Plant nucleolar DNA: Green light shed on the role of Nucleolin in genome organization
- PMID: 27644794
- PMCID: PMC5287095
- DOI: 10.1080/19491034.2016.1236167
Plant nucleolar DNA: Green light shed on the role of Nucleolin in genome organization
Abstract
The nucleolus forms as a consequence of ribosome biogenesis, but it is also implicated in other cell functions. The identification of nucleolus-associated chromatin domains (NADs) in animal and plant cells revealed the presence of DNA sequences other than rRNA genes in and around the nucleolus. NADs display repressive chromatin signatures and harbour repetitive DNA, but also tRNA genes and RNA polymerase II-transcribed genes. Furthermore, the identification of NADs revealed a specific function of the nucleolus and the protein Nucleolin 1 (NUC1) in telomere biology. Here, we discuss the significance of these data with regard to nucleolar structure and to the role of the nucleolus and NUC1 in global genome organization and stability.
Keywords: genome stability; heterochromatin; nuclear architecture; nucleolus; nucleolus-associated chromatin domains.
Figures
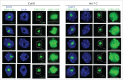
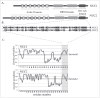
Erratum for
- Extra View to: Pontvianne F, Carpentier MC, Durut N, Pavlištová V, Jaške K, Schořová Š, Parrinello H, Rohmer M, Pikaard CS, Fojtová M, Fajkus J, Sáez-Vásquez J. Identification of Nucleolus-Associated Chromatin Domains Reveals a Role for the Nucleolus in 3D Organization of the A. thaliana Genome. PCell Rep. 2016. 16(6):1574–87. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.07
Similar articles
-
Identification of Nucleolus-Associated Chromatin Domains Reveals a Role for the Nucleolus in 3D Organization of the A. thaliana Genome.Cell Rep. 2016 Aug 9;16(6):1574-1587. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.07.016. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27477271 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of AtNUC-L1 reveals a central role of nucleolin in nucleolus organization and silencing of AtNUC-L2 gene in Arabidopsis.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Feb;18(2):369-79. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-08-0751. Epub 2006 Nov 15. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17108323 Free PMC article.
-
A Method to Identify Nucleolus-Associated Chromatin Domains (NADs).Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1675:99-109. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7318-7_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29052188
-
Genome Organization in and around the Nucleolus.Cells. 2019 Jun 12;8(6):579. doi: 10.3390/cells8060579. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31212844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and functions of nucleolin.J Cell Sci. 1999 Mar;112 ( Pt 6):761-72. doi: 10.1242/jcs.112.6.761. J Cell Sci. 1999. PMID: 10036227 Review.
Cited by
-
The overlooked manipulation of nucleolar functions by plant pathogen effectors.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Aug 7;15:1445097. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1445097. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39175483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The formation of perinucleolar bodies is important for normal leaf development and requires the zinc-finger DNA-binding motif in Arabidopsis ASYMMETRIC LEAVES2.Plant J. 2020 Mar;101(5):1118-1134. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14579. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Plant J. 2020. PMID: 31639235 Free PMC article.
-
Heat Shock Protein HSP101 Affects the Release of Ribosomal Protein mRNAs for Recovery after Heat Shock.Plant Physiol. 2017 Jun;174(2):1216-1225. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.00269. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Plant Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28381501 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional nuclear organization in Arabidopsis thaliana.J Plant Res. 2020 Jul;133(4):479-488. doi: 10.1007/s10265-020-01185-0. Epub 2020 Apr 2. J Plant Res. 2020. PMID: 32240449 Review.
-
Tidying-up the plant nuclear space: domains, functions, and dynamics.J Exp Bot. 2020 Aug 17;71(17):5160-5178. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa282. J Exp Bot. 2020. PMID: 32556244 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 2007; 128:693-705; PMID:17320507; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sequeira-Mendes J, Araguez I, Peiro R, Mendez-Giraldez R, Zhang X, Jacobsen SE, Bastolla U, Gutierrez C. The functional topography of the arabidopsis genome is organized in a reduced number of linear motifs of chromatin states. Plant Cell 2014; 26:2351-66; PMID:24934173; http://dx.doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.124578 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nemeth A, Conesa A, Santoyo-Lopez J, Medina I, Montaner D, Peterfia B, Solovei I, Cremer T, Dopazo J, Längst G. Initial genomics of the human nucleolus. PLoS Genet 2010; 6:e1000889; PMID:20361057; http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1000889 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Koningsbruggen S, Gierlinski M, Schofield P, Martin D, Barton GJ, Ariyurek Y, den Dunnen JT, Lamond AI. High-resolution whole-genome sequencing reveals that specific chromatin domains from most human chromosomes associate with nucleoli. Mol Biol Cell 2010; 21:3735-48; PMID:20826608; http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E10-06-0508 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
