[Effect of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 overexpression on airway inflammation and remodeling in mice with allergic asthma]
- PMID: 27655548
- PMCID: PMC7389976
- DOI: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2016.09.018
[Effect of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 overexpression on airway inflammation and remodeling in mice with allergic asthma]
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM-2) overexpression on airway inflammation and remodeling in mice with asthma.
Methods: A total of 40 BALB/c mice were randomly divided into normal control, asthma, empty vector, and TREM-2 overexpression groups (n=10 each). Ovalbumin (OVA) sensitization and challenge were performed to establish the model of asthma. The mice in the control group were given normal saline, and those in the empty vector and TREM-2 overexpression groups were transfected with adenovirus vector and TREM-2 adenovirus, respectively. RT-PCR and Western blot were used to measure the expression of TREM-2, MMP-2, MMP-9, ADAM33, and ADAM8. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was collected to perform cell counting and classification. ELISA was used to measure the total serum level of IgE and the levels of cytokines in BALF.
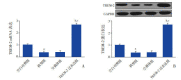
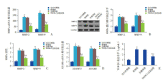
Results: Compared with the control group, the asthma group showed significant reductions in the mRNA and protein expression of TREM-2 (P<0.05), a significantly increased level of Th2 cytokine (P<0.05), and significantly increased numbers of total cells and classified cells. Compared with the asthma group, the TREM-2 overexpression group showed a significantly reduced level of Th2 cytokine (P<0.05), a significantly reduced level of IgE (P<0.05), and significantly reduced numbers of total cells and classified cells (P<0.05), as well as significantly downregulated expression of the inflammatory factors and growth factors MMP-2, MMP-9, TGF-β1, ADAM8, and ADAM33 (P<0.05).
Conclusions: TREM-2 overexpression significantly alleviates airway inflammation and airway remodeling in mice with asthma and may become a potential target for the prevention and treatment of childhood asthma.
目的: 探讨过表达髓样细胞触发受体2(TREM-2)对哮喘模型小鼠气道炎症及气道重塑的影响。
方法: 将40只BALB/c小鼠随机分成空白对照组、哮喘组、空载体组和TREM-2过表达组(n=10)。采用卵白蛋白(OVA)致敏及激发建立哮喘模型,对照组以生理盐水替代致敏液,空载体组和TREM-2过表达组分别转染腺病毒载体和TREM-2腺病毒。采用RT-PCR和Western blot法检测TREM-2、基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)-2、MMP-9、解整合素-金属蛋白酶(ADAM)33和ADAM8的表达。收集各组支气管肺泡灌洗液进行细胞计数、分类。酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)检测血清总IgE水平及BALF中细胞因子水平。
结果: 与对照组相比,哮喘组小鼠TREM-2 mRNA及蛋白水平均有所下降(P < 0.05);Th2细胞因子及总IgE水平升高(P < 0.05);总细胞数及分类细胞数增多(P < 0.05)。与哮喘组相比,过表达TREM-2组Th2细胞因子及总IgE水平下降(P < 0.05);总细胞及分类细胞数减少(P < 0.05);与气道重塑相关的MMP-2、MMP-9、TGF-β1、ADAM8和ADAM33的mRNA及蛋白表达均下调(P < 0.05)。
结论: TREM-2过表达减轻哮喘小鼠的气道炎症和气道重塑,从而为儿童哮喘的防治提供潜在的新靶点。
Figures
Similar articles
-
MFG-E8/integrin β3 signaling contributes to airway inflammation response and airway remodeling in an ovalbumin-induced murine model of asthma.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Nov;119(11):8887-8896. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27142. Epub 2018 Aug 4. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30076648
-
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 (TREM-1) modulates immune responses to Aspergillus fumigatus during fungal asthma in mice.Immunol Invest. 2011;40(7-8):692-722. doi: 10.3109/08820139.2011.578270. Epub 2011 May 19. Immunol Invest. 2011. PMID: 21592044 Free PMC article.
-
Increased TREM-2 expression on the subsets of CD11c+ cells in the lungs and lymph nodes during allergic airway inflammation.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 19;7(1):11853. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12330-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28928485 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanism of action of BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 in treating airway remodeling in asthmatic mice].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Dec;19(12):1278-1284. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2017.12.011. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29237530 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Experimental protocol for development of adjuvant-free murine chronic model of allergic asthma.J Immunol Methods. 2019 May;468:10-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2019.03.002. Epub 2019 Mar 14. J Immunol Methods. 2019. PMID: 30880263
References
-
- 沈 叶菊, 陈 晓兵, 石 远峰, et al. 乌司他丁对急性肺损伤大鼠肺TLR4及TREM-1和TREM-2表达的影响. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/YIYA201517006.htm 江苏医药. 2015;41(17):2002–2005.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

