The Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk Variant CCR6DNP Regulates CCR6 via PARP-1
- PMID: 27626929
- PMCID: PMC5023119
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006292
The Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk Variant CCR6DNP Regulates CCR6 via PARP-1
Abstract
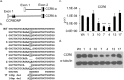
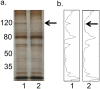
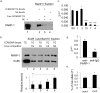
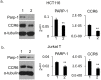
Understanding the implications of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) for disease biology requires both identification of causal variants and definition of how these variants alter gene function. The non-coding triallelic dinucleotide polymorphism CCR6DNP is associated with risk for rheumatoid arthritis, and is considered likely causal because allelic variation correlates with expression of the chemokine receptor CCR6. Using transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN) gene editing, we confirmed that CCR6DNP regulates CCR6. To identify the associated transcription factor, we applied a novel assay, Flanking Restriction Enhanced Pulldown (FREP), to identify specific association of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) with CCR6DNP consistent with the established allelic risk hierarchy. Correspondingly, manipulation of PARP-1 expression or activity impaired CCR6 expression in several lineages. These findings show that CCR6DNP is a causal variant through which PARP-1 regulates CCR6, and introduce a highly efficient approach to interrogate non-coding genetic polymorphisms associated with human disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A regulatory variant in CCR6 is associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility.Nat Genet. 2010 Jun;42(6):515-9. doi: 10.1038/ng.583. Epub 2010 May 9. Nat Genet. 2010. PMID: 20453841
-
A Functional Variant rs3093023 in CCR6 Is Associated With IgA Nephropathy by Regulating Th17 Cells in a North Han Chinese Population.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 25;12:600598. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.600598. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33717080 Free PMC article.
-
A CCR6 variant strongly associated with rheumatoid arthritis in two populations is not associated with ankylosing spondylitis.Rheumatol Int. 2013 Sep;33(9):2443-4. doi: 10.1007/s00296-012-2404-6. Epub 2012 Apr 8. Rheumatol Int. 2013. PMID: 22527137 No abstract available.
-
The role and modulation of CCR6+ Th17 cell populations in rheumatoid arthritis.Cytokine. 2015 Jul;74(1):43-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.02.002. Epub 2015 Mar 28. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 25828206 Review.
-
CCR6 and CCL20: emerging players in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.Immunol Cell Biol. 2014 Apr;92(4):354-8. doi: 10.1038/icb.2013.97. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Immunol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24394994 Review.
Cited by
-
The potential of PARP inhibitors in targeted cancer therapy and immunotherapy.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Dec 1;9:1073797. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1073797. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36533080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of CCR6 functional polymorphisms with Primary Biliary Cholangitis.J Transl Autoimmun. 2024 Feb 15;8:100234. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2024.100234. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Transl Autoimmun. 2024. PMID: 38405661 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokines and chemokine receptors as promising targets in rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 13;14:1100869. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1100869. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36860872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An integrative drug repositioning framework discovered a potential therapeutic agent targeting COVID-19.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Apr 24;6(1):165. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00568-6. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 33895786 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput identification of noncoding functional SNPs via type IIS enzyme restriction.Nat Genet. 2018 Aug;50(8):1180-1188. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0159-z. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Nat Genet. 2018. PMID: 30013183 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

