Subcutaneous Biological Treatments for Moderate to Severe Psoriasis: Interpreting Safety Data by Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 27747609
- PMCID: PMC4883196
- DOI: 10.1007/s40801-014-0006-1
Subcutaneous Biological Treatments for Moderate to Severe Psoriasis: Interpreting Safety Data by Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: When multiple treatments are available, network meta-analysis can synthesize evidence and rank their relative profile in terms of effectiveness and/or safety. We applied this approach to the safety of subcutaneous biologicals used in the treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis.
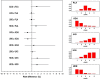
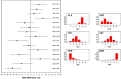
Methods: Our literature search covered the articles published from January 2000 to September 2014 and was restricted to randomized controlled trials. The agents eligible for our analysis were subcutaneous biological drugs used in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. A network meta-analysis was conducted using the Bayesian model. The analysis was aimed to compare the safety of these treatments based on 95 % credible intervals and to consequently generate a ranking in safety across the treatments. Two safety end-points were considered: any serious adverse events (AE) and any infectious AE. Risk difference was the outcome measure. The analysis estimated 95 % credible intervals for all direct and indirect comparisons as well as the ranking histogram across the treatments which was determined according to model-based probabilistic analysis.
Results: Our literature search selected a total of 13 randomized controlled trials of which three evaluated adalimumab, five ustekinumab (45 and 90 mg), four etanercept (both high-dose and low-dose) and one high-dose etanercept and ustekinumab (45 and 90 mg). For both end-points of any serious AE and any infectious AE, the Bayesian analysis showed no significant difference in all indirect head-to-head comparisons between active agents. For the end-point of any serious AE, the ranking was ustekinumab 45 mg and ustekinumab 90 mg (at the same rank), followed by placebo and by adalimumab and high-dose etanercept (at the same rank). For any infectious AE, the ranking was: low-dose etanercept, placebo, ustekinumab 45 mg and ustekinumab 90 mg, adalimumab and high-dose etanercept.
Conclusion: Our analysis synthesized the current evidence on the safety of subcutaneous biological treatments for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis and was successful in defining their respective rankings.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of biologics in the treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Br J Dermatol. 2012 Jan;166(1):179-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10583.x. Epub 2011 Nov 11. Br J Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 21910698 Review.
-
Comparative effectiveness of targeted immunomodulators for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Jul;79(1):135-144.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.02.027. Epub 2018 Feb 10. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29438757
-
Comparative efficacy of biological treatments for moderate-to-severe psoriasis: a network meta-analysis adjusting for cross-trial differences in reference arm response.Br J Dermatol. 2015 Feb;172(2):504-12. doi: 10.1111/bjd.13437. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Br J Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25288183 Review.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of targeted DMARDs for active psoriatic arthritis during induction therapy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019 Dec;49(3):381-388. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.06.001. Epub 2019 Jun 10. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019. PMID: 31272807
-
Biological drugs for the treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis by subcutaneous route: determining statistical equivalence according to evidence-based methods.Clin Drug Investig. 2014 Aug;34(8):593-8. doi: 10.1007/s40261-014-0214-1. Clin Drug Investig. 2014. PMID: 24972775
Cited by
-
The Value of Indirect Comparisons of Systemic Biologics for Psoriasis: Interpretation of Efficacy Findings.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022 Aug;12(8):1711-1727. doi: 10.1007/s13555-022-00765-3. Epub 2022 Jul 14. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022. PMID: 35834062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methods used for indirect comparisons of systemic treatments for psoriasis. A systematic review.Skin Health Dis. 2022 Apr 23;3(1):e112. doi: 10.1002/ski2.112. eCollection 2023 Feb. Skin Health Dis. 2022. PMID: 36751312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the Quality and Coherence of Network Meta-Analyses of Biologics in Plaque Psoriasis: What Does All This Evidence Synthesis Tell Us?Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021 Feb;11(1):181-220. doi: 10.1007/s13555-020-00463-y. Epub 2020 Dec 22. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021. PMID: 33351178 Free PMC article.
-
Infections in Patients Receiving Subcutaneous Biological Treatments for Moderate to Severe Psoriasis.Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2015 Sep;2(3):319-321. doi: 10.1007/s40801-015-0040-7. Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2015. PMID: 27747575 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lucka TC, Pathirana D, Sammain A, Bachmann F, Rosumeck S, Erdmann R, Schmitt J, Orawa H, Rzany B, Nast A. Efficacy of systemic therapies for moderate-to-severe psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of long-term treatment. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26(11):1331–1344. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2012.04492.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Messori A, Trippoli S. Effectiveness of biologics in psoriasis: application of Bayesian model of network meta-analysis. eBMJ 349. doi:10.1136/bmj.g4026.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

