Crosstalk of HNF4 α with extracellular and intracellular signaling pathways in the regulation of hepatic metabolism of drugs and lipids
- PMID: 27709008
- PMCID: PMC5045537
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2016.07.003
Crosstalk of HNF4 α with extracellular and intracellular signaling pathways in the regulation of hepatic metabolism of drugs and lipids
Abstract
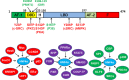
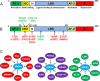
The liver is essential for survival due to its critical role in the regulation of metabolic homeostasis. Metabolism of xenobiotics, such as environmental chemicals and drugs by the liver protects us from toxic effects of these xenobiotics, whereas metabolism of cholesterol, bile acids (BAs), lipids, and glucose provide key building blocks and nutrients to promote the growth or maintain the survival of the organism. As a well-established master regulator of liver development and function, hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4α) plays a critical role in regulating a large number of key genes essential for the metabolism of xenobiotics, metabolic wastes, and nutrients. The expression and activity of HNF4α is regulated by diverse hormonal and signaling pathways such as growth hormone, glucocorticoids, thyroid hormone, insulin, transforming growth factor-β, estrogen, and cytokines. HNF4α appears to play a central role in orchestrating the transduction of extracellular hormonal signaling and intracellular stress/nutritional signaling onto transcriptional changes in the liver. There have been a few reviews on the regulation of drug metabolism, lipid metabolism, cell proliferation, and inflammation by HNF4α. However, the knowledge on how the expression and transcriptional activity of HNF4α is modulated remains scattered. Herein I provide comprehensive review on the regulation of expression and transcriptional activity of HNF4α, and how HNF4α crosstalks with diverse extracellular and intracellular signaling pathways to regulate genes essential in liver pathophysiology.
Keywords: Drug metabolism; HNF4α; Hormone; Inflammation; Lipid metabolism; Liver.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha regulation of bile acid and drug metabolism.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2009 Feb;5(2):137-47. doi: 10.1517/17425250802707342. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 19239393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation of cytochrome p450 genes by the nuclear receptor hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha.Curr Drug Metab. 2009 Jun;10(5):508-19. doi: 10.2174/138920009788898000. Curr Drug Metab. 2009. PMID: 19689247 Review.
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha (nuclear receptor 2A1) is essential for maintenance of hepatic gene expression and lipid homeostasis.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Feb;21(4):1393-403. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.4.1393-1403.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11158324 Free PMC article.
-
PPARα/HNF4α interplay on diversified responsive elements. Relevance in the regulation of liver peroxisomal fatty acid catabolism.Curr Drug Metab. 2012 Dec;13(10):1436-53. doi: 10.2174/138920012803762738. Curr Drug Metab. 2012. PMID: 22978398 Review.
-
Hepatitis C virus suppresses Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4 alpha, a key regulator of hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Sep;78:315-326. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2016.07.027. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27477312
Cited by
-
Probenecid Inhibits Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) Replication In Vitro and in BALB/c Mice.Viruses. 2024 Jul 6;16(7):1087. doi: 10.3390/v16071087. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39066249 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Regulation in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Metabolites. 2020 Jul 9;10(7):283. doi: 10.3390/metabo10070283. Metabolites. 2020. PMID: 32660130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cisd2 slows down liver aging and attenuates age-related metabolic dysfunction in male mice.Aging Cell. 2021 Dec;20(12):e13523. doi: 10.1111/acel.13523. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Aging Cell. 2021. PMID: 34811857 Free PMC article.
-
Andrographolide, an Anti-Inflammatory Multitarget Drug: All Roads Lead to Cellular Metabolism.Molecules. 2020 Dec 22;26(1):5. doi: 10.3390/molecules26010005. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33374961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha in gastrointestinal and liver diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Aug 14;25(30):4074-4091. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i30.4074. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31435165 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gonzalez F.J. Regulation of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α-mediated transcription. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2008;23:2–7. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

