Prospects for the Use of ATR Inhibitors to Treat Cancer
- PMID: 27713304
- PMCID: PMC4033983
- DOI: 10.3390/ph3051311
Prospects for the Use of ATR Inhibitors to Treat Cancer
Abstract
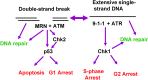
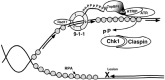
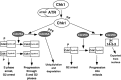
ATR is an apical kinase in one of the DNA-damage induced checkpoint pathways. Despite the development of inhibitors of kinases structurally related to ATR, as well as inhibitors of the ATR substrate Chk1, no ATR inhibitors have yet been developed. Here we review the effects of ATR downregulation in cancer cells and discuss the potential for development of ATR inhibitors for clinical use.
Keywords: ATM; ATR; Chk1; Replication checkpoint; chemotherapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of ATR-dependent feedback activation of Chk1 sensitises cancer cells to Chk1 inhibitor monotherapy.Cancer Lett. 2016 Dec 1;383(1):41-52. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.09.024. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27693461
-
The ATM-Chk2 and ATR-Chk1 pathways in DNA damage signaling and cancer.Adv Cancer Res. 2010;108:73-112. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-380888-2.00003-0. Adv Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21034966 Review.
-
ATR/CHK1 inhibitors and cancer therapy.Radiother Oncol. 2018 Mar;126(3):450-464. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.09.043. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Radiother Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29054375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chk1- and claspin-dependent but ATR/ATM- and Rad17-independent DNA replication checkpoint response in HeLa cells.Cancer Res. 2006 Sep 1;66(17):8672-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4443. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16951182
-
The ATM and Rad3-Related (ATR) Protein Kinase Pathway Is Activated by Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and Required for Efficient Viral Replication.J Virol. 2018 Feb 26;92(6):e01884-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01884-17. Print 2018 Mar 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29263259 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effect of caffeine on cisplatin-induced apoptosis of lung cancer cells.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2015 Feb 11;4:5. doi: 10.1186/2162-3619-4-5. eCollection 2015. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25937999 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting the DNA damage response as a therapeutic manoeuvre in cancer.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;169(8):1745-65. doi: 10.1111/bph.12244. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23682925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation-Dependent Pin1 Isomerization of ATR: Its Role in Regulating ATR's Anti-apoptotic Function at Mitochondria, and the Implications in Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Apr 30;8:281. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00281. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32426354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of ATR kinase with the selective inhibitor VE-821 results in radiosensitization of cells of promyelocytic leukaemia (HL-60).Radiat Environ Biophys. 2013 Nov;52(4):471-9. doi: 10.1007/s00411-013-0486-5. Epub 2013 Aug 11. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2013. PMID: 23934411
-
Progress towards a clinically-successful ATR inhibitor for cancer therapy.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021 Feb 5;2:100017. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2021.100017. eCollection 2021. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 34909652 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhou B.B., Elledge S.J. The DNA damage response: putting checkpoints in perspective. Nature. 2000;408:433–439. - PubMed
-
- Kastan M.B., Bartek J. Cell-cycle checkpoints and cancer. Nature. 2004;432:316–323. - PubMed
-
- Keith C.T., Schreiber S.L. PIK-Related Kinases: DNA Repair, Recombination, and Cell Cycle Checkpoints. Science. 1995;270:50–51. - PubMed
-
- Engelman J.A., Luo J., Cantley L.C. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006;7:606–619. - PubMed
-
- Bosotti R., Isacchi A., Sonnhammer E.L. FAT: a novel domain in PIK-related kinases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000;25:225–227. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

