Memory deficits, gait ataxia and neuronal loss in the hippocampus and cerebellum in mice that are heterozygous for Pur-alpha
- PMID: 27651147
- PMCID: PMC5458736
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.09.018
Memory deficits, gait ataxia and neuronal loss in the hippocampus and cerebellum in mice that are heterozygous for Pur-alpha
Abstract
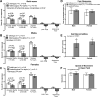
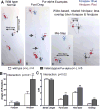
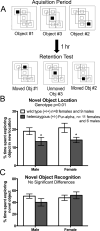
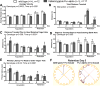
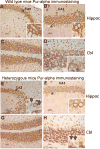
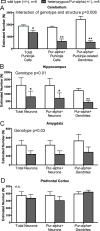
Pur-alpha is a highly conserved sequence-specific DNA and RNA binding protein with established roles in DNA replication, RNA translation, cell cycle regulation, and maintenance of neuronal differentiation. Prior studies have shown that mice lacking Pur-alpha (-/-) display decreased neurogenesis and impaired neuronal differentiation. We sought to examine for the first time, the behavioral phenotype and brain histopathology of mice that are heterozygous (+/-) for Pur-alpha. Standardized behavioral phenotyping revealed a decreased escape response to touch, limb and abdominal hypotonia, and gait abnormalities in heterozygous Pur-alpha (+/-) mice, compared to wild-type (+/+) littermates. Footprint pattern analyses showed wider-based steps, increased missteps and more outwardly rotated hindpaws in heterozygous Pur-alpha (+/-) mice, suggestive of cerebellar pathology. The Barnes maze and novel object location testing revealed significant memory deficits in heterozygous Pur-alpha mice, suggestive of hippocampal pathology. Quantitative immunohistochemical assays of the vermal region of the cerebellum and CA1-3 regions of the hippocampus revealed reduced numbers of neurons in general, as well as reduced numbers of Pur-alpha+-immunopositive neurons and dendrites in heterozygous Pur-alpha mice, compared to wild-type littermates. Past studies have implicated mutations in Pur-alpha in several diseases of brain development and neurodegeneration. When combined with these new findings, the Pur-alpha heterozygous knockout mice may provide an animal model to study mechanisms of and treatments for Pur-alpha-related cognitive deficiencies and neuropathology.
Keywords: PURA; animals; brain pathology; knockout; mice; puralpha.
Copyright © 2016 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
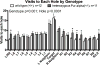
Similar articles
-
Role of Pur alpha in targeting mRNA to sites of translation in hippocampal neuronal dendrites.J Neurosci Res. 2006 May 1;83(6):929-43. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20806. J Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16511857
-
Puralpha is essential for postnatal brain development and developmentally coupled cellular proliferation as revealed by genetic inactivation in the mouse.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Oct;23(19):6857-75. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.19.6857-6875.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12972605 Free PMC article.
-
PURA, the gene encoding Pur-alpha, member of an ancient nucleic acid-binding protein family with mammalian neurological functions.Gene. 2018 Feb 15;643:133-143. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.12.004. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29221753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pur-alpha regulates RhoA developmental expression and downstream signaling.J Cell Physiol. 2013 Jan;228(1):65-72. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24105. J Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 22553010 Free PMC article.
-
The pur protein family: genetic and structural features in development and disease.J Cell Physiol. 2013 May;228(5):930-7. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24237. J Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23018800 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heterozygous c.175C>T variant in PURA gene causes severe developmental delay.Clin Case Rep. 2023 Sep 7;11(9):e7779. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.7779. eCollection 2023 Sep. Clin Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37692153 Free PMC article.
-
PURA-Related Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathy: Phenotypic and Genotypic Spectrum.Neurol Genet. 2021 Nov 15;7(6):e613. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000613. eCollection 2021 Dec. Neurol Genet. 2021. PMID: 34790866 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of the Joining Region in Junctophilin-2 With the L-Type Ca2+ Channel Is Pivotal for Cardiac Dyad Assembly and Intracellular Ca2+ Dynamics.Circ Res. 2021 Jan 8;128(1):92-114. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315715. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Circ Res. 2021. PMID: 33092464 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and validation of PURA as a transcription target of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol: Implications for the treatment of cognitive dysfunction.J Ginseng Res. 2023 Sep;47(5):662-671. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2023.04.007. Epub 2023 Apr 29. J Ginseng Res. 2023. PMID: 37720572 Free PMC article.
-
Complex Movement Disorders in a Boy with PURA Syndrome.Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2021 Jul 8;8(7):1137-1139. doi: 10.1002/mdc3.13272. eCollection 2021 Oct. Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2021. PMID: 34631953 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bach ME, Hawkins RD, Osman M, Kandel ER, Mayford M. Impairment of spatial but not contextual memory in CaMKII mutant mice with a selective loss of hippocampal LTP in the range of the theta frequency. Cell. 1995;81:905–915. - PubMed
-
- Benice TS, Raber J. Object recognition analysis in mice using nose-point digital video tracking. J Neurosci Methods. 2008;168:422–430. - PubMed
-
- Benice TS, Rizk A, Kohama S, Pfankuch T, Raber J. Sex-differences in age-related cognitive decline in C57BL/6J mice associated with increased brain microtubule-associated protein 2 and synaptophysin immunoreactivity. Neuroscience. 2006;137:413–423. - PubMed
-
- Chepenik LG, Tretiakova AP, Krachmarov CP, Johnson EM, Khalili K. The single-stranded DNA binding protein, Pur-alpha, binds HIV-1 TAR RNA and activates HIV-1 transcription. Gene. 1998;210:37–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

