Label-free LC-MS/MS shotgun proteomics to investigate the anti-inflammatory effect of rCC16
- PMID: 27748820
- PMCID: PMC5101986
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5841
Label-free LC-MS/MS shotgun proteomics to investigate the anti-inflammatory effect of rCC16
Abstract
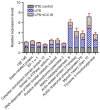
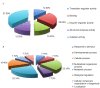
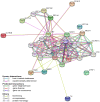
Clara cell protein (CC16) is an anti-inflammatory protein, which is expressed in the airway epithelium. It is involved in the development of airway inflammatory diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. However, the exact molecular mechanism underlying its anti‑inflammatory action remains to be fully elucidated. The aim of the present study was to define the protein profiles of the anti‑inflammatory effect of CC16 in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)‑treated rat tracheal epithelial (RTE) cells using shotgun proteomics. Protein extracts were obtained from control RTE cells, RTE cells treated with LPS and RTE cells treated with LPS and recombinant CC16 (rCC16). Subsequent label‑free quantification and bioinformatics analyses identified 12 proteins that were differentially expressed in the three treatment groups as a cluster of five distinct groups according to their molecular functions. Five of the twelve proteins were revealed to be associated with the cytoskeleton: Matrix metalloproteinase‑9, myosin heavy chain 10, actin‑related protein‑3 homolog, elongation factor 1‑α‑1 (EF‑1‑α‑1), and acidic ribosomal phosphoprotein P0. Five of the twelve proteins were associated with cellular proliferation: DNA‑dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit, EF‑1‑α‑1, tyrosine 3‑monooxygenase, caspase recruitment domain (CARD) protein 12 and adenosylhomocysteinase (SAHH) 3. Three proteins were associated with gene regulation: EF‑1‑α‑1, SAHH 3 and acidic ribosomal phosphoprotein P0. Three proteins were associated with inflammation: Tyrosine 3‑monooxygenase, CARD protein 12 and statin‑related protein. ATPase (H+‑transporting, V1 subunit A, isoform 1) was revealed to be associated with energy metabolism, and uridine diphosphate glycosyltransferase 1 family polypeptide A8 with drug metabolism and detoxification. The identified proteins were further validated using reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction. These protein profiles, and their interacting protein network, may facilitate the elucidation of the molecular mechanisms underlying the anti‑inflammatory effects of CC16.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recombinant rat CC16 protein inhibits LPS-induced MMP-9 expression via NF-κB pathway in rat tracheal epithelial cells.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015 Oct;240(10):1266-78. doi: 10.1177/1535370215570202. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015. PMID: 25716019 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant club cell protein 16 (CC16) ameliorates cigarette smoke‑induced lung inflammation in a murine disease model of COPD.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Aug;18(2):2198-2206. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9216. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29956762 Free PMC article.
-
Club Cell Protein 16 (CC16) Augmentation: A Potential Disease-modifying Approach for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016 Jul;20(7):869-83. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2016.1139084. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016. PMID: 26781659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of N-acetylcysteine on Clara cells in rats with cigarette smoke exposure.Chin Med J (Engl). 2010 Feb 20;123(4):412-7. Chin Med J (Engl). 2010. PMID: 20193479
-
The proteomic advantage: label-free quantification of proteins expressed in bovine milk during experimentally induced coliform mastitis.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010 Dec 15;138(4):252-66. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2010.10.004. Epub 2010 Oct 14. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010. PMID: 21067814 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic variations after short-term heat shock treatment reveal differentially expressed proteins involved in early microspore embryogenesis in cabbage (Brassica oleracea).PeerJ. 2020 Apr 8;8:e8897. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8897. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32337101 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of key factors in Gingival Crevicular fluids from patients undergoing Periodontally Accelerated Osteogenic Orthodontics (PAOO) using proteome analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Nov 27;23(1):934. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03606-7. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 38012627 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome Investigation of Rat Lungs subjected to Ex Vivo Perfusion (EVLP).Molecules. 2018 Nov 22;23(12):3061. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123061. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30467300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vestbo J, Hurd SS, Agustí AG, Jones PW, Vogelmeier C, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Fabbri LM, Martinez FJ, Nishimura M, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:347–365. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201204-0596PP. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pilette C, Godding V, Kiss R, Delos M, Verbeken E, Decaestecker C, De Paepe K, Vaerman JP, Decramer M, Sibille Y. Reduced epithelial expression of secretory component in small airways correlates with airflow obstruction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:185–194. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.163.1.9912137. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

