Epidermal growth factor receptor and notch signaling in non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 27770511
- PMCID: PMC5224843
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.944
Epidermal growth factor receptor and notch signaling in non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
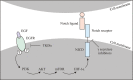
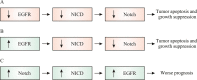
Lung cancer is the most common reason of cancer deaths and about 85% of these are non-small-cell lung cancer. Currently, lung cancer therapy is mainly based on the tumor node metastasis (TNM) disease staging and tumor histological classification. Despite therapeutic innovations, the prognosis for lung cancer patients has not significantly changed in the last years. Therefore, a proper understanding of cell signaling pathways involved in cancer pathogenesis seems to be essential for improvement in cancer therapy field. The knowledge of crosstalk between epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and Notch pathway can lead to enhanced screening for the expression of these genes allowing patients to optimize treatment options and predict potential treatment resistance. This review focuses on recent advances related to the mechanisms of EGFR and Notch signaling in non-small-cell lung cancer and the effectiveness of current Notch- and EGFR-targeted therapies.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor receptor; Notch; non-small-cell lung cancer; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
© 2016 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advances in molecular-based personalized non-small-cell lung cancer therapy: targeting epidermal growth factor receptor and mechanisms of resistance.Cancer Med. 2015 Nov;4(11):1621-32. doi: 10.1002/cam4.506. Epub 2015 Aug 26. Cancer Med. 2015. PMID: 26310719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Next-Generation EGFR-TKIs in Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1533033820940426. doi: 10.1177/1533033820940426. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32723164 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the MET gene for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014 Feb;89(2):284-99. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2013.11.006. Epub 2013 Dec 1. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24355409 Review.
-
Characteristics and overall survival of EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer treated with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a retrospective analysis for 1660 Japanese patients.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2016 May;46(5):462-7. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyw014. Epub 2016 Mar 13. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26977054 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Pathway, Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) and the Regulation of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 5;20(15):3821. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153821. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31387256 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of EGFR as a Novel Key Gene in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC) through Bioinformatics Analysis and Meta-Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Feb 13;2019:6480865. doi: 10.1155/2019/6480865. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30895194 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional Nanocarriers for Lung Drug Delivery.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Jan 21;10(2):183. doi: 10.3390/nano10020183. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31973051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Notch intracellular domain regulates glioblastoma proliferation through the Notch1 signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2021 Apr;21(4):303. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12564. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33732379 Free PMC article.
-
Analyses of the possible anti-tumor effect of yokukansan.J Nat Med. 2019 Jun;73(3):468-479. doi: 10.1007/s11418-019-01283-x. Epub 2019 Feb 9. J Nat Med. 2019. PMID: 30739283
-
Expansion of murine and human olfactory epithelium/mucosa colonies and generation of mature olfactory sensory neurons under chemically defined conditions.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(2):684-699. doi: 10.7150/thno.46750. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33391499 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ciardiello, F. , and Tortora G.. 2008. EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 358:1160–1174. - PubMed
-
- Ciardiello, F. , and Tortora G.. 1998. Interactions between the epidermal growth factor receptor and type I protein kinase A: biological significance and therapeutic implications. Clin. Cancer Res. 4:821–828. - PubMed
-
- Lynch, T. J., Bell D. W., Sordella R., Gurubhagavatula S., Okimoto R. A., Brannigan B. W., et al. 2004. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non‐small‐cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 350:2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Pao, W. , and Miller V. A.. 2005. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations, small‐molecule kinase inhibitors, and non‐small‐cell lung cancer: current knowledge and future directions. J. Clin. Oncol. 23:556–2568. - PubMed
-
- Cheng, L. , and Zhang D.. 2008. Molecular genetic pathology. Humana Press/Springer, New York, NY.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

