The serologically defined colon cancer antigen-3 (SDCCAG3) is involved in the regulation of ciliogenesis
- PMID: 27767179
- PMCID: PMC5073310
- DOI: 10.1038/srep35399
The serologically defined colon cancer antigen-3 (SDCCAG3) is involved in the regulation of ciliogenesis
Abstract
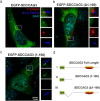
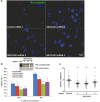
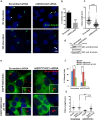
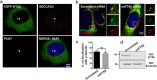
A primary cilium is present on most eukaryotic cells and represents a specialized organelle dedicated to signal transduction and mechanosensing. Defects in cilia function are the cause for several human diseases called ciliopathies. The serologically defined colon cancer antigen-3 (SDCCAG3) is a recently described novel endosomal protein mainly localized at early and recycling endosomes and interacting with several components of membrane trafficking pathways. Here we describe localization of SDCCAG3 to the basal body of primary cilia. Furthermore, we demonstrate that decreased expression levels of SDCCAG3 correlate with decreased ciliary length and a reduced percentage of ciliated cells. We show that SDCCAG3 interacts with the intraflagellar transport protein 88 (IFT88), a crucial component of ciliogenesis and intraciliary transport. Mapping experiments revealed that the N-terminus of SDCCAG3 mediates this interaction by binding to a region within IFT88 comprising several tetratricopeptide (TRP) repeats. Finally, we demonstrate that SDCCAG3 is important for ciliary localization of the membrane protein Polycystin-2, a protein playing an important role in the formation of polycystic kidney disease, but not for Rab8 another ciliary protein. Together these data suggest a novel role for SDCCAG3 in ciliogenesis and in localization of cargo to primary cilia.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The serologically defined colon cancer antigen-3 interacts with the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN13 and is involved in the regulation of cytokinesis.Oncogene. 2013 Sep 26;32(39):4602-13. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.485. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 23108400
-
Casein kinase 1δ functions at the centrosome and Golgi to promote ciliogenesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2014 May;25(10):1629-40. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-10-0598. Epub 2014 Mar 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24648492 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of polycystin-1 ciliary trafficking by motifs at its C-terminus and polycystin-2 but not by cleavage at the GPS site.J Cell Sci. 2015 Nov 15;128(22):4063-73. doi: 10.1242/jcs.160556. Epub 2015 Oct 1. J Cell Sci. 2015. PMID: 26430213 Free PMC article.
-
Primary cilia and signaling pathways in mammalian development, health and disease.Nephron Physiol. 2009;111(3):p39-53. doi: 10.1159/000208212. Epub 2009 Mar 10. Nephron Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19276629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Study of the Primary Cilia in ADPKD.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;933:45-57. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-2041-4_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27730434 Review.
Cited by
-
The retromer complex regulates C. elegans development and mammalian ciliogenesis.J Cell Sci. 2022 May 15;135(10):jcs259396. doi: 10.1242/jcs.259396. Epub 2022 May 17. J Cell Sci. 2022. PMID: 35510502 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of polycystin expression, maturation and trafficking.Cell Signal. 2020 Aug;72:109630. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109630. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 32275942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DLG1 functions upstream of SDCCAG3 and IFT20 to control ciliary targeting of polycystin-2.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 14:2023.11.10.566524. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.10.566524. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: EMBO Rep. 2024 Jul;25(7):3040-3063. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00170-1 PMID: 37987012 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Retromer associates with the cytoplasmic amino-terminus of polycystin-2.J Cell Sci. 2018 Jun 6;131(11):jcs211342. doi: 10.1242/jcs.211342. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 29724910 Free PMC article.
-
BLOC-1 is required for selective membrane protein trafficking from endosomes to primary cilia.J Cell Biol. 2017 Jul 3;216(7):2131-2150. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201611138. Epub 2017 Jun 2. J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28576874 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

