Macrophages promote matrix protrusive and invasive function of breast cancer cells via MIP-1β dependent upregulation of MYO3A gene in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 27622050
- PMCID: PMC5006911
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1196299
Macrophages promote matrix protrusive and invasive function of breast cancer cells via MIP-1β dependent upregulation of MYO3A gene in breast cancer cells
Abstract
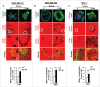
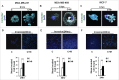
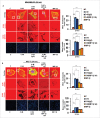
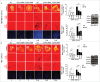
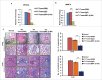
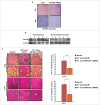
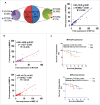
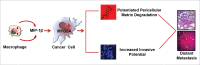
The potential of a tumor cell to metastasize profoundly depends on its microenvironment, or "niche" interactions with local components. Tumor-associated-macrophages (TAMs) are the most abundant subpopulation of tumor stroma and represent a key component of tumor microenvironment. The dynamic interaction of cancer cells with neighboring TAMs actively drive cancer progression and metastatic transformation through intercellular signaling networks that need better elucidation. Thus, current study was planned for discerning paracrine communication networks operational between TAMs, and breast cancer cells with special reference to cancer cell invasion and dissemination to distant sites. Here, we report role of MIP-1β in enhancing invasive potential of metastatic breast cancer MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells. In addition, the poorly metastatic MCF-7 cells were also rendered invasive by MIP-1β. The MIP-1β-driven cancer cell invasion was dependent on upregulated expression levels of MYO3A gene, which encodes an unconventional myosin super-family protein harboring a kinase domain. Ex ovo study employing Chick-embryo-model and in vivo Syngenic 4T1/BALB/c mice-model further corroborated aforementioned in vitro findings, thereby substantiating their physiological relevance. Concordantly, human breast cancer specimen exhibited significant association between mRNA expression levels of MIP-1β and MYO3A. Both, MIP-1β and MYO3A exhibited positive correlation with MMP9, an established molecular determinant of cancer cell invasion. Higher expression of these genes correlated with poor survival of breast cancer patients. Collectively, these results point toward so far undisclosed MIP-1β/MYO3A axis being operational during metastasis, wherein macrophage-derived MIP-1β potentiated cancer cell invasion and metastasis via up regulation of MYO3A gene within cancer cells. Our study exposes opportunities for devising potential anti-metastatic strategies for efficient clinical management of breast cancer.
Keywords: Invadopodia; MIP-1β; MMP-9; MYO3A; invasion; migration.
Figures
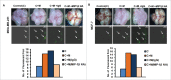
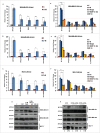
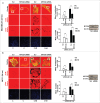
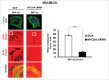
Similar articles
-
The matrix environmental and cell mechanical properties regulate cell migration and contribute to the invasive phenotype of cancer cells.Rep Prog Phys. 2019 Jun;82(6):064602. doi: 10.1088/1361-6633/ab1628. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Rep Prog Phys. 2019. PMID: 30947151 Review.
-
Suppressive Effects of Plumbagin on Invasion and Migration of Breast Cancer Cells via the Inhibition of STAT3 Signaling and Down-regulation of Inflammatory Cytokine Expressions.Bone Res. 2013 Dec 31;1(4):362-70. doi: 10.4248/BR201304007. eCollection 2013 Dec. Bone Res. 2013. PMID: 26273514 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoprotegerin mediates tumor-promoting effects of Interleukin-1beta in breast cancer cells.Mol Cancer. 2017 Feb 1;16(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0606-y. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28143606 Free PMC article.
-
NOTCH3 expression is linked to breast cancer seeding and distant metastasis.Breast Cancer Res. 2018 Sep 4;20(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13058-018-1020-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30180881 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insights into prostate cancer progression: the missing link of tumor microenvironment.J Urol. 2005 Jan;173(1):10-20. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000141582.15218.10. J Urol. 2005. PMID: 15592017 Review.
Cited by
-
MYO3B promotes cancer progression in endometrial cancer by mediating the calcium ion-RhoA/ROCK1 signaling pathway.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Sep 19;150(9):424. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05940-x. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39297944 Free PMC article.
-
Integrins: Moonlighting Proteins in Invadosome Formation.Cancers (Basel). 2019 May 2;11(5):615. doi: 10.3390/cancers11050615. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31052560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyprenol-Based Lipofecting Agents for In Vivo Delivery of Therapeutic DNA to Treat Hypertensive Rats.Biochem Genet. 2021 Feb;59(1):62-82. doi: 10.1007/s10528-020-09992-9. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Biochem Genet. 2021. PMID: 32767051 Free PMC article.
-
CC Chemokines in a Tumor: A Review of Pro-Cancer and Anti-Cancer Properties of Receptors CCR5, CCR6, CCR7, CCR8, CCR9, and CCR10 Ligands.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 15;21(20):7619. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207619. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33076281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methylation silencing CDH23 is a poor prognostic marker in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jul 12;13(13):17768-17788. doi: 10.18632/aging.203268. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34252883 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bendre M, Gaddy D, Nicholas RW, Suva LJ. Breast cancer metastasis to bone: it is not all about PTHrP. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2003; (415 Suppl):S39-45; PMID:14600591; http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.blo.0000093844.72468.f4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eckert MA, Yang J. Targeting invadopodia to block breast cancer metastasis. Oncotarget 2011; 2(7):562-8; PMID:21725138; http://dx.doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.301 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Viadana E, Bross ID, Pickren JW. An autopsy study of the metastatic patterns of human leukemias. Oncology 1978; 35(2):87-96; PMID:274679; http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000225262 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shaffrey ME, Mut M, Asher AL, Burri SH, Chahlavi A, Chang SM, Farace E, Fiveash JB, Lang FF, Lopes MB et al.. Brain metastases. Curr Probl Surg 2004; 41(8):665-741; PMID:15354117; http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/j.cpsurg.2004.06.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sica A, Schioppa T, Mantovani A, Allavena P. Tumour-associated macrophages are a distinct M2 polarised population promoting tumour progression: potential targets of anti-cancer therapy. Eur J Cancer 2006; 42(6):717-27; PMID:16520032; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2006.01.003 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
