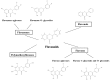
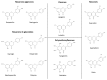
Neurodegenerative Diseases: Might Citrus Flavonoids Play a Protective Role?
- PMID: 27706034
- PMCID: PMC6274333
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21101312
Neurodegenerative Diseases: Might Citrus Flavonoids Play a Protective Role?
Abstract
Neurodegenerative diseases (ND) result from the gradual and progressive degeneration of the structure and function of the central nervous system or the peripheral nervous system or both. They are characterized by deterioration of neurons and/or myelin sheath, disruption of sensory information transmission and loss of movement control. There is no effective treatment for ND, and the drugs currently marketed are symptom-oriented, albeit with several side effects. Within the past decades, several natural remedies have gained attention as potential neuroprotective drugs. Moreover, an increasing number of studies have suggested that dietary intake of vegetables and fruits can prevent or delay the onset of ND. These properties are mainly due to the presence of polyphenols, an important group of phytochemicals that are abundantly present in fruits, vegetables, cereals and beverages. The main class of polyphenols is flavonoids, abundant in Citrus fruits. Our review is an overview on the scientific literature concerning the neuroprotective effects of the Citrus flavonoids in the prevention or treatment of ND. This review may be used as scientific basis for the development of nutraceuticals, food supplements or complementary and alternative drugs to maintain and improve the neurophysiological status.
Keywords: Citrus; flavonoids; neurodegeneration; neurodegenerative disorders; nutraceutical.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of citrus flavonoids.J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Feb 1;60(4):877-85. doi: 10.1021/jf204452y. Epub 2012 Jan 23. J Agric Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 22224368 Review.
-
Anti-neuroinflammatory activities of extract and polymethoxyflavonoids from immature fruit peels of Citrus 'Hebesu'.J Food Biochem. 2019 Jun;43(6):e12813. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12813. Epub 2019 Feb 25. J Food Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31353615
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Citrus Fruit-Derived Flavonoids, Nobiletin and Tangeretin in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Disease.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2017;16(4):387-397. doi: 10.2174/1871527316666170328113309. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2017. PMID: 28474543 Review.
-
Understanding the broad-spectrum neuroprotective action profile of green tea polyphenols in aging and neurodegenerative diseases.J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;25(2):187-208. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-101803. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011. PMID: 21368374 Review.
-
Biosynthesis of citrus flavonoids and their health effects.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020;60(4):566-583. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1544885. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020. PMID: 30580548 Review.
Cited by
-
Agaricus Mushroom-Enriched Diets Modulate the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis and Reduce Brain Oxidative Stress in Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Mar 31;11(4):695. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040695. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453380 Free PMC article.
-
The clock modulator Nobiletin mitigates astrogliosis-associated neuroinflammation and disease hallmarks in an Alzheimer's disease model.FASEB J. 2022 Mar;36(3):e22186. doi: 10.1096/fj.202101633R. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 35120261 Free PMC article.
-
A Synthetic Snake-Venom-Based Tripeptide Protects PC12 Cells from the Neurotoxicity of Acrolein by Improving Axonal Plasticity and Bioenergetics.Neurotox Res. 2020 Jan;37(1):227-237. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-00111-0. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Neurotox Res. 2020. PMID: 31654382
-
A flavonoid-rich extract from bergamot juice prevents carcinogenesis in a genetic model of colorectal cancer, the Pirc rat (F344/NTac-Apcam1137).Eur J Nutr. 2020 Apr;59(3):885-894. doi: 10.1007/s00394-019-01948-z. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Eur J Nutr. 2020. PMID: 30919084
-
The protective effects of crocin in the management of neurodegenerative diseases: a review.Am J Neurodegener Dis. 2018 Feb 5;7(1):1-10. eCollection 2018. Am J Neurodegener Dis. 2018. PMID: 29531865 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Manach C., Scalbert A., Morand C., Remesy C., Jimenez L. Polyphenols: Food sources and bioavailability. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004;79:727–747. - PubMed
-
- Middleton E., Jr., Kandaswami C., Theoharides T.C. The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells: Implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000;52:673–751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous