miR-135a promotes gastric cancer progression and resistance to oxaliplatin
- PMID: 27683111
- PMCID: PMC5342584
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12208
miR-135a promotes gastric cancer progression and resistance to oxaliplatin
Abstract
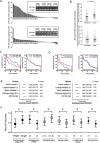
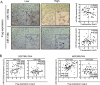
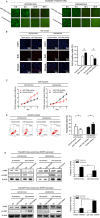
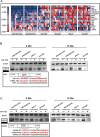
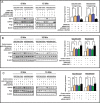
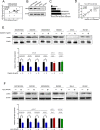
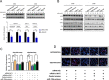
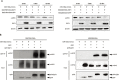
Resistance to oxaliplatin (OXA)-based chemotherapy regimens continues to be a major cause of gastric cancer (GC) recurrence and metastasis. We analyzed GC samples and matched non-tumorous control stomach tissues from 280 patients and found that miR-135a was overexpressed in GC samples relative to control tissues. Tumors with high miR-135a expression were more likely to have aggressive characteristics (high levels of carcino-embryonic antigen, vascular invasion, lymphatic metastasis, and poor differentiation) than those with low levels. Patients with greater tumoral expression of miR-135a had shorter overall survival times and times to disease recurrence. Furthermore, miR-135a, which promotes the proliferation and invasion of OXA-resistant GC cells, inhibited E2F transcription factor 1 (E2F1)-induced apoptosis by downregulating E2F1 and Death-associated protein kinase 2 (DAPK2) expression. Our results indicate that higher levels of miR-135a in GC are associated with shorter survival times and reduced times to disease recurrence. The mechanism whereby miR-135a promotes GC pathogenesis appears to be the suppression of E2F1 expression and Sp1/DAPK2 pathway signaling.
Keywords: gastric cancer; transcription factor E2F1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Upregulation of miR-34c after silencing E2F transcription factor 1 inhibits paclitaxel combined with cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Feb 7;26(5):499-513. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i5.499. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32089626 Free PMC article.
-
miR-493 mediated DKK1 down-regulation confers proliferation, invasion and chemo-resistance in gastric cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 9;7(6):7044-54. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6951. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26799283 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA NNT-AS1 sponges miR-424/E2F1 to promote the tumorigenesis and cell cycle progression of gastric cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Oct;22(10):4751-4759. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13726. Epub 2018 Jul 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30006956 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs and the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway in gastric cancer (Review).Oncol Rep. 2019 Mar;41(3):1439-1454. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.6962. Epub 2019 Jan 10. Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30628706 Review.
-
Dysregulation of miRNAs as a signature for diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer and their involvement in the mechanism underlying gastric carcinogenesis and progression.IUBMB Life. 2020 May;72(5):884-898. doi: 10.1002/iub.2259. Epub 2020 Feb 20. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 32078236 Review.
Cited by
-
A miRNA signature suggestive of nodal metastases from laryngeal carcinoma.Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2017 Dec;37(6):467-474. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-851. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2017. PMID: 29327732 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs in gastric cancer: implications for drug resistance.Mol Cancer. 2020 Mar 19;19(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01185-7. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32192494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of miR-19a partially reversed the resistance of colorectal cancer to oxaliplatin via PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Mar 25;12(7):5640-5650. doi: 10.18632/aging.102929. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32209726 Free PMC article.
-
The role of non-coding RNAs in chemotherapy for gastrointestinal cancers.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Oct 8;26:892-926. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.10.004. eCollection 2021 Dec 3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 34760336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction/reversal of drug resistance in gastric cancer by non-coding RNAs (Review).Int J Oncol. 2019 May;54(5):1511-1524. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4751. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Int J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30896792 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yu S, Yang CS, Li J, You W, Chen J, Cao Y, Dong Z, Qiao Y. Cancer Prevention Research in China. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2015;8:662–674. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

