Cardiovascular Disease, Statins, and HIV
- PMID: 27625435
- PMCID: PMC5021243
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiw288
Cardiovascular Disease, Statins, and HIV
Erratum in
Abstract
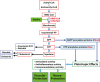
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected patients are at an increased risk of serious, non-AIDS-defining comorbidities, even in the setting of viral suppression with combination antiretroviral therapy. This increased risk is due in part to immune dysfunction and heightened inflammation and immune activation associated with chronic HIV infection. Statins have wide-reaching immunomodulatory effects, and their use in the HIV-infected population may be of particular benefit. In this article, we review the pathogenesis of increased inflammation during HIV infection and how it contributes to the risk of cardiovascular disease among HIV-infected individuals. We then we review the immunomodulatory effects of statins and how they may attenuate the risk of cardiovascular disease and other comorbidities in this unique patient population.
Keywords: HIV; cardiovascular disease; hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors; immune activation; inflammation; statins.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of statins in the setting of HIV infection.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2015 Sep;12(3):305-12. doi: 10.1007/s11904-015-0273-9. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2015. PMID: 26126687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Statins in HIV-Infected Patients: Potential Beneficial Effects and Clinical Use.AIDS Rev. 2017 Apr-Jun;19(2):59-71. AIDS Rev. 2017. PMID: 28182617 Review.
-
Cardiovascular risk and dyslipidemia among persons living with HIV: a review.BMC Infect Dis. 2017 Aug 9;17(1):551. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2626-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28793863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of statins beyond lipid-lowering agents in ART-treated HIV infection.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 9;15:1339338. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1339338. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38655259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Statins for primary cardiovascular disease prevention among people with HIV: emergent directions.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2022 Sep 1;17(5):293-300. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000752. Epub 2022 Jul 16. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2022. PMID: 35938463 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin D supplementation decreases immune activation and exhaustion in HIV-1-infected youth.Antivir Ther. 2018;23(4):315-324. doi: 10.3851/IMP3199. Antivir Ther. 2018. PMID: 28994661 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evidence-based review of statin use in patients with HIV on antiretroviral therapy.J Clin Transl Endocrinol. 2017 Feb 22;8:6-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jcte.2017.01.004. eCollection 2017 Jun. J Clin Transl Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 29067253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease thresholds for statin initiation among people living with HIV in Thailand: A cost-effectiveness analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Sep 9;16(9):e0256926. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256926. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34499685 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship of Carotid and Brachial Artery Wall Thickness Measurement with Cardiovascular Risk Scoring in Individuals Living with HIV.Infect Dis Clin Microbiol. 2024 Aug 6;6(3):164-173. doi: 10.36519/idcm.2024.323. eCollection 2024 Sep. Infect Dis Clin Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39399750 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of drug candidates targeting monocyte reprogramming in people living with HIV.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 20;14:1275136. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1275136. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38077315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kristoffersen US, Kofoed K, Kronborg G, Giger AK, Kjaer A, Lebech AM. Reduction in circulating markers of endothelial dysfunction in HIV-infected patients during antiretroviral therapy. HIV Med 2009; 10:79–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

