Gene and miRNA expression signature of Lewis lung carcinoma LLC1 cells in extracellular matrix enriched microenvironment
- PMID: 27729023
- PMCID: PMC5057255
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2825-9
Gene and miRNA expression signature of Lewis lung carcinoma LLC1 cells in extracellular matrix enriched microenvironment
Abstract
Background: The extracellular matrix (ECM), one of the key components of tumor microenvironment, has a tremendous impact on cancer development and highly influences tumor cell features. ECM affects vital cellular functions such as cell differentiation, migration, survival and proliferation. Gene and protein expression levels are regulated in cell-ECM interaction dependent manner as well. The rate of unsuccessful clinical trials, based on cell culture research models lacking the ECM microenvironment, indicates the need for alternative models and determines the shift to three-dimensional (3D) laminin rich ECM models, better simulating tissue organization. Recognized advantages of 3D models suggest the development of new anticancer treatment strategies. This is among the most promising directions of 3D cell cultures application. However, detailed analysis at the molecular level of 2D/3D cell cultures and tumors in vivo is still needed to elucidate cellular pathways most promising for the development of targeted therapies. In order to elucidate which biological pathways are altered during microenvironmental shift we have analyzed whole genome mRNA and miRNA expression differences in LLC1 cells cultured in 2D or 3D culture conditions.
Methods: In our study we used DNA microarrays for whole genome analysis of mRNA and miRNA expression differences in LLC1 cells cultivated in 2D or 3D culture conditions. Next, we indicated the most common enriched functional categories using KEGG pathway enrichment analysis. Finally, we validated the microarray data by quantitative PCR in LLC1 cells cultured under 2D or 3D conditions or LLC1 tumors implanted in experimental animals.
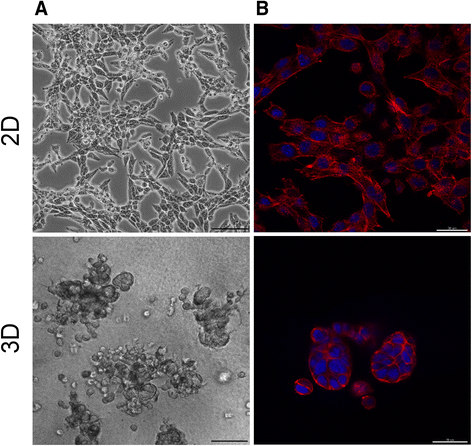
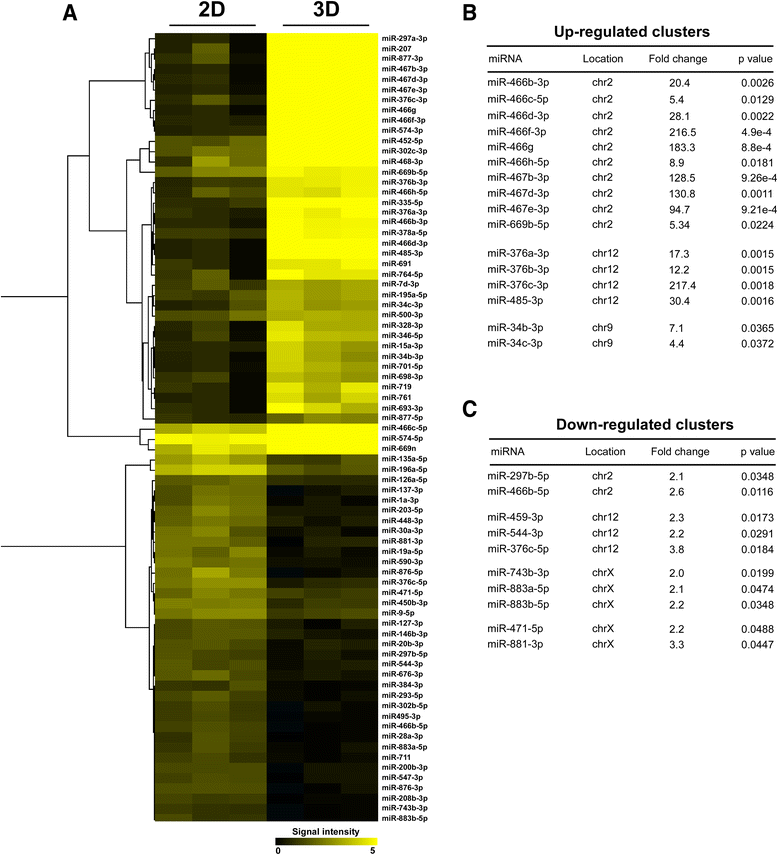
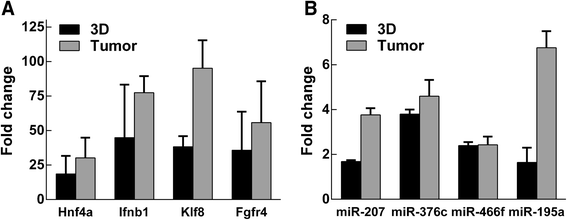
Results: Microarray gene expression analysis revealed that 1884 genes and 77 miRNAs were significantly altered in LLC1 cells after 48 h cell growth under 2D and ECM based 3D cell growth conditions. Pathway enrichment results indicated metabolic pathway, MAP kinase, cell adhesion and immune response as the most significantly altered functional categories in LLC1 cells due to the microenvironmental shift from 2D to 3D. Comparison of the expression levels of selected genes and miRNA between LLC1 cells grown in 3D cell culture and LLC1 tumors implanted in the mouse model indicated correspondence between both model systems.
Conclusions: Global gene and miRNA expression analysis in LLC1 cells under ECM microenvironment indicated altered immune response, adhesion and MAP kinase pathways. All these processes are related to tumor development, progression and treatment response, suggesting the most promising directions for the development of targeted therapies using the 3D cell culture models.
Keywords: 3D cell culture; Cell adhesion; ECM; Gene and miRNA expression signature; Inflammatory response; MAPK signaling pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular Matrix-dependent Pathways in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines Reveal Potential Targets for Anticancer Therapies.Anticancer Res. 2016 Sep;36(9):4559-67. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11004. Anticancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27630296
