BLOS2 negatively regulates Notch signaling during neural and hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell development
- PMID: 27719760
- PMCID: PMC5094856
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.18108
BLOS2 negatively regulates Notch signaling during neural and hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell development
Abstract
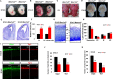
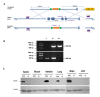
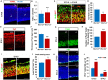
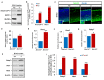
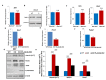
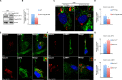
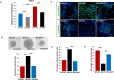
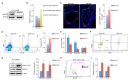
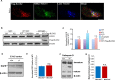
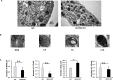
Notch signaling plays a crucial role in controling the proliferation and differentiation of stem and progenitor cells during embryogenesis or organogenesis, but its regulation is incompletely understood. BLOS2, encoded by the Bloc1s2 gene, is a shared subunit of two lysosomal trafficking complexes, biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex-1 (BLOC-1) and BLOC-1-related complex (BORC). Bloc1s2-/- mice were embryonic lethal and exhibited defects in cortical development and hematopoiesis. Loss of BLOS2 resulted in elevated Notch signaling, which consequently increased the proliferation of neural progenitor cells and inhibited neuronal differentiation in cortices. Likewise, ablation of bloc1s2 in zebrafish or mice led to increased hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell production in the aorta-gonad-mesonephros region. BLOS2 physically interacted with Notch1 in endo-lysosomal trafficking of Notch1. Our findings suggest that BLOS2 is a novel negative player in regulating Notch signaling through lysosomal trafficking to control multiple stem and progenitor cell homeostasis in vertebrates.
Keywords: BLOS2; Notch; cell biology; developmental biology; endo-lysosomal trafficking; hematopoiesis; mouse; neurogenesis; stem and progenitor cell development; stem cells; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
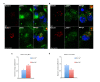
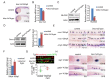
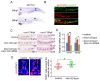

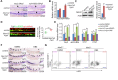
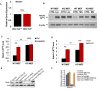
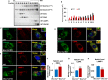
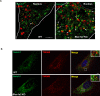
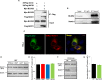

Similar articles
-
BLOS2 maintains hematopoietic stem cells in the fetal liver via repressing Notch signaling.Exp Hematol. 2017 Jul;51:1-6.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2017.03.002. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Exp Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28456747
-
Identification of Cdca7 as a novel Notch transcriptional target involved in hematopoietic stem cell emergence.J Exp Med. 2014 Nov 17;211(12):2411-23. doi: 10.1084/jem.20131857. Epub 2014 Nov 10. J Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 25385755 Free PMC article.
-
Notch1 activation reduces proliferation in the multipotent hematopoietic progenitor cell line FDCP-mix through a p53-dependent pathway but Notch1 effects on myeloid and erythroid differentiation are independent of p53.Cell Death Differ. 2008 Feb;15(2):398-407. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402277. Epub 2007 Nov 30. Cell Death Differ. 2008. PMID: 18049480
-
Notch signaling in stem cell systems.Stem Cells. 2006 Nov;24(11):2437-47. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2005-0661. Epub 2006 Aug 3. Stem Cells. 2006. PMID: 16888285 Review.
-
Regulation of hematopoiesis by hedgehog signaling (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2023 May;27(5):100. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.12987. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 36999588 Review.
Cited by
-
Biological implications of genetic variations in autism spectrum disorders from genomics studies.Biosci Rep. 2021 Jul 30;41(7):BSR20210593. doi: 10.1042/BSR20210593. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34240107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The road to lysosome-related organelles: Insights from Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome and other rare diseases.Traffic. 2019 Jun;20(6):404-435. doi: 10.1111/tra.12646. Traffic. 2019. PMID: 30945407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA methylation is associated with prenatal exposure to sulfur dioxide and childhood attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder symptoms.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 1;13(1):3501. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29843-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36859453 Free PMC article.
-
Notch4 inhibition suppresses invasion and vasculogenic mimicry formation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017 Oct;37(5):719-725. doi: 10.1007/s11596-017-1794-9. Epub 2017 Oct 20. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29058285
-
Genome-wide identification of loci associated with growth in rainbow trout.BMC Genomics. 2020 Mar 5;21(1):209. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6617-x. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32138655 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

