Metabolic Regulation of Apoptosis in Cancer
- PMID: 27692180
- PMCID: PMC5819894
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2016.06.006
Metabolic Regulation of Apoptosis in Cancer
Abstract
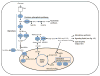
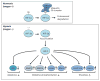
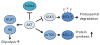
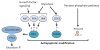
Apoptosis is a cellular suicide program that plays a critical role in development and human diseases, including cancer. Cancer cells evade apoptosis, thereby enabling excessive proliferation, survival under hypoxic conditions, and acquired resistance to therapeutic agents. Among various mechanisms that contribute to the evasion of apoptosis in cancer, metabolism is emerging as one of the key factors. Cellular metabolites can regulate functions of pro- and antiapoptotic proteins. In turn, p53, a regulator of apoptosis, also controls metabolism by limiting glycolysis and facilitating mitochondrial respiration. Consequently, with dysregulated metabolism and p53 inactivation, cancer cells are well-equipped to disable the apoptotic machinery. In this article, we review how cellular apoptosis is regulated and how metabolism can influence the signaling pathways leading to apoptosis, especially focusing on how glucose and lipid metabolism are altered in cancer cells and how these alterations can impact the apoptotic pathways.
Keywords: BCL-2 family; caspase; cell death; ceramide; glucose; hypoxia; lipids; p53.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel 1 in tumor cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1848(10 Pt B):2547-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.10.040. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25448878 Review.
-
Mevalonate metabolism in cancer.Cancer Lett. 2015 Jan 28;356(2 Pt A):192-6. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.01.013. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 24467965 Review.
-
Sugar-free approaches to cancer cell killing.Oncogene. 2011 Jan 20;30(3):253-64. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.466. Epub 2010 Oct 25. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 20972457 Review.
-
Cyclic exposure to hypoxia and reoxygenation selects for tumor cells with defects in mitochondrial apoptotic pathways.FASEB J. 2004 Dec;18(15):1906-8. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-1918fje. Epub 2004 Sep 28. FASEB J. 2004. PMID: 15456741
-
Reducing VDAC1 expression induces a non-apoptotic role for pro-apoptotic proteins in cancer cell differentiation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Aug;1857(8):1228-1242. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27080741
Cited by
-
Controlled temperature-mediated curcumin release from magneto-thermal nanocarriers to kill bone tumors.Bioact Mater. 2021 Oct 5;11:107-117. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.09.028. eCollection 2022 May. Bioact Mater. 2021. PMID: 34938916 Free PMC article.
-
Atractylenolide I Induces Apoptosis and Suppresses Glycolysis by Blocking the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 26;11:273. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00273. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32273843 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots fabricated from cellulolytic enzyme lignin and its application to the determination of cytochrome c and trypsin.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021 Aug;413(20):5239-5249. doi: 10.1007/s00216-021-03496-0. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021. PMID: 34212211
-
Stress Hormone Cortisol Enhances Bcl2 Like-12 Expression to Inhibit p53 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells.Dig Dis Sci. 2017 Dec;62(12):3495-3500. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4798-1. Epub 2017 Oct 17. Dig Dis Sci. 2017. PMID: 29043595
-
Metabolic role of fatty acid binding protein 7 in mediating triple-negative breast cancer cell death via PPAR-α signaling.J Lipid Res. 2019 Nov;60(11):1807-1817. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M092379. Epub 2019 Sep 4. J Lipid Res. 2019. PMID: 31484694 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acehan D, Jiang X, Morgan DG, Heuser JE, Wang X, Akey CW. Three-dimensional structure of the apoptosome: implications for assembly, procaspase-9 binding, and activation. Mol Cell. 2002;9:423–432. - PubMed
-
- Altomare DA, Testa JR. Perturbations of the AKT signaling pathway in human cancer. Oncogene. 2005;24:7455–7464. - PubMed
-
- Alves NL, Derks IAM, Berk E, Spijker R, van Lier RAW, Eldering E. The Noxa/Mcl-1 axis regulates susceptibility to apoptosis under glucose limitation in dividing T cells. Immunity. 2006;24:703–716. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