-
3D Cell Culture-Based Global miRNA Expression Analysis Reveals miR-142-5p as a Theranostic Biomarker of Rectal Cancer Following Neoadjuvant Long-Course Treatment.Biomolecules. 2020 Apr 16;10(4):613. doi: 10.3390/biom10040613. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32316138 Free PMC article.
-
Microenvironment dependent gene expression signatures in reprogrammed human colon normal and cancer cell lines.BMC Cancer. 2018 Feb 27;18(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4145-8. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29482503 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Interplay between miRNAs and the Extracellular Matrix Influences the Tumor Microenvironment.Trends Biochem Sci. 2019 Dec;44(12):1076-1088. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2019.06.007. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Trends Biochem Sci. 2019. PMID: 31288968 Review.
-
Multicellular 3D Models to Study Tumour-Stroma Interactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 5;22(4):1633. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041633. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33562840 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of tumor related signaling pathways with known compounds to determine potential agents for lung adenocarcinoma.Thorac Cancer. 2018 Aug;9(8):974-988. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12773. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Thorac Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29870138 Free PMC article.
-
The multi-receptor inhibitor axitinib reverses tumor-induced immunosuppression and potentiates treatment with immune-modulatory antibodies in preclinical murine models.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2018 May;67(5):815-824. doi: 10.1007/s00262-018-2136-x. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2018. PMID: 29487979 Free PMC article.
-
Orthotopic Models Using New, Murine Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines Simulate Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Immunotherapy.Cells. 2024 Jun 28;13(13):1120. doi: 10.3390/cells13131120. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38994972 Free PMC article.
-
Biomaterials-Based Approaches to Tumor Spheroid and Organoid Modeling.Adv Healthc Mater. 2018 Mar;7(6):e1700980. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201700980. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. PMID: 29205942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of Metadherin Suppresses Colorectal and Lung Cancer Progression and Metastasis.Cancer Res. 2021 Feb 15;81(4):1014-1025. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-1876. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33239430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 1. Hanahan D, Weinberg Robert A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell.144(5):646–74. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013 - PubMed
-
- Hehlgans S, Haase M, Cordes N. Signalling via integrins: implications for cell survival and anticancer strategies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1775(1):163–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

