Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Artemisia Leaf Extract in Mice with Contact Dermatitis In Vitro and In Vivo
- PMID: 27647952
- PMCID: PMC5018339
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/8027537
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Artemisia Leaf Extract in Mice with Contact Dermatitis In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
The leaves of Artemisia argyi Lev. et Vant. and A. princeps Pamp. are well known medicinal herbs used to treat patients in China, Japan, and Korea with skin problems such as eczema and itching, as well as abdominal pain and dysmenorrhoea. We investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of Artemisia leaf extract (ALE) using CD mice and Raw 264.7 cells. The effects of ALE on histopathological changes and cytokine production in ear tissues were assessed in mice with CD induced by 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (DNFB). Moreover, the anti-inflammatory effects on production levels of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and nitric oxide (NO) and expression levels of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) were investigated in Raw 264.7 cells. Topical application of ALE effectively prevented ear swelling induced by repeated DNFB application. ALE prevented epidermal hyperplasia and infiltration of immune cells and lowered the production of interferon- (IFN-) gamma (γ), tumour necrosis factor- (TNF-) alpha (α), and interleukin- (IL-) 6 in inflamed tissues. In addition, ALE inhibited expression of COX-2 and iNOS and production of NO and PGE2 in Raw 264.7 cells. These results indicate that Artemisia leaf can be used as a therapeutic agent for inflammatory skin diseases and that its anti-inflammatory effects are closely related to the inhibition of inflammatory mediator release from macrophages and inflammatory cytokine production in inflamed tissues.
Figures
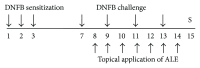
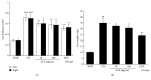
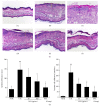
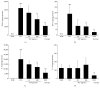
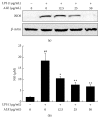
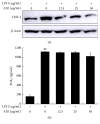
Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory and antitumoural effects of Uncaria guianensis bark.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Dec 12;150(3):1154-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.10.055. Epub 2013 Nov 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24212077
-
Anti-inflammatory activity of Kochia scoparia fruit on contact dermatitis in mice.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Feb;13(2):1695-700. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4698. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 26707133
-
Anti-inflammatory activities of Dictamnus dasycarpus Turcz., root bark on allergic contact dermatitis induced by dinitrofluorobenzene in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Sep 16;149(2):471-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.06.055. Epub 2013 Jul 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23850712
-
Legume Proteins as a Promising Source of Anti-Inflammatory Peptides.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2019;20(12):1204-1217. doi: 10.2174/1389203720666190430110647. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2019. PMID: 31208309 Review.
-
Mechanisms of quinolone phototoxicity.Toxicol Lett. 1998 Dec 28;102-103:369-73. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4274(98)00234-3. Toxicol Lett. 1998. PMID: 10022281 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome sequencing reveals chromosome fusion and extensive expansion of genes related to secondary metabolism in Artemisia argyi.Plant Biotechnol J. 2022 Oct;20(10):1902-1915. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13870. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Plant Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35689517 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Active Ingredients and Potential Bioactivities of Essential Oils from Artemisia argyi and A. verlotorum.Molecules. 2023 May 6;28(9):3927. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093927. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175336 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of potent antileishmanial agents from Artemisia kermanensis Podlech using bioguided fractionation.J Parasit Dis. 2023 Jun;47(2):297-305. doi: 10.1007/s12639-023-01569-8. Epub 2023 Feb 13. J Parasit Dis. 2023. PMID: 37193491 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Hepatotoxins Found in Herbal Medicinal Products: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 16;21(14):5011. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145011. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32708570 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Artemisia herba-alba or olive leaf (Olea europaea) powder supplementation on growth performance, carcass yield, and blood biochemical parameters in broilers.Vet World. 2018 Nov;11(11):1624-1629. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2018.1624-1629. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Vet World. 2018. PMID: 30587899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim C. M., Shin M. G., An D. G., Lee K. S. The Encyclopedia of Oriental Herbal Medicine. Seoul, Republic of Korea: Jeongdam; 1997.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

