The clinicopathological significance of RUNX3 hypermethylation and mRNA expression in human breast cancer, a meta-analysis
- PMID: 27616890
- PMCID: PMC5008647
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S77828
The clinicopathological significance of RUNX3 hypermethylation and mRNA expression in human breast cancer, a meta-analysis
Abstract
Aberrant promoter methylation of RUNX3 has been reported in several tumors including human breast cancer (BC). However, the association between RUNX3 hypermethylation and incidence of BC remains elusive. In this study, a detailed literature search was performed in Medline and Google Scholar for related research publications. Analysis of pooled data were executed. Odds ratios with corresponding confidence intervals were determined and summarized, respectively. Finally, 13 studies were identified for the meta-analysis. Analysis of the pooled data showed that RUNX3 hypermethylation was significantly higher in both ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) than in normal breast tissues. In addition, RUNX3 methylation was significantly higher in IDC than in benign tumor. However, RUNX3 methylation was not significantly higher in IDC than in ductal carcinoma in situ. We also determined that RUNX3 hypermethylation was significantly higher in ER positive BC than in ER negative BC. In addition, high RUNX3 mRNA expression was found to be correlated with better overall survival and relapse-free survival for all BC patients. Our results strongly support that RUNX3 hypermethylation may play an important role in BC incidence. RUNX3 methylation is a valuable early biomarker for the diagnosis of BC. Further large-scale studies will provide more insight into the role of RUNX3 hypermethylation in the carcinogenesis and clinical diagnosis of BC patients.
Keywords: RUNX3; breast cancer; estrogen receptor; meta-analysis; methylation; odds ratio.
Figures
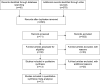




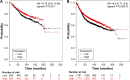
Similar articles
-
An early biomarker and potential therapeutic target of RUNX 3 hypermethylation in breast cancer, a system review and meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 28;8(13):22166-22174. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13125. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27825140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinicopathological significance and potential drug target of RUNX3 in breast cancer.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 Dec 5;8:2423-30. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S71815. eCollection 2014. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 25525332 Free PMC article.
-
The association of PTEN hypermethylation and breast cancer: a meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Sep 12;9:5643-50. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S111684. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27672335 Free PMC article.
-
The clinicopathological significance and drug target potential of FHIT in breast cancer, a meta-analysis and literature review.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Oct 1;9:5439-45. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S89861. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26491255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinicopathological significance and potential drug target of RUNX3 in non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Jun 3;9:2855-65. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S76358. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26082616 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ethanol promotes alcohol-related colorectal cancer metastasis via the TGF-β/RUNX3/Snail axis by inducing TGF-β1 upregulation and RUNX3 cytoplasmic mislocalization.EBioMedicine. 2019 Dec;50:224-237. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.11.011. Epub 2019 Nov 19. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31757777 Free PMC article.
-
RUNX3 mediates keloid fibroblast proliferation through deacetylation of EZH2 by SIRT1.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Dec 7;23(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12860-022-00451-4. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 36476345 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA MT1JP Suppresses Biological Activities of Breast Cancer Cells in vitro and in vivo by Regulating the miRNA-214/RUNX3 Axis.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jun 4;13:5033-5046. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S241503. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32581560 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of determining the hypermethylation of the RUNX3 gene promoter and its cohypermethylation with the BRCA1 gene for patients with breast cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Oct;149(13):11919-11927. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05034-0. Epub 2023 Jul 7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37420018
-
RUNX3 Epigenetic Inactivation Is Associated With Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer.J Histochem Cytochem. 2018 Oct;66(10):709-721. doi: 10.1369/0022155418797315. Epub 2018 Aug 22. J Histochem Cytochem. 2018. PMID: 30133331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O’Connell P, Pekkel V, Fuqua S, Osborne CK, Allred DC. Molecular genetic studies of early breast cancer evolution. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1994;32(1):5–12. - PubMed
-
- Hilton HN, Kantimm S, Graham JD, Clarke CL. Changed lineage composition is an early event in breast carcinogenesis. Histol Histopathol. 2013;28(9):1197–1204. - PubMed
-
- Coleman RE, Gregory W, Marshall H, Wilson C, Holen I. The metastatic microenvironment of breast cancer: clinical implications. Breast. 2013;22(Suppl 2):S50–S56. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

