The treatment of nonunions with application of BMP-7 increases the expression pattern for angiogenic and inflammable cytokines: a matched pair analysis
- PMID: 27703392
- PMCID: PMC5036623
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S110621
The treatment of nonunions with application of BMP-7 increases the expression pattern for angiogenic and inflammable cytokines: a matched pair analysis
Abstract
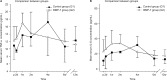
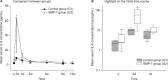
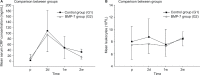
The local application of bone morphogenetic protein-7 (BMP-7) in combination with the transplantation of autologous bone graft improves the outcome in nonunion treatment; however, the specific reasons remain unclear. In this study, we sought to determine if the local application of BMP-7 contributes to improved bone regeneration in nonunion therapy by modulation of the angiogenic and inflammable cytokine expression patterns of the early inflammation response. Therefore, we utilized the analysis of serological cytokine expression patterns. As a matched pair analysis, best-fitting patients who were treated with transplantation of autologous bone graft (G1, n=10) were compared with patients who were treated with additional application of BMP-7 (G2, n=10). The changes in the cytokine expression patterns were monitored and correlated to clinical data of bone healing. Significant differences in angiogenesis potential (vascular endothelial growth factor [VEGF] serum levels) could be found in the first days after surgery (P<0.05). Furthermore, the increase and absolute amount of VEGF levels in the BMP-7 group were considerably higher than in the control group during the first 2 weeks after surgery. The expression pattern of inflammable cytokines showed noticeable differences in the time point of significant elevated levels, in particular, inflammable cytokines showed an earlier peak in G2. Furthermore, interleukin-6 was significantly elevated within the first week only, comparing G2 to G1 (P<0.05). Our findings indicate that BMP-7 induces an early and more intense expression of VEGF via a direct and postulated indirect pathway, thereby providing a favorable environment for bone healing. Moreover, application of BMP-7 leads to an earlier expression of known proinflammatory cytokines. The results of this study show that application of BMP-7 leads to costimulatory effect on both angiogenic and inflammable cytokine expression patterns that may serve as a possible stimulus for bone regeneration.
Keywords: IL-6; VEGF; angiogenesis; bone regeneration; cytokines; inflammation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Temporal and spatial vascularization patterns of unions and nonunions: role of vascular endothelial growth factor and bone morphogenetic proteins.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012 Jan 4;94(1):49-58. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.J.00795. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012. PMID: 22218382
-
Safety study: is there a pathologic IGF-1, PDGF and TGF-β cytokine expression caused by adjunct BMP-7 in tibial and femoral non-union therapy?Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018 Apr 16;14:691-697. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S160064. eCollection 2018. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018. PMID: 29713178 Free PMC article.
-
The local cytokine and growth factor response to recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2) after spinal fusion.Spine J. 2018 Aug;18(8):1424-1433. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.03.006. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Spine J. 2018. PMID: 29550606
-
Non-unions treated with bone morphogenic protein 7: introducing the quantitative measurement of human serum cytokine levels as promising tool in evaluation of adjunct non-union therapy.J Inflamm (Lond). 2016 Jan 22;13:3. doi: 10.1186/s12950-016-0111-x. eCollection 2016. J Inflamm (Lond). 2016. PMID: 26807043 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of local sequential VEGF and BMP-2 delivery on ectopic and orthotopic bone regeneration.Biomaterials. 2009 May;30(14):2816-25. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.01.031. Epub 2009 Feb 20. Biomaterials. 2009. PMID: 19232714
Cited by
-
Does Age Influence the Outcome of Lower Limb Non-Union Treatment? A Matched Pair Analysis.J Clin Med. 2019 Aug 22;8(9):1276. doi: 10.3390/jcm8091276. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31443475 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Union Treatment Based on the "Diamond Concept" Is a Clinically Effective and Safe Treatment Option in Older Adults.Clin Interv Aging. 2020 Jul 21;15:1221-1230. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S241936. eCollection 2020. Clin Interv Aging. 2020. PMID: 32801671 Free PMC article.
-
LIPUS vs. reaming in non-union treatment: Cytokine expression course as a tool for evaluation and differentiation of non-union therapy.J Orthop. 2019 Aug 13;17:208-214. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2019.08.018. eCollection 2020 Jan-Feb. J Orthop. 2019. PMID: 31889743 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Evaluation of the clinical effectiveness of bioactive glass (S53P4) in the treatment of non-unions of the tibia and femur: study protocol of a randomized controlled non-inferiority trial.Trials. 2018 May 30;19(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-2681-9. Trials. 2018. PMID: 29843766 Free PMC article.
-
Sub-clinical dose of bone morphogenetic protein-2 does not precipitate rampant, sustained inflammatory response in bone wound healing.Wound Repair Regen. 2019 Jul;27(4):335-344. doi: 10.1111/wrr.12710. Epub 2019 Mar 9. Wound Repair Regen. 2019. PMID: 30805987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giannoudis PV, Einhorn TA, Marsh D. Fracture healing: the diamond concept. Injury. 2007;38(suppl 4):S3–S6. - PubMed
-
- Takemoto R, Forman J, Taormina DP, Egol KA. No advantage to rhBMP-2 in addition to autogenous graft for fracture nonunion. Orthopedics. 2014;37(6):e525–e530. - PubMed
-
- Schmidmaier G, Schwabe P, Wildemann B, Haas NP. Use of bone morphogenetic proteins for treatment of non-unions and future perspectives. Injury. 2007;38(suppl 4):S35–S41. - PubMed
-
- Giannoudis PV, Einhorn TA, Schmidmaier G, Marsh D. The diamond concept – open questions. Injury. 2008;39(suppl 2):S5–S8. - PubMed
-
- Zimmermann G, Moghaddam A, Reumann M, et al. TGF-β1 als pathophysiologischer Faktor bei der Frakturheilung [TGF-beta1 as a pathophysiological factor in fracture healing] Unfallchirurg. 2007;110(2):130–136. German. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

