Tumor control by human cytomegalovirus in a murine model of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 27626063
- PMCID: PMC5008266
- DOI: 10.1038/mto.2016.12
Tumor control by human cytomegalovirus in a murine model of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
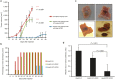
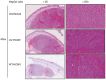
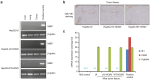
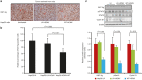
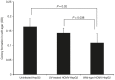
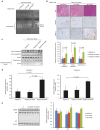
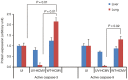
Although viruses can cause cancer, other studies reported the regression of human tumors upon viral infections. We investigated the cytoreductive potential of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) in a murine model of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in severe-immunodeficient mice. Infection of HepG2 cells with HCMV resulted in the absence of tumor or in a limited tumor growth following injection of cells subcutaneously. By contrast all mice injected with uninfected HepG2 cells and with HepG2 cells infected with UV-treated HCMV did develop tumors without any significant restriction. Analysis of tumors indicated that in mice injected with HCMV-infected-HepG2 cells, but not in controls, a restricted cellular proliferation was observed parallel to a limited activation of the STAT3-cyclin D1 axis, decreased formation of colonies in soft agar, and activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. We conclude that HCMV can provide antitumoral effects in a murine model of HCC which requires replicative virus at some stages that results in limitation of tumor cell proliferation and enhanced apoptosis mediated through the intrinsic caspase pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Human Cytomegalovirus, from Oncomodulation to Oncogenesis.Viruses. 2018 Aug 3;10(8):408. doi: 10.3390/v10080408. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30081496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HCMV activates the IL-6-JAK-STAT3 axis in HepG2 cells and primary human hepatocytes.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59591. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059591. Epub 2013 Mar 26. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555719 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus UL111A and US27 Gene Products Enhance the CXCL12/CXCR4 Signaling Axis via Distinct Mechanisms.J Virol. 2018 Feb 12;92(5):e01981-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01981-17. Print 2018 Mar 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29237840 Free PMC article.
-
Total alkaloids of Rubus aleaefolius Poir inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma growth in vivo and in vitro via activation of mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis.Int J Oncol. 2013 Mar;42(3):971-8. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1779. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23338043
-
Modulatory effects of human cytomegalovirus infection on malignant properties of cancer cells.Intervirology. 1996;39(4):259-69. doi: 10.1159/000150527. Intervirology. 1996. PMID: 9078467 Review.
Cited by
-
Uncovering the Anticancer Potential of Murine Cytomegalovirus against Human Colon Cancer Cells.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020 Jan 29;16:250-261. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.01.007. eCollection 2020 Mar 27. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020. PMID: 32140563 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of the human cytomegalovirus UL111A is correlated with favorable survival of patients with gastric cancer and changes T-cell infiltration and suppresses carcinogenesis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020 Mar;146(3):555-568. doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-03092-x. Epub 2020 Feb 5. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32025866 Free PMC article.
-
Patients with Helicobacter pylori-positive gastric cancer with human cytomegalovirus infection have a low tendency of advanced lymphatic metastasis in a Chinese population.Oncol Lett. 2021 May;21(5):402. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12663. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33777225 Free PMC article.
-
The Human Cytomegalovirus, from Oncomodulation to Oncogenesis.Viruses. 2018 Aug 3;10(8):408. doi: 10.3390/v10080408. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30081496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Control by Cytomegalovirus: A Door Open for Oncolytic Virotherapy?Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020 Mar 29;17:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.03.004. eCollection 2020 Jun 26. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020. PMID: 32300639 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coaquette, A, Bourgeois, A, Dirand, C, Varin, A, Chen, W and Herbein, G (2004). Mixed cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B genotypes in immunocompromised patients. Clin Infect Dis 39: 155–161. - PubMed
-
- Melnick, M, Sedghizadeh, PP, Allen, CM and Jaskoll, T (2012). Human cytomegalovirus and mucoepidermoid carcinoma of salivary glands: cell-specific localization of active viral and oncogenic signaling proteins is confirmatory of a causal relationship. Exp Mol Pathol 92: 118–125. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

