NF-κB Pathways in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis and the Therapeutic Implications
- PMID: 27695399
- PMCID: PMC5023675
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00084
NF-κB Pathways in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis and the Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
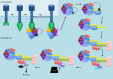
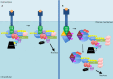
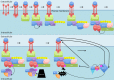
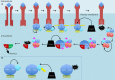
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling pathways are involved in cell immune responses, apoptosis and infections. In multiple sclerosis (MS), NF-κB pathways are changed, leading to increased levels of NF-κB activation in cells. This may indicate a key role for NF-κB in MS pathogenesis. NF-κB signaling is complex, with many elements involved in its activation and regulation. Interestingly, current MS treatments are found to be directly or indirectly linked to NF-κB pathways and act to adjust the innate and adaptive immune system in patients. In this review, we will first focus on the intricacies of NF-κB signaling, including the activating pathways and regulatory elements. Next, we will theorize about the role of NF-κB in MS pathogenesis, based on current research findings, and discuss some of the associated therapeutic implications. Lastly, we will review four new MS treatments which interrupt NF-κB pathways-fingolimod, teriflunomide, dimethyl fumarate (DMF) and laquinimod (LAQ)-and explain their mechanisms, and the possible strategy for MS treatments in the future.
Keywords: IKK; IκB-α; NF-κB; multiple sclerosis; signaling pathway.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reduced IκB-α Protein Levels in Peripheral Blood Cells of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis-A Possible Cause of Constitutive NF-κB Activation.J Clin Med. 2020 Aug 6;9(8):2534. doi: 10.3390/jcm9082534. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32781504 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
NF-κB, IκB, and IKK: Integral Components of Immune System Signaling.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1172:207-226. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-9367-9_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31628658 Review.
-
Classical NF-κB activation impairs skeletal muscle oxidative phenotype by reducing IKK-α expression.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Feb;1842(2):175-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Nov 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24215713
-
NF-kappaB as an integrator of diverse signaling pathways: the heart of myocardial signaling?Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2003;3(3):229-54. doi: 10.1385/ct:3:3:229. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2003. PMID: 14555789 Review.
Cited by
-
Replication study of GWAS risk loci in Greek multiple sclerosis patients.Neurol Sci. 2019 Feb;40(2):253-260. doi: 10.1007/s10072-018-3617-6. Epub 2018 Oct 26. Neurol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30361804
-
Multiple sclerosis disease progression: Contributions from a hypoxia-inflammation cycle.Mult Scler. 2019 Nov;25(13):1715-1718. doi: 10.1177/1352458518791683. Epub 2018 Jul 27. Mult Scler. 2019. PMID: 30052113 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Apolipoprotein D in Cuprizone-Induced Cell Line Models: A Potential Therapeutic Approach for Multiple Sclerosis and Demyelinating Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 27;22(3):1260. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031260. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33514021 Free PMC article.
-
Small-Molecule Inhibitor of 8-Oxoguanine DNA Glycosylase 1 Regulates Inflammatory Responses during Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection.J Immunol. 2020 Oct 15;205(8):2231-2242. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901533. Epub 2020 Sep 14. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32929043 Free PMC article.
-
Role of fenofibrate in multiple sclerosis.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Feb 9;29(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01700-2. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38336772 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aune T. M., Mora A. L., Kim S., Boothby M., Lichtman A. H. (1999). Costimulation reverses the defect in IL-2 but not effector cytokine production by T cells with impaired IκBα degradation. J. Immunol. 162, 5805–5812. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

