The circadian coordination of cell biology
- PMID: 27738003
- PMCID: PMC5057284
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201603076
The circadian coordination of cell biology
Abstract
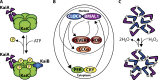
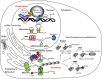
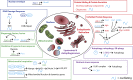
Circadian clocks are cell-autonomous timing mechanisms that organize cell functions in a 24-h periodicity. In mammals, the main circadian oscillator consists of transcription-translation feedback loops composed of transcriptional regulators, enzymes, and scaffolds that generate and sustain daily oscillations of their own transcript and protein levels. The clock components and their targets impart rhythmic functions to many gene products through transcriptional, posttranscriptional, translational, and posttranslational mechanisms. This, in turn, temporally coordinates many signaling pathways, metabolic activity, organelles' structure and functions, as well as the cell cycle and the tissue-specific functions of differentiated cells. When the functions of these circadian oscillators are disrupted by age, environment, or genetic mutation, the temporal coordination of cellular functions is lost, reducing organismal health and fitness.
© 2016 Chaix et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional rewiring of an evolutionarily conserved circadian clock.EMBO J. 2024 May;43(10):2015-2034. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00088-3. Epub 2024 Apr 16. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 38627599 Free PMC article.
-
The transcriptional regulators, the immune system and the the circadian clock.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2013 Jan-Mar;27(1):9-22. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2013. PMID: 23489683
-
Ribosome profiling reveals an important role for translational control in circadian gene expression.Genome Res. 2015 Dec;25(12):1836-47. doi: 10.1101/gr.191296.115. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Genome Res. 2015. PMID: 26338483 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Control of Circadian Rhythms and Metabolism: A Matter of Time and Space.Endocr Rev. 2020 Oct 1;41(5):707-32. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnaa014. Endocr Rev. 2020. PMID: 32392281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Molecular and genetic aspects of interactions of the circadian clock and the energy-producing substrate metabolism in mammals].Genetika. 2014 Feb;50(2):125-37. Genetika. 2014. PMID: 25711020 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Disruption of the intestinal clock drives dysbiosis and impaired barrier function in colorectal cancer.Sci Adv. 2024 Sep 27;10(39):eado1458. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ado1458. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39331712 Free PMC article.
-
Time-of-day effects of cancer drugs revealed by high-throughput deep phenotyping.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 22;15(1):7205. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51611-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39169017 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative rhythmic transcriptome profiling of human and mouse striatal subregions.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024 Apr;49(5):796-805. doi: 10.1038/s41386-023-01788-w. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38182777
-
Role of the Circadian Gas-Responsive Hemeprotein NPAS2 in Physiology and Pathology.Biology (Basel). 2023 Oct 22;12(10):1354. doi: 10.3390/biology12101354. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circadian regulation of metabolism across photosynthetic organisms.Plant J. 2023 Nov;116(3):650-668. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16405. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Plant J. 2023. PMID: 37531328 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Atger F., Gobet C., Marquis J., Martin E., Wang J., Weger B., Lefebvre G., Descombes P., Naef F., and Gachon F.. 2015. Circadian and feeding rhythms differentially affect rhythmic mRNA transcription and translation in mouse liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 112:E6579–E6588. 10.1073/pnas.1515308112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

