Coordinated recruitment of Spir actin nucleators and myosin V motors to Rab11 vesicle membranes
- PMID: 27623148
- PMCID: PMC5021521
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.17523
Coordinated recruitment of Spir actin nucleators and myosin V motors to Rab11 vesicle membranes
Abstract
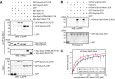
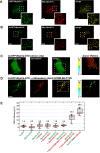
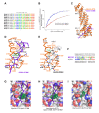
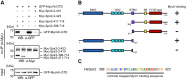
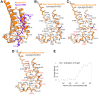
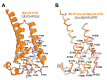
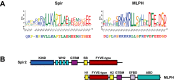
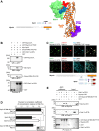
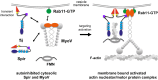
There is growing evidence for a coupling of actin assembly and myosin motor activity in cells. However, mechanisms for recruitment of actin nucleators and motors on specific membrane compartments remain unclear. Here we report how Spir actin nucleators and myosin V motors coordinate their specific membrane recruitment. The myosin V globular tail domain (MyoV-GTD) interacts directly with an evolutionarily conserved Spir sequence motif. We determined crystal structures of MyoVa-GTD bound either to the Spir-2 motif or to Rab11 and show that a Spir-2:MyoVa:Rab11 complex can form. The ternary complex architecture explains how Rab11 vesicles support coordinated F-actin nucleation and myosin force generation for vesicle transport and tethering. New insights are also provided into how myosin activation can be coupled with the generation of actin tracks. Since MyoV binds several Rab GTPases, synchronized nucleator and motor targeting could provide a common mechanism to control force generation and motility in different cellular processes.
Keywords: Rab11; Spire; actin motor proteins; actin nucleation; biophysics; cell biology; myosin V; none; structural biology; vesicle transport.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Exploring the iceberg: Prospects of coordinated myosin V and actin assembly functions in transport processes.Small GTPases. 2019 Mar;10(2):111-121. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1281863. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Small GTPases. 2019. PMID: 28394692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and functional insights into the Spir/formin actin nucleator complex.Biol Chem. 2013 Dec;394(12):1649-60. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2013-0176. Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23863697 Review.
-
Structural basis of myosin V Rab GTPase-dependent cargo recognition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Dec 17;110(51):20443-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1314329110. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24248336 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the interaction between the molecular motor Myosin Vc and the small GTPase Rab3A.J Proteomics. 2020 Feb 10;212:103549. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2019.103549. Epub 2019 Nov 5. J Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 31698103
-
Ypt32p and Mlc1p bind within the vesicle binding region of the class V myosin Myo2p globular tail domain.Mol Microbiol. 2008 Mar;67(5):1051-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06106.x. Epub 2008 Jan 23. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18221262
Cited by
-
Disulfidptosis: a novel cell death modality induced by actin cytoskeleton collapse and a promising target for cancer therapeutics.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Oct 11;22(1):491. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01871-9. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39394612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crystal Structure of the SH3 Domain of ASAP1 in Complex with the Proline Rich Motif (PRM) of MICAL1 Reveals a Unique SH3/PRM Interaction Mode.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 11;24(2):1414. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021414. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674928 Free PMC article.
-
The actin nucleator Spir-1 is a virus restriction factor that promotes innate immune signalling.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Feb 11;18(2):e1010277. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010277. eCollection 2022 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35148361 Free PMC article.
-
CCB is Involved in Actin-Based Axonal Transport of Selected Synaptic Proteins.J Neurosci. 2020 Jan 15;40(3):542-556. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0915-18.2019. Epub 2019 Nov 21. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31754011 Free PMC article.
-
Roles and regulation of myosin V interaction with cargo.Adv Biol Regul. 2021 Jan;79:100787. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2021.100787. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Adv Biol Regul. 2021. PMID: 33541831 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung LW, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH. PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallographica Section D Biological Crystallography. 2010;66:213–221. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909052925. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bricogne G, Blanc E, Brandl M, Flensburg C, Keller P, Paciorek W, Roversi P, Sharff A, Smart OS, Vonrhein C, Womack TO. BUSTER. version 2.10. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Global Phasing Ltd; 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

