MiR-182 promotes proliferation and invasion and elevates the HIF-1α-VEGF-A axis in breast cancer cells by targeting FBXW7
- PMID: 27648365
- PMCID: PMC5004079
MiR-182 promotes proliferation and invasion and elevates the HIF-1α-VEGF-A axis in breast cancer cells by targeting FBXW7
Abstract
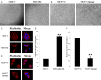
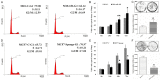
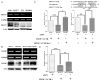
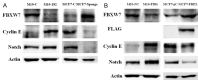
The feature of imperfect complementary effect of miRNAs to mRNAs implies that miRNAs may simultaneously target different mRNAs to affect multiple aspects of tumorigenesis. In our previous results, we demonstrated that miR-182 was over-expressed in breast cancer cell lines and clinical tumor tissues and its up-regulation increased tumorigenicity and invasiveness by repressing a tumor suppressor RECK. In this study, we showed that overexpression miR-182 regulated actin distribution and filopodia formation to increase invasiveness of breast cancer cells. In addition, miR-182 enhanced cell cycle progression and proliferation. We further identified the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase FBXW7 as a target gene of miR-182. We also demonstrated that miR-182-overexpressing cells were highly sensitive to hypoxia. Under hypoxic condition, HIF-1α and VEGF-A proteins were significantly upregulated in these cells. In addition, the conditioned medium of miR-182-overexpressing cells contained more VEGF-A than the control cells and induced angiogenesis more efficiently in vitro. All these effects could be counteracted by ectopic expression of FBXW7 in cells or neutralization of VEGF-A in the conditioned media by specific antibody. Finally, our data showed that miR-182 expression was inversely correlated with FBXW7 in breast tumor tissues. In conclusion, our study explores a novel mechanism by which miR-182 elevates HIF-1α expression to promote breast cancer progression.
Keywords: FBXW7; HIF-1α; MiR-182; VEGF-A; breast cancer.
Figures
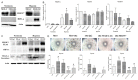
Similar articles
-
miR-497 suppresses angiogenesis in breast carcinoma by targeting HIF-1α.Oncol Rep. 2016 Mar;35(3):1696-702. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4529. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 26718330
-
Hypoxia-inducible microRNA-224 promotes the cell growth, migration and invasion by directly targeting RASSF8 in gastric cancer.Mol Cancer. 2017 Feb 7;16(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0603-1. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28173803 Free PMC article.
-
PRL-3 promotes gastric cancer migration and invasion through a NF-κB-HIF-1α-miR-210 axis.J Mol Med (Berl). 2016 Apr;94(4):401-15. doi: 10.1007/s00109-015-1350-7. Epub 2015 Nov 9. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016. PMID: 26548949
-
miR-92a is upregulated in cervical cancer and promotes cell proliferation and invasion by targeting FBXW7.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Feb 27;458(1):63-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.01.066. Epub 2015 Jan 24. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 25623537
-
MicroRNA-100 shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes suppresses in vitro angiogenesis through modulating the mTOR/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling axis in breast cancer cells.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2017 Oct;40(5):457-470. doi: 10.1007/s13402-017-0335-7. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2017. PMID: 28741069
Cited by
-
Construction and Comparison of ceRNA Regulatory Network for Different Age Female Breast Cancer.Front Genet. 2021 Apr 21;12:603544. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.603544. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33968126 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Expression and miRNAs Profiling: Function and Regulation in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2)-Positive Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 May 10;11(5):646. doi: 10.3390/cancers11050646. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31083383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angioregulatory microRNAs in breast cancer: Molecular mechanistic basis and implications for therapeutic strategies.J Adv Res. 2021 Jun 26;37:235-253. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.06.019. eCollection 2022 Mar. J Adv Res. 2021. PMID: 35499045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying miRNA biomarkers for breast cancer and ovarian cancer: a text mining perspective.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Aug;201(1):5-14. doi: 10.1007/s10549-023-06996-y. Epub 2023 Jun 17. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 37329459 Review.
-
A transcription-independent role for HIF-1α in modulating microprocessor assembly.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Oct 28;52(19):11806-11821. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae792. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39319577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259–269. - PubMed
-
- Kim VN. MicroRNA biogenesis: coordinated cropping and dicing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:376–385. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Garcia I, Miska EA. MicroRNA functions in animal development and human disease. Development. 2005;132:4653–4662. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
