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00479-21. Epub 2021 Jun 23. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34160242 Free PMC article.
-
Current Animal Models for Understanding the Pathology Caused by the Respiratory Syncytial Virus.Front Microbiol. 2019 May 3;10:873. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00873. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31130923 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Awate S., Wilson H.L., Lai K., Babiuk L.A., Mutwiri G. Activation of adjuvant core response genes by the novel adjuvant PCEP. Mol. Immunol. 2012;51:292–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

